2019 India–Pakistan border skirmishes
Series of armed skirmishes between India and Pakistan in Kashmir From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The 2019 India–Pakistan border skirmishes were a series of armed clashes consisting of cross-border airstrikes and exchanges of gunfire between India and Pakistan across the de facto border in the disputed Kashmir region, which is subject to extensive territorial claims by both countries.[12]
| 2019 India–Pakistan skirmishes | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Indo−Pakistani conflicts and the Kashmir conflict | ||||||||
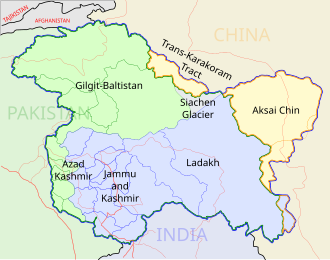 Map of Kashmir, showing the territory controlled by India and Pakistan in blue and green, respectively | ||||||||
| ||||||||
| Belligerents | ||||||||
| Jaish-e-Mohammed | ||||||||
| Casualties and losses | ||||||||
Before onset of hostilities:
| ||||||||
The heightened tensions stemmed from the 14 February 2019 Pulwama attack in Jammu and Kashmir, which killed 40 Indian Central Reserve Police Force personnel. Responsibility for the attack was claimed by a Pakistan-based militant group, Jaish-e-Mohammed.[13] India blamed Pakistan for the attack and promised a robust response, while the latter condemned the attack and denied having any connection to it.[14][15]
Twelve days later, in the early morning of 26 February 2019, India carried out a cross-border airstrike near Balakot, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan.[16][17]
Pakistan's military, the first to announce the airstrike that same morning,[18] claimed that Indian warplanes had crossed the international border and dropped their payload in an uninhabited wooded hilltop area near Balakot in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa.[19] India, confirming the airstrike later that day, characterized it to be a preemptive strike directed against a terrorist training camp, and claimed that it had caused the deaths of a "large number" of terrorists.[20][21]
The second airstrike, a retaliatory one by Pakistan,[22] was conducted in the daytime on 27 February, inside Indian-administered Kashmir. A dogfight between Indian and Pakistani fighter jets during this airstrike resulted in the downing of an Indian MiG-21 Bison by the Pakistan Air Force, following which its pilot, Wing Commander Abhinandan Varthaman, was taken prisoner by the Pakistani military before being returned to India on 1 March.[23][24][25]
On the same hours of PAF retaliatory strikes on 27 February 2019, an Indian Mi-17 helicopter was brought down by friendly fire in which all IAF airmen on board were killed, including Squadron Leaders Siddharth Vashisht and Ninad Mandavgan.[26] IAF Chief RKS Bahaduria acknowledged IAF's failure only a year latter on 4 October 2019, terming friendly fire as "a big mistake".[27][26] Resultantly Group Captain Suman Roy Choudhry Chief Operations Officers (COO) of Srinagar Air Force Station was dismissed from his service in 2023.[28]
Aftermath analysis of open-source satellite imagery by the American Atlantic Council's Digital Forensics Laboratory,[29] San Francisco-based Planet Labs,[30] European Space Imaging[31] and the Australian Strategic Policy Institute[32] concluded that India did not hit any targets of significance on the Jaba hilltop site near Balakot in Pakistan.[33][34]
On 10 April 2019, one and a half months later, a group of international journalists, who were taken to the Jaba hilltop in a tightly controlled trip arranged by the Pakistani government, although unable to make a knowledgeable evaluation,[35][36] found the largest building there to show no evidence of damage or recent rebuilding efforts.[37][38][39][36]
The US count of PAF's F-16 fleet confirmed PAF lost no aircraft during its dogfight with IAF.[40][41] The claim of IAF of shooting down a F-16 was also rejected by various international observers.[42]
Background
Summarize
Perspective
India and Pakistan have long been at odds with each other, having engaged in several wars, conflicts, and military standoffs. The roots of the continued tension are complex, but have centred mainly around the erstwhile princely state of Jammu and Kashmir. After the 1947 Partition of India, the newly formed independent states of Pakistan and India squabbled over it, which led to the Indo-Pakistani War of 1947–1948 and a subsequent sharing of the state. The settlement was non-agreeable to both the parties and since then, this had become an ongoing intractable issue leading to a war in 1965. The nations also partook in another war in 1971 which led to the formation of Bangladesh. Both countries developed nuclear weapons in the 1990s and this had a sobering effect on the next major conflict – the 1999 Kargil War.[43]
