Loading AI tools
The Australian Broadcasting Corporation (ABC) is the national broadcaster of Australia. It is principally funded by the Australian taxpayer and is administered by a government-appointed board. The ABC is a publicly owned body that is politically independent and accountable such as through its production of annual reports and is bound by provisions contained within the Public Interest Disclosure Act 2013 and the Public Governance, Performance and Accountability Act 2013, with its charter enshrined in legislation, the Australian Broadcasting Corporation Act 1983.[2] ABC Commercial, a profit-making division of the corporation, also helps to generate funding for content provision.
 | |
| Formerly | Australian Broadcasting Commission (1932–1983) |
|---|---|
| Company type | Statutory corporation |
| Industry | Mass media |
| Predecessors | |
| Founded | 1 July 1932 |
| Founder | Lyons government |
| Headquarters | ABC Ultimo Centre, Sydney , Australia |
Area served | Australia, Worldwide |
Key people |
|
| Products |
|
| Services |
|
| $100.363 billion (2024) | |
| –$2.205 million (2024) | |
| Total assets | $1.953 billion (2024) |
| Total equity | $1.169 billion (2024) |
| Owner | Australian Government |
Number of employees | 4,682[note 1] (2024) |
| Divisions | |
| Website | www |
| Footnotes / references [1] | |
The ABC was established as the Australian Broadcasting Commission on 1 July 1932 by an act of federal parliament. It effectively replaced the Australian Broadcasting Company, a private company established in 1924 to provide programming for A-class radio stations. The ABC was given statutory powers that reinforced its independence from the government and enhanced its news-gathering role. Modelled after the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC), which is funded by a television licence, the ABC was originally financed by licence fees on households with a broadcast receiver. However, the licence fees soon proved to be insufficient due to Australia's small population and the vast area to be serviced. In 1947 a proposal to increase the fee for a broadcast listeners' licence from £1 to £1/5/[3] was scotched,[4] and in 1949 the Chifley government decided that the ABC would be directly funded by the taxpayer,[5][6] with licence fees subsumed into general revenue. Later funding was supplemented with commercial activities related to its core broadcasting mission. The Australian Broadcasting Commission became the Australian Broadcasting Corporation in 1983.
The ABC provides radio, television, online, and mobile services throughout metropolitan and regional Australia. ABC Radio operates four national networks, a large number of ABC Local Radio stations, several digital stations, and the international service Radio Australia. ABC Television operates five free-to-air channels, as well as the ABC iview streaming service and the ABC Australia satellite channel. News and current affairs content across all platforms is produced by the news division.
The postal address of the ABC in every Australian capital city is PO Box 9994, as a tribute to the record-breaking Test batting average of Australian cricketer Sir Donald Bradman.[7][8][9]
Origins
After public radio stations were established independently in the state capitals from 1924, a licensing scheme administered by the Postmaster-General's Department was established, allowing certain stations (with "Class A" licences") government funding, albeit with restrictions placed on their advertising content.[10] In 1928, the government established the National Broadcasting Service to take over the 12 A-Class licences as they came up for renewal, and contracted the Australian Broadcasting Company,[11] a private company established in 1924,[12][13] to supply programs to the new national broadcaster.[11][14]
After it became politically unpopular to continue to allow the Postmaster-General to run the National Broadcasting Service, the government established the Australian Broadcasting Commission (ABC) on 1 July 1932, under the Australian Broadcasting Commission Act 1932.[15] to take over the Australian Broadcasting Company and run the National Broadcasting Service.[16][17]
The ABC became informally referred to as "Aunty",[18][19][20] originally in imitation of the British Broadcasting Corporation's nickname.[21] The structure and programming was broadly modelled on the British Broadcasting Corporation, and programs not created in Australia were mostly bought in from the BBC.[11]
In 1940 one of the ABC Board's most prominent members, Dick Boyer, was appointed to the ABC, becoming chairman on 1 April 1945. Today known for the continuing series of Boyer Lectures initiated by him in 1959, he had a good but not too close working relationship with Sir Charles Moses (general manager 1935–1965[22][23]), and remained chair until his retirement in 1961. He was determined to maintain the autonomy of the ABC.[24]
War years
In 1942 The Australian Broadcasting Act was passed, giving the ABC the power to decide when, and in what circumstances, political speeches should be broadcast. Directions from the minister about whether or not to broadcast any matter now had to be made in writing, and any exercise of the power had to be mentioned in the commission's annual report.[25]
1950–2000

The ABC commenced television broadcasting in 1956. ABN-2 in Sydney was inaugurated by prime minister Robert Menzies on 5 November 1956, with the first broadcast presented by Michael Charlton, and James Dibble reading the first television news bulletin.[26] Television relay facilities were not in place until the early 1960s, so news bulletins had to be sent to each capital city by teleprinter, to be prepared and presented separately in each city.[27] In 1975, colour television was permanently introduced into Australia, and within a decade, the ABC had moved into satellite broadcasting, greatly enhancing its ability to distribute content nationally.[28]
Also in 1975 the ABC introduced a 24-hour-a-day AM rock station in Sydney, 2JJ (Double Jay), which was eventually expanded into the national Triple J FM network.[28] A year later, a national classical music network was established on the FM band, broadcasting from Adelaide. It was initially known as ABC-FM (later ABC Classic FM) – referring both to its "fine music programming and radio frequency".[28]
ABC budget cuts began in 1976[29] and continued until 1998,[30] the largest cuts (calculated by the ABC as 25% in real terms) coming between 1985 and 1996.[31]
The Australian Broadcasting Corporation Act 1983 changed the name of the organisation to the Australian Broadcasting Corporation, effective 1 July 1983. Although funded and owned by the government, the ABC remains editorially independent as ensured by the 1983 Act.[32] At the same time, the newly formed corporation underwent significant restructuring, including a split into separate television and radio divisions, and ABC Radio was restructured significantly again in 1985.[33] Geoffrey Whitehead was managing director of the ABC at this time.[34] Following his resignation in 1986, David Hill (at the time chair of the ABC Board) took over his position[35] and local production trebled from 1986 to 1991.[33]

Live television broadcasts of selected parliamentary sessions started in 1990, and by the early 1990s, all major ABC broadcasting outlets moved to 24-hour-a-day operation.
