List of AM cannabinoids
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Alexandros Makriyannis is a professor in the Department of Medicinal Chemistry at Northeastern University, where his research group has synthesized many new compounds with cannabinoid activity. Some of those are:
| Name | Class | Ki / nM at CB1 | Ki / nM at CB2 | Selectivity | CLogP | Structure | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AM-087 | Dibenzopyran | 0.43 | 6.47 | 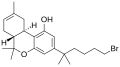 |
An analgesic CB1 agonist derived from Δ8-THC substituted with a side chain on the 3-position, roughly 100 times as potent as THC. | ||
| AM-251 | Pyrazole derivative | 7.5 | 7.08 |  |
An inverse agonist at the CB1 cannabinoid receptor that is structurally related to SR141716A (rimonabant), but has a higher binding affinity.[1] | ||
| AM-279 | A Schedule I substance in Alabama.[2] | ||||||
| AM-281 | N-(morpholin-4-yl)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-5-(4-iodophenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide[1] | ||||||
| AM-356 | 17.9 | 868 | 5.55 | 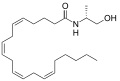 |
A synthetically created stable chiral analog of anandamide, it acts on both cannabinoid receptors.[3] | ||
| AM-374 | Palmitylsulfonyl fluoride[4] | ||||||
| AM-381 | Stearylsulfonyl fluoride | ||||||
| AM-404 | 7.02 |  |
An active metabolite of paracetamol (acetaminophen) and a likely inhibitor of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) | ||||
| AM-411 | 6.80 | 52.0 |  |
An adamantyl-substituted derivative of Δ8-THC, it is a potent and fairly selective CB1 full agonist and a moderately potent CB2 agonist. | |||
| AM-630 | 32.1 | CB2 (165×) | 4.19 |  |
A potent and selective inverse agonist for the cannabinoid receptor CB2 and a weak partial agonist at CB1. | ||
| AM-661 | 1-(N-methyl-2-piperidine)methyl-2-methyl-3-(2-iodo)benzoylindole[5] | ||||||
| AM-678 | 9.00 ± 5.00 | 2.94 ± 2.65 | CB2 | 5.68 |  |
Another name for JWH-018, it is a full agonist at both cannabinoid receptors with some selectivity for CB2. | |
| AM-679 | 13.5 | 49.5 | 6.04 |  |
An iodobenzoylindole which acts as a moderately potent agonist for both cannabinoid receptors. | ||
| AM-694 | 0.08 | 1.44 | CB1 (18×) | 5.54 |  |
An iodobenzoylindole which acts as a potent and selective agonist for the CB1 cannabinoid receptor.[6] | |
| AM-735 | 8.9 | 7.4 | 3-bornyl-Δ8-THC, a mixed CB1 / CB2 agonist.[7] | ||||
| AM-855 | 22.3 | 58.6 | CB1 | 7.1 |  |
An analgesic derivative of Δ8-tetrahydrocannabinol, it is an agonist at both CB1 and CB2 with moderate selectivity for CB1. | |
| AM-881 | 5.3 | 95 | A chlorine-substituted stereoisomer of anandamide.[3] | ||||
| AM-883 | 9.9 | 226 | An allyl-substituted stereoisomer of anandamide.[3] | ||||
| AM-905 | 1.2 | 5.3 | CB1 | 4.98 | 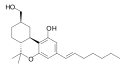 |
A potent and reasonably selective agonist for the CB1 cannabinoid receptor. | |
| AM-906 | 0.8 | 9.5 | CB1 | 4.98 |  |
A potent and dodecally selective agonist for the CB1 cannabinoid receptor. | |
| AM-919 | 2.2 | 3.4 | CB1 | 6.21 | 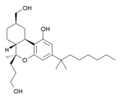 |
A potent agonist at both CB1 and CB2 with moderate selectivity for CB1. It is a derivative of HU-210 and represents a hybrid structure between the classical and nonclassical cannabinoid families. | |