As of now, the Line of Control demarcates the areas of administration: Pakistan administers the territory to the northwest of the line; India administers the territory to the southeast.[44] Since 1989, a militant-fueled insurgency has raged in Indian-administered Kashmir, driven by a desire for either independence or union with Pakistan.[45][46] The United Nations has stated Pakistan was providing material support to the militants[47] and stated India was committing human rights violations.[48]
The standoff occurred ahead of the 2019 Indian general election.[49][50] After the Pulwama attack, Pakistan's PM attributed Indian government's desire to retaliate against Pakistan to the upcoming election.[51][52] The Indian government rejected the allegation.[51] Many analysts have stated that a military response to Pakistan would improve the electoral prospects of India's ruling party.[53][54][50][55]
Military events
Summarize
Perspective
Pulwama attack
The 2019 India–Pakistan military standoff was a result of[56] a militant attack in February 2019, when a Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF) convoy carrying security personnel on the Jammu–Srinagar National Highway was attacked by a vehicle-borne suicide bomber at Lethpora in the Pulwama district, Jammu and Kashmir, India. Over 40 CRPF personnel and the perpetrator were killed in the attack, which Jaish-e-Mohammed took responsibility for. The attacker was identified as Adil Ahmad Dar, a militant from Jammu and Kashmir, and a member of Jaish-e-Mohammed.[57] This was the deadliest attack on Indian forces in Kashmir since 1989.[58]
Balakot airstrike
On 26 February 2019, the Indian Air Force conducted airstrikes at Balakot in Pakistan. The strikes were subsequently stated to be "non-military" and "preemptive" in nature; targeting a Jaish-e-Mohammed facility within Pakistan. The Indian government stated that the airstrike was in retaliation to the Pulwama attack and that "a very large number of JeM terrorists, trainers, senior commanders and groups of jihadis" were eliminated who were preparing for launching another suicide attack targeting Indian assets.[59]
Indian media reported to have confirmed from official sources that twelve Mirage 2000 jets were involved in the operation and that they struck multiple militant camps in Balakot, Chakothi and Muzaffarabad operated by Jaish-e-Mohammed, Lashkar-e-Taiba and Hizbul Mujahideen,[60] killing about 350 militants. The exact figures varied across media-houses.[61]
Pakistani officials acknowledged the intrusion of Indian aircraft into the country's airspace but rejected the statements about the results. They stated that the Indian jets were intercepted and that the payloads were dropped in unpopulated areas and resulted in no casualties or infrastructural damage.[62] Pervez Khattak, the Pakistani Defence Minister, stated that the Pakistani Air Force did not retaliate at that time because "they could not gauge the extent of the damage".[63]
Business Today India stated that the area around Balakot had been cordoned off by the Pakistan Army and evidences such as the dead bodies were being cleared from the area.[64] Praveen Swami writing for Firstpost said that Indian intelligence estimated a figure of about 20 casualties and that there were five confirmed kills per burial records.[65] He also said there was a JeM rally in Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa on 28 February, wherein Masood Azhar's brother, Abdul Rauf Rasheed Alvi mentioned India's attack of their headquarters and vowed revenge.[65] In another piece he stated that RAW analysts estimated 90 casualties including three Pakistani Army trainers, based on intercepted communications.[66] Swami also said there was a lack of witness testimony to independently assess the validity of above statements.[66]
This airstrike was the first time since the Indo-Pakistani War of 1971 that aerial attacks had been carried out across the Line of Control.[66]
Villagers from the area said that four bombs struck a nearby forest and a field resulting in damage to a building and injuring a local man around 3:00 am.[67][68][69] On 28 February 2019, Pakistani