In 1991 the ABC helped launch Australian children's music band The Wiggles, under the ABC music label.
In 1991 the corporation's Sydney radio and orchestral operations moved to a new building,[36] the ABC Ultimo Centre,[37] in the inner-city suburb of Ultimo. In Melbourne, the ABC Southbank Centre was completed in 1994.[36]
In 1992 Australian children's television series Bananas in Pyjamas first aired.
International television service ABC Australia was established in 1993, while at the same time Radio Australia increased its international reach. Reduced funding in 1997 for Radio Australia resulted in staff and programming cuts.[36]
The ABC Multimedia Unit was established in July 1995 to manage the new ABC website, which was launched in August.[36]
The ABC was registered on the Australian Business Register as a Commonwealth Government Entity on 1 November 1999.[38]
2000s–2010s
In 2001 digital television commenced (see Online, below). At the same time the ABC's multimedia division was renamed "ABC New Media", becoming an output division of the ABC alongside television and radio.[39]
In 2002 the ABC launched ABC Asia Pacific, the replacement for the defunct Australia Television International operated previously by the Seven Network.[35] A digital radio service, ABC DiG, was also launched in November that year.
On 8 February 2008 ABC TV was rebranded as ABC1, and a new channel for children, ABC3, was funded and announced by the Rudd government in June.[40][41] A new online video-on-demand service launched in July of the same year, titled ABC iview.[42]
ABC News 24, now known as ABC News, a channel dedicated to news, launched on 22 July 2010.[43] On 20 July 2014, ABC1 reverted to its original name of ABC TV.[44]
In November 2014 a cut of $254 million (4.6%[45]) to funding over the following five years together with the additional unfunded cost of the news channel[46] meant that the ABC would have to shed about 10% of its staff, around 400 people. There were several programming changes, with regional and local programming losing out to national programs, and the Adelaide TV production studio had to close.[47]
In November 2016 the ABC announced that ABC News 24, ABC NewsRadio, as well as its online and digital news brands, would be rebranded under a unified ABC News brand,[48] which was launched on 10 April 2017.[49][50]
Michelle Guthrie took over from managing director Mark Scott, whose second five-year contract finished in April 2016.[51] Between July 2017 and June 2018, the whole of the ABC underwent an organisational restructure, after which the Radio and Television Divisions were no longer separate entities each under a director, instead being split across several functional divisions,[52] with different teams producing different genres of content for television, radio and digital platforms. The Entertainment & Specialist (E&S) team focussed on comedy, kids' programs, drama, Indigenous-related programs, music, other entertainment and factual content; the new ABC Specialist team created content across the arts, science, religion & ethics, education and society & culture; while the Regional & Local team focussed on regional and local content.[53]
Around 23 September 2018 Guthrie was fired.[54] A leadership crisis ensued after allegations arose that Chair, Justin Milne, had, according to the MEAA, engaged in "overt political interference in the running of the ABC that is in clear breach of the ABC charter and the role of the chairperson" by interfering in editorial and staffing matters. After pressure for an independent inquiry or statement from Milne, or his resignation, following meetings by ABC staff in various locations, on 27 September Milne resigned.[55]
In February 2019, after the roles of ABC chair and managing director had been vacant for more than four months,[56][57] Ita Buttrose was named chair. Buttrose named David Anderson as managing director in May 2019.[58]
On 5 June 2019 Australian Federal Police (AFP) raided the headquarters of the ABC looking for articles written in 2017 about alleged misconduct by Australian special forces in Afghanistan, later dubbed the Afghan Files.[59][60] The raid was countered by lawyers for the ABC in litigation against the AFP, challenging the examination of over 9,200 documents, including internal emails.[61][62][63][64] In February 2020 the case was dismissed by the federal court.[65][66][67] In June 2020, the AFP sent a brief of evidence to the Commonwealth Director of Public Prosecutions (CDPP), the federal public prosecutor, recommending charges be laid against journalist Dan Oakes for breaking the Afghan Files story,[68] but in October 2020, the CDPP dropped the case.[69]