| AM-926 | 2.2 | 4.3 | CB1 | A potent agonist at both CB1 and CB2 with moderate selectivity for CB1. It is a derivative of HU-210 and represents a hybrid structure between the classical and nonclassical cannabinoid families. | |||
| AM-938 | 1.2 | 0.3 | CB2 (4×) | 5.92 | 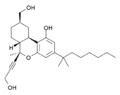 |
A potent agonist at both CB1 and CB2. It is a derivative of HU-210 and represents a hybrid structure between the classical and nonclassical cannabinoid families. | |
| AM-1116 | 7.4 | A dimethylated stereoisomer of anandamide.[3] | |||||
| AM-1172 | An endocannabinoid analog specifically designed to be a potent and selective inhibitor of AEA uptake that is resistant to FAAH hydrolysis. | ||||||
| AM-1220 | 3.88 | 73.4 | CB1 (19×) | 4.73 |  |
A potent and selective analgesic CB1 agonist (as racemate). The (R) enantiomer has around 1000× higher affinity for CB1 than (S) enantiomer.[8][9] | |
| AM-1221 | 52.3 | 0.28 | CB2 (187×) |  |
A potent and selective CB2 agonist. | ||
| AM-1235 | 1.5 | 20.4 | CB1 (13×) |  |
A moderately CB1 selective agonist.[10] | ||
| AM-1241 | 3.4 | CB2 (80×) |  |
A potent and selective analgesic CB2 agonist.[11] | |||
| AM-1248 | CB1 |  |
A moderately potent agonist with some selectivity for CB1, containing an unusual 3-(adamant-1-oyl) substitution on the indole ring. | ||||
| AM-1710 | Cannabilactone | CB2 (54×) | 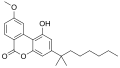 |
A CB2 selective cannabilactone.[12] Acts as a dual CB2 agonist / CB1 antagonist.[13] | |||
| AM-1714 | Cannabilactone | CB2 (490×) | 6.17 |  |
A CB2 selective cannabilactone.[12] | ||
| AM-1902 | A nonclassical cannabinoid[14] | ||||||
| AM-2201 | 1.0 | 2.6 | CB1 | 5.18 |  |
A potent agonist at both CB1 and CB2 with moderate selectivity for CB1. | |
| AM-2212 | 1.4 | 18.9 | CB1 | A potent agonist at both CB1 and CB2 with dodecal selectivity for CB1.[5] | |||
| AM-2213 | 3.0 | 30 | CB1 (10×) | A potent agonist at both CB1 and CB2.[5] | |||
| AM-2232 | 0.28 | 1.48 | 4.75 |  |
A potent agonist at both CB1 and CB2.[10] | ||
| AM-2233 | 1.8 | 2.2 | CB1 | 5.09 |  |
The (R) enantiomer is potent and selective CB1 agonist used in 131I radiolabelled form to map distribution of CB1 receptors in brain.[15][16][17][18][19][20] | |
| AM-2389 | 0.16 | CB1 (26×) | 6 | 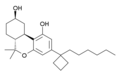 |
Classical cannabinoid derivative. | ||
| AM-3102 | 33000 | 26000 | An analog of oleoylethanolamide, the endogenous agonist for proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα). It also acts as a weak cannabinoid agonist. | ||||
| AM-4030 | 0.7 | 8.6 | CB1 (12×) | 6.17 |  |
A potent agonist at both CB1 and CB2, it is dodecally selective for CB1. It is a derivative of HU-210 and represents a hybrid structure between the classical and nonclassical cannabinoid families. | |
| AM-4054 | 2.2 | CB1 (40×) | A potent but slow-onset agonist.[21][22] | ||||
| AM-4056 | 0.041 | 6.51 |  |
Another name for HU-243, it is a potent agonist at both the CB1 and CB2 receptors. | |||
| AM-4113 | CB1 | A CB1 selective neutral antagonist.[23] | |||||
| AM-6545 | CB1 | 4.06 |  |
A peripherally selective silent antagonist of CB1 receptors. | |||
| AM-7438 |  |
A potent agonist of CB1 and CB2 with reduced duration of action.[24] | |||||
| AM-11245 | 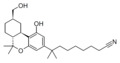 |
||||||
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.