4-Aminoquinoline
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
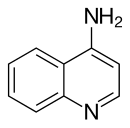
4-Aminoquinoline is a form of aminoquinoline with the amino group at the 4-position of the quinoline. The compound has been used as a precursor for the synthesis of its derivatives.[1]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Quinolin-4-amine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.167.771 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H8N2 | |
| Molar mass | 144.177 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Powder to crystalline, White/Yellow/Orange |
| Melting point | 151–155 °C (304–311 °F; 424–428 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards |
Causes skin and serious eye irritation |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
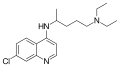
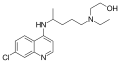
A variety of derivatives of 4-aminoquinoline are antimalarial agents useful in treating erythrocytic plasmodial infections.[2] Examples include amodiaquine, chloroquine, and hydroxychloroquine.[3] Other uses for the derivatives are: anti-asthmatic, antibacterial, anti-fungal, anti-malarial, antiviral and anti-inflammatory agents.[1]
A patent application for 4-aminoquinoline compounds was filed in 2002 and published in 2005.[4]
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.