2020s
In June 2020 the ABC announced it needed to cut 229 jobs,[70] a number of programs, and reduce its travel and production budgets after the Turnbull government's announcement of a freeze to indexation of its budget in 2018[71] this was estimated at the time to cost the ABC A$84 million over three years, however the actual appropriation did not decrease[72] and the ABC chair was quoted as saying it would actually increase "but by a reduced amount".[73][74][75]
In all, over a five-year period, there were 737 redundancies, a further 866 resignations, and 203 retirements; but the total number of staff only fell by 313 due to the ABC hiring 650 staff over that period.[76]
In June 2021 the ABC announced its plan to move around 300 staff to offices in Parramatta, in a plan which would see 75% of journalists and producers moving out of the Ultimo building by 2025 to reduce costs. Rental from some of the vacant space in the city centre would earn additional income to offset the ongoing effects of the significant funding cuts since 2014 and the recent indexation freeze.[77]
In December 2021 the ABC announced that, in addition to the 83 additional positions already established, it was to create an additional "50-plus" new jobs in regional Australia as a result of commercial agreements with digital platforms flowing from the Morrison government's News Media Bargaining Code.[78]
In May 2024 the ABC started moving from its Ultimo office to a new Parramatta office. The first program to be broadcast from the new studio in Parramatta was ABC Radio Sydney Mornings.[79][80]
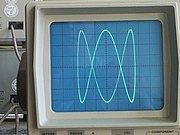
The ABC logo is one of the most recognisable logos in Australia.[81][82][83] In the early years of television, the ABC had been using Lissajous curves as fillers between programmes.[84] In July 1963, the ABC conducted a staff competition to create a new logo for use on television, stationery, publications, microphone badges and ABC vehicles.[85][86] In 1965, ABC graphics designer Bill Kennard submitted a design representing a Lissajous display, as generated when a sine wave signal is applied to the "X" input of an oscilloscope and another at three times the frequency at the "Y" input. The letters "ABC" were added to the design and it was adopted as the ABC's official logo. Kennard was presented with £25 (about AU$715 in 2021) for his design.[85]
On 19 October 1974 the Lissajous curve design experienced its first facelift with the line thickened to allow for colour to be used. It would also be treated to the 'over and under' effect, showing the crossover of the line in the design. To celebrate its 70th anniversary on 1 July 2002, the ABC adopted a new logo, which was created by (Annette) Harcus Design in 2001. This logo used a silver 3D texture but the crossover design was left intact and was then used across the ABC's media outlets. After the on-air revival of the 1974 logo since 2014, the ABC gradually reinstated the classic symbol.[87] The most recent change happened in February 2018, with a new logotype and brand positioning under its tagline, Yours.[88] The 2002 silver logo is no longer in use by the corporation.
The operations of the ABC are governed by a board of directors,[89] consisting of a managing director,[90] five to seven directors,[90] and until 2006, a staff-elected director.[90][91] The managing director is appointed by the board for a period of up to five years, but is eligible for renewal.[92] The authority and guidelines for the appointment of directors is provided for in the Australian Broadcasting Corporation Act 1983.[93][94][95]
Appointments to the ABC Board made by successive governments have often resulted in criticism of the appointees' political affiliation, background, and relative merit.[96][97] Past appointments have associated directly with political parties – five of fourteen appointed chairmen have been accused of political affiliation or friendship, include Richard Downing and Ken Myer (both of whom publicly endorsed the Australian Labor Party at the 1972 election),[35] as well as Sir Henry Bland, David Hill was close to Neville Wran, while Donald McDonald was considered to be a close friend of John Howard.
From 2003 the Howard government made several controversial appointments to the ABC Board, including prominent ABC critic Janet Albrechtsen,[98] Ron Brunton,[99] and Keith Windschuttle.[97][100]
During their 2007 federal election campaign Labor announced plans to introduce a new system, similar to that of the BBC, for appointing members to the board.[101][102] Under the new system, candidates for the ABC Board would be considered by an independent panel established "at arm's length" from the Communications Minister.[103] If the minister chose someone not on the panel's shortlist, they would be required to justify this to parliament. The ABC chairman would be nominated by the prime minister and endorsed by the leader of the opposition.[101][104][105]
A new merit-based appointment system was announced on 16 October 2008, in advance of the new triennial funding period starting in 2009.[106][107]
In 2013 the Coalition government introduced a merit-based system for appointing the board based on the recommendations of a nominations panel. However, the panel was ultimately only advisory, with almost all of the board members in 2018 directly appointed by the Communications minister, despite some being rejected by the panel or not being considered at all.[108]
As of March 2024[update] board members include:[109]
| Name | Functional role | Start of term | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kim Williams | Chair | 7 March 2024 | Term ends 6 March 2029[1] |
| David Anderson | Managing director | 6 May 2019 | First term ended 1 July 2023[note 2] Second term ends 30 June 2028[110][1] |
| Laura Tingle | Staff-elected director | 1 May 2023 | Term ends 30 April 2028[1] |
| Nicolette Maury | 16 October 2023 | Term ends 15 October 2028[1] | |
| Peter Lewis | 2 October 2014 | First term ended 1 October 2019 Second term ended 1 October 2024[1] | |
| Georgie Somerset | 23 February 2017 | Term ends 22 Feb 2027[1] | |
| Louise McElvogue | 16 October 2023 | Term ends 15 October 2028[1] | |
| Mario D'Orazio | 13 May 2021 | Term ends 12 May 2026[1] | |
| Peter Tonagh | Deputy Chair | 13 May 2021 | Term ends 12 May 2026[1] |
The ABC is primarily funded by the Australian government, in addition to some revenue received from commercial offerings and its retail outlets. The ABC's funding system is set and reviewed every three years.[111]
Until 1948 the ABC was funded directly by radio licence fees; amendments were also made to the Australian Broadcasting Act that meant the ABC would receive its funding directly from the federal government. Licence fees remained until 1973, when they were abolished by the Whitlam Labor government, on the basis that the near-universality of television and radio services meant that public funding was a fairer method of providing revenue for government-owned radio and television broadcasters.[citation needed]
In 2014 the ABC absorbed $254 million in federal budget deficits.[112]
In the 2018–19 budget handed down by then-Treasurer Scott Morrison, the ABC was subject to a pause of indexation of operation funding, saving the federal government a total of $83.7 million over 3 years.[113] In fiscal year 2016–17, the ABC received $861 million in federal funding, which increased to $865 million per year from 2017 to 2018 to 2018–19, representing a cut in funding of $43 million over three years when accounting for inflation.[52][53] In the 2019–20 federal budget funding was around $3.2 billion over three years ($1.06 billion per year) for the ABC. The Enhanced Newsgathering Fund, a specialised fund for regional and outer-suburban news gathering set up in 2013 by the Gillard government,[114][115] was $44 million over three years as of the 2019–20 budget, a reduction of $28 million per year since the 2016 Australian federal election. This came after speculation that the fund would be removed, to which Acting managing director David Anderson wrote to Communications Minister Mitch Fifield expressing concerns.[112]
Despite the cuts made by Prime Minister Tony Abbott and Communications Minister Malcolm Turnbull and the freeze introduced by Prime Minister Malcolm Turnbull and Communications Minister Mitch Fifield, the ABC itself has published financial data that shows an increase in the taxpayer appropriation to the ABC of 10% in real terms (i.e. above inflation) between 1998 and 2021.[116]
In 2023, fulfilling one of Labor's election pledges, the ABC moved into a five instead of three-year funding term.[117]
The term "where your 8 cents a day goes", coined in the late 1980s during funding negotiations,[118] is often used in reference to the services provided by the ABC.[119] It was estimated that the cost of the ABC per head of population per day was 7.1 cents a day, based on the corporation's 2007–08 "base funding" of A$543 million.[120]
Radio

The ABC operates 54 local radio stations, in addition to four national networks and international service Radio Australia. In addition, DiG Radio (rebranded to Double J in 2014)[121][122]) launched on digital platforms in 2002,[123] and later spinning off ABC Country and ABC Jazz.
ABC Local Radio is the corporation's flagship radio station in each broadcast area. There are 54 individual stations,[when?] each with a similar format consisting of locally presented light entertainment, news, talk back, music, sport and interviews, in addition to some national programming such as AM, PM, The World Today, sporting events and Nightlife.
As of June 2021[update] the ABC operates 15 radio networks, variously available on AM and FM as well as on digital platforms and the internet.[124]
- Radio National – A generalist station, also known as RN, broadcasting more than 60 special interest programmes per week covering a range of topics including music, comedy, book readings, radio dramas, poetry, science, health, the arts, religion, social history and current affairs.
- ABC NewsRadio – A news based service, also known as ABC News on Radio, broadcasting federal parliamentary sittings and news on a 24/7 format with updates on the quarter-hour. Broadcast's news content produced by the ABC itself, as well as programmes relayed from ABC Radio Australia, the BBC World Service, NPR, Deutsche Welle, Radio Netherlands and CNN Radio.
- ABC Classic – A classical music based station, formerly known as ABC Classic FM. It also plays some jazz and world music. ABC Classic was the ABC's first FM radio service. It was originally known simply as "ABC FM", and for a short time "ABC Fine Music".
- Triple J – A youth-oriented radio network, with a strong focus on alternative and independent music (especially Australian artists); it is targeted at people aged 18–35.
The ABC also operates several stations only available online and on digital platforms:[needs update]
- ABC Classic 2 – a sister station to ABC Classic, focussing on performances by Australian artists. Only available on streaming platforms.
- Double J – a Triple J sister station, focussed on an older audience to Triple J.
- Triple J Unearthed – a Triple J sister station, playing unsigned and independent Australian talent.
- Triple j Hottest – a Triple J sister station, playing tracks from the past 30 years of Triple J Hottest 100 countdowns.
- ABC Jazz – A station exclusively dedicated to Jazz from Australia and the world.
- ABC Country – An exclusively country music station, mainly focussing on Australian country music.
- ABC Grandstand – Since November 2020 merged to ABC Sport.[125]
- ABC Extra – A temporary special events station.
- ABC Kids – Children's based programming, and a sister station to the ABC Kids television channel.
There is also ABC Radio Australia, the international radio station of the ABC (see below).
ABC Listen app
The ABC Radio app was launched in 2012. This was replaced by the ABC Listen app in September 2017, which included 45 ABC radio stations and audio networks.[126][127][128]
Television
The ABC operates five national television channels:[129]
- ABC TV (formerly ABC1 from 2008 to 2014), the corporation's original television service, receives the bulk of funding for television and shows first-run comedy, drama, documentaries, and news and current affairs. In each state and territory a local news bulletin is shown at 7 pm nightly.
- ABC Family (formerly ABC2 and ABC Comedy and ABC TV Plus), launched in 2005, shows comedic content in addition to some repeats from ABC TV of which the amount has decreased gradually since ABC TV Plus's inception. It is not a 24-hour channel, but is broadcast daily from 7:30 pm to around 3 am the following night. The channel shares airspace with the ABC Kids programming block from 5 am to 7:30 pm.
- ABC Entertains (originally ABC3 and ABC Me) became a fully fledged channel on 4 December 2009, but has been part of the electronic guide line-up since 2008, broadcasting an ABC1 simulcast until 4 December 2009, then an ABC Radio simulcast and teaser graphic until its official launch. It is broadcast from 6 am to around 10 pm on weekdays and 6 am to 2 am the next day on weekends, and consists of a broad range programmes aimed at a young audience aged 6–15, with a core demographic of 8–12.
- ABC Kids (formerly ABC For Kids on 2 and ABC 4 Kids) is a preschool children's block featuring children's programming aimed at the 0 to 5 age groups. ABC Kids broadcasts during ABC Family downtime, from 4 am to 7:30 pm daily.
- ABC News (originally ABC News 24), a 24-hour news channel, featuring the programming from ABC News and Current Affairs, selected programs from the BBC World News channel, coverage of the Federal Parliament's Question Time, documentaries and factual, arts programming and state or national election coverage.
Although the ABC's headquarters in Sydney serve as a base for program distribution nationally, ABC Television network is composed of eight state and territory based stations, each based in their respective state capital and augmented by repeaters:
The eight ABC stations carry opt outs for local programming. In addition to the nightly 7 pm news, the stations also broadcast weekly state editions of 7.30 on Friday evenings (until 5 December 2014), state election coverage and in most areas, live sport on Saturday afternoons.
There is also ABC Australia, the international TV service of the ABC (see below).

Online and digital
ABC Online is the name given to the online services of the ABC, which have evolved to cover a large network of websites including those for ABC News, its various television channels, ABC radio; podcasts; SMS, mobile apps and other mobile phone services; vodcasts and video-on-demand through ABC iView.[130]
The official launch of ABC Online, then part of the ABC's Multimedia Unit, was on 14 August 1995,[130] charged with developing policy for the ABC's work in web publishing. At first it relied upon funding allocation to the corporation's TV and radio operations, but later began to receive its own. The ABC provided live, online election coverage for the first time in 1996, and limited news content began to be provided in 1997.[36] This unit continued until 2000, when the New Media division was formed, bringing together the ABC's online output as a division similar to television or radio. In 2001 the New Media division became New Media and Digital Services, reflecting the broader remit to develop content for digital platforms such as digital television, becoming an "output division" similar to Television or Radio.[39] In addition to ABC Online, the division also had responsibility over the ABC's two digital television services, Fly TV and the ABC Kids channel, until their closure in 2003.[131]
ABC TV Plus, a digital-only free-to-air television channel, launched on 7 March 2005, as ABC2. Unlike its predecessors the new service was not dependent on government funding, instead running on a budget of A$3 million per year.[35] Minister for Communications Helen Coonan inaugurated the channel at Parliament House three days later.[132] Genre restrictions limiting the types of programming the channel could carry were lifted in October 2006 – ABC TV Plus (then ABC2) was henceforth able to carry programming classified as comedy, drama, national news, sport, and entertainment.[133]
In conjunction with the ABC's radio division, New Media and Digital Services implemented the ABC's first podcasts in December 2004. By mid-2006 the ABC had become an international leader in podcasting with over fifty podcast programmes delivering hundreds of thousands of downloads per week,[134] including trial video podcasts of The Chaser's War on Everything and jtv.[135]
In February 2007 the New Media & Digital Services division was dissolved and divided up among other areas of the ABC. It was replaced by a new Innovation division, to manage ABC Online and investigate new technologies for the ABC.[136]
In 2008 Crikey reported that certain ABC Online mobile sites in development were planned to carry commercial advertising.[137] Screenshots, developed in-house, of an ABC Radio Grandstand sport page include advertising for two private companies. Media Watch later revealed that the websites were to be operated by ABC Commercial and distinguished from the main, advertising-free, mobile website by a distinct logo.[138]
In 2015 the Innovation Division was replaced with the Digital Network Division.[139] Angela Clark was head from 2012 until at least the end of financial year 2015/6,[140] but by 2017 she was gone, and the Digital Network fell into the Technology division under the Chief Technology Officer.[52]
In May 2017 Helen Clifton was appointed to the new role of Chief Digital and Information Officer.[141] She retired from this role in 2022[142]
In December 2019 a refreshed ABC homepage was launched.[143] ABC News is one of Australia's largest and most-visited web sites; from its position as 11th most popular in the country in 2008,[144] in recent years up to 2021 it has maintained its top position in the rankings.[145][146][147]
In June 2023 the broadcaster released its five-year plan, outlining that it would move its resources away from radio and television, and instead dedicate these resources to improving and promoting its digital platforms.[148]
International
ABC International is responsible for its international operations, which include the internationally broadcast Radio Australia, the Asia-Pacific TV channel ABC Australia,[149] and its ABC International Development (ABCID) branch.[150]
In June 2012 Lynley Marshall, former head of ABC Commercial, was appointed CEO of ABC International, filling a role left empty by the retirement of Murray Green.[149] At the time, it was intended that Radio Australia, ABC Australia and ABC News would work together more closely[151] ABC International was at this time a division of the ABC, but it has not been represented as a separate division in the organisational structure of the ABC since 2016,[152][140][52][53][153][116] after Marshall's departure in February 2017.[154]
There were fears of job losses in the division after the huge budget cuts in 2014, as well as an earlier termination of a A$220 million contract with the Department of Foreign Affairs, one year into the 10-year contract.[155]
On 24 May 2021 Claire Gorman was appointed to an expanded role to manage both the International Strategy and the International Development teams.[156]
ABC Australia is an international satellite television service operated by the Australian Broadcasting Corporation, funded by advertising and grants from the Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade. Aimed at the Asia-Pacific region, the service broadcasts a mixture of English language programming, including general entertainment, sport, and current affairs.
Radio Australia is an international satellite and internet radio service with transmissions aimed at South-East Asia and the Pacific Islands, although its signals are also audible in many other parts of the world. It features programmes in various languages spoken in these regions, including Mandarin, Indonesian, Vietnamese, Khmer and Tok Pisin. Before 31 January 2017 Radio Australia broadcast short-wave radio signals. Radio Australia bulletins are also carried on WRN Broadcast, available via satellite in Europe and North America.
ABC International Development, or ABCID, is a media development unit that promotes public interest journalism and connects with local media in the region. ABCID employs local people in Papua New Guinea and many Pacific countries.[157][158] The team "provides expertise, training, technical and program support to partner organisations", by working with a variety of organisations, including international development donors,[153] for example through the Pacific Media Assistance Scheme (PACMAS).[159]
Under the Australian Broadcasting Corporation Act 1983, the ABC Board is bound to "maintain the independence and integrity of the Corporation" and to ensure that "the gathering and presentation by the Corporation of news and information is accurate and impartial according to the recognised standards of objective journalism".[93]
The ABC's editorial policy on impartiality requires it to take "no editorial stance other than its commitment to fundamental democratic principles including the rule of law, freedom of speech and religion, parliamentary democracy and non-discrimination".[160] The ABC follows the following "hallmarks of impartiality": "a balance that follows the weight of evidence, fair treatment, open-mindedness and opportunities over time for principal relevant perspectives on matters of contention to be expressed".[160]
The editorial policy on diversity also requires the broadcaster "to present, over time, content that addresses a broad range of subjects from a diversity of perspectives reflecting a diversity of experiences, presented in a diversity of ways from a diversity of sources". However, it also notes that this "does not require that every perspective receives equal time, nor that every facet of every argument is presented".[160]
The commercial arm of the ABC was established in 1974 under the name Enterprises as a self-funding unit, marketing products relating to the ABC's activities. It was renamed in 2007 to ABC Commercial,[161][136] The aim of ABC Commercial was "to create, market and retail high quality consumer products which reflect and extend the scope of the ABC's activities".[161] At this time it comprised the ABC Shop, ABC Consumer Publishing and Content Sales, ABC Resource Hire, and ABC Content Services (Archives).[162][163]
ABC Commercial was registered as a business name under Australian Broadcasting Corporation in April 2007 and continues to exist as of June 2021[update].[38] It includes ABC Music, a leading independent record label; ABC Events, which stages concerts and other events; and publishing and licensing activities by ABC Books, ABC Audio, ABC Magazines and ABC Licensing.[153]
ABC Shop Online was wound up at the end of 2018, along with the in-store ABC Centres.[164] In early 2019, ABC Commercial split from the Finance division and became an independent business unit of the ABC.
In the financial year 2018–2019, ABC Commercial turned a profit of A$4.4 million, which was invested in content production.[153]
The ABC Studios and Media Production hires out some of the ABC studios and sound stages, operating as part of ABC Commercial. The studios for hire are in Sydney (Studios 21, 22, 16), Melbourne (31), Adelaide (51B) and Perth (61).[165]
Up until the installation of disc recording equipment in 1935, all content broadcast on the ABC was produced live, including music.[16] For this purpose the ABC established broadcasting orchestras in each state, and in some centres also employed choruses and dance bands. This became known as the ABC Concert Music Division, which was controlled by the Federal Director of Music – the first of whom was W. G. James.[166]
In 1997 the ABC divested all ABC orchestras from the Concerts Department of the ABC into separate subsidiary companies, allied to a service company known as Symphony Australia,[167][36] and on 1 January 2007 the orchestras were divested into independent companies.[168] The six state orchestras are:
ABC Friends, formerly Friends of the ABC (FABC), consists of independent organisations in each state and territory, under an umbrella organisation established in December 2016, ABC Friends National Inc. In 1976 three independent groups were formed: Aunty's Nieces and Nephews in Melbourne, Friends of the ABC (NSW) Inc.[169] (now ABC Friends NSW & ACT[170]) and Friends of the ABC (SA) (since 2007/2008, ABC Friends SA/NT).[171] The groups were formed by citizens who were concerned about government threats to make deep cuts to the ABC's budget. Historian Ken Inglis wrote that "The Friends were in the line of those people who had affirmed over the years that the ABC was essential to the nation". Over the years, independent state organisations were established, run by committees, and in January 2014 the name of each was changed to ABC Friends.[169]
The objectives of ABC Friends National are stated as follows:[169]
To represent community interest in defending and promoting the vital role of Australia's independent national public broadcaster, the Australian Broadcasting Corporation (ABC) to ensure:
- that the ABC be properly funded to maintain and advance its role as the national public broadcaster in all media, promoting and reflecting Australian culture and diversity
- that it remain editorially independent of government and commercial interests.
Defamation
In 2023 the ABC lost a defamation case against Heston Russell, where the corporation withdrew a truth defence and opted for the case to be heard under a public interest defence.[172]
In the landmark ruling Justice Lee awarded Russell $390,000 in addition to interest and damages. Estimates of legal expenses ranged between $1.2 million and $3 million. The broadcaster did not take up an earlier settlement offer of $99,000 and removal of the published articles. The ABC managing director, David Anderson, who took home a six-figure pay rise shortly after the defamation case loss, outlined in senate estimates that he would not apologise to Russell for the false reporting.[173]
Recordings of Mark Willacy's interviews that formed part of the defamation case were garnished as part of the legal discovery process. They were made available to Ben Fordham's 2GB radio program.
In December 2023 Antoinette Lattouf was hired for five days to fill in for Sarah Macdonald on ABC Radio Sydney and then sacked three days later due to her outspoken activism on the Israel-Gaza conflict by reposting a Human Rights Watch story covering alleged actions taken by Israeli soldiers in Gaza. Two days later Lattouf initiated law action with the Fair Work Commission against the ABC for alleged racial discrimination. ABC members of the Media, Entertainment and Arts Alliance voted no confidence in Anderson partly due to WhatsApp messages that had come to light from a pro-Israel lobby group known as "Lawyers for Israel". The next day the ABC Board voted unanimous confidence in Anderson.[174][175][176]
In March 2024 the ABC aired a documentary titled "Ukraine's War: The Other Side," by Sean Langan which has been criticised by Ukrainian ambassador Vasyl Myroshnychenko as the "journalistic equivalent of a bowl of vomit" and seemed to repeat Russian justification for the War in Ukraine and structured in a way that seems to favor the Russian side.[177] The ABC has defended its position with a spokesperson stating "we believe Australian audiences also have the right to watch it and make up their own minds."[178]
Perceived bias
External critics have complained in particular of left-wing political bias at the broadcaster,[130] citing a prominence of Labor Party-connected journalists hosting masthead political programs or a tendency to favour "progressive" over "conservative" political views on issues such as immigration, asylum seekers, the republic, multiculturalism, Indigenous reconciliation, feminism, environmentalism, and same-sex marriage.[179][180][18][181]
In December 2013 former judge and ABC chair James Spigelman announced that four independent audits would be conducted each year in response to the allegations of bias in the reporting of news and current affairs. ABC Friends have observed that: "Most of the complaints about bias in the ABC have come from the government of the day – Labor or Liberal. Significantly both parties have been far less hostile to the ABC when in opposition".[130]
Reviews and investigations
Reviews of the ABC are regularly commissioned and sometimes not released.[182][183]
Both internal and external research has been conducted on the question of bias at the ABC. These include the following:
- A 2004 Roy Morgan media credibility survey found that journalists regarded ABC Radio as the most accurate news source in the country and the ABC as the second "most politically biased media organisation in Australia".[184]
- A 2013 University of the Sunshine Coast study of the voting intentions of journalists found that 73.6% of ABC journalists supported Labor or the Greens – with 41% supporting the Greens (whereas only around 10% of people in the general population voted Green).[185][186]
- At the 2016 federal election, a study commissioned by the ABC and conducted by Isentia compiled share-of-voice data and found that the ABC devoted 42.6% of election coverage to the Coalition government (this compares to the 42.04% vote received by the Coalition in the House of Representatives (HOR)), 35.9% to the Labor opposition (34.73% HOR), 8% to the Greens(10.23% HOR), 3.1% to independents (1.85% HOR), 2.2% to the Nick Xenophon Team (1.85% HOR) and 8.1% to the rest. However, the ABC itself notes the "significant limitations around the value of share of voice data" as "duration says nothing about tone or context".[187]
- In December 2020, the Board commissioned its 19th editorial review by an independent reviewer, which found that the ABC's news coverage of lead-up to the 2019 Australian election was "overwhelmingly positive and unbiased", although it also found that specific episodes of The Drum and Insiders reflected too narrow a range of viewpoints. The government forced the publication of the report after Coalition senator James McGrath raised a motion in the Senate, which led to ABC Chair Ita Buttrose and managing director David Anderson writing to the president of the Senate, Scott Ryan, to express their concerns about the use of the such powers, which went against the public interest.[188]
Relationships with government
Labor prime minister Bob Hawke considered the ABC's coverage of the 1991 Gulf War to be biased.[189] In 1996, conservative opposition leader John Howard refused to have Kerry O'Brien of the ABC moderate the television debates with Labor prime minister Paul Keating because Howard saw O'Brien as biased against the Coalition.[190]
Liberal Prime Minister Tony Abbott perceived the ABC to be left wing and hostile to his government, while Malcolm Turnbull enjoyed better relations with the national broadcaster.[191][192][193] Turnbull's successor, Scott Morrison, once again presided over "strained" relations between the government and the ABC.[194] Under Morrison's leadership, an investigation was launched into the ABC and its complaints-handling process—a decision which was criticised by Ita Buttrose as "political interference".[194] The inquiry was abandoned the following June.[195]
Specific topics
The Catholic Church and George Pell
The ABC's coverage of the issue of sexual abuse in the Catholic Church received praise and criticism. The Melbourne Press Club presented the 2016 Quill for Coverage of an Issue or Event for the report George Pell and Sexual Abuse in the Catholic Church, and the 2016 Golden Quill award to Louise Milligan and Andy Burns for their extensive coverage of Cardinal George Pell's evidence given at the Royal Commission into Institutional Responses to Child Sexual Abuse.[196][197]
The ABC Media Watch program of 20 April 2020 noted that the ABC had been accused of leading a "witch hunt" against Cardinal Pell. Media Watch reported that, following his acquittal, Pell said the ABC gave an "overwhelming presentation of one view and only one view". Media Watch also canvassed other criticisms including from The Australian newspaper's editor-at-large Paul Kelly, who charged the ABC with having run a "sustained campaign against Pell". Media Watch also offered criticism of its own, noting Louise Milligan and the Four Corners program had failed to canvass any of Pell's defence from the trial and "lined up witnesses condemning Pell", while social media commentary by Barrie Cassidy and Quentin Dempster had undermined the presumption of innocence.[198] Margaret Simons similarly noted in The Guardian that "there has been some social media activity by ABC journalists that looks very much like lobbying against Pell..."[199]
Environmentalism
Planet Slayer was an ABC website run by scientist Bernie Hobbs to teach children about the environment in around 2008/9.[200] It included a "Greenhouse Calculator" which aimed to help children to work out their carbon footprint by providing an estimate of the age a person needs to die if they are not to use more than their fair share of the Earth's resources.[201] Victorian Liberal senator Mitch Fifield criticised a cartoon series on the site for portraying those who eat meat, loggers, and workers in the nuclear industry as "evil".[202] ABC managing director Mark Scott said the site was not designed to offend anyone, but instead have children think about environmental issues.[203]
Wikiwand in your browser!
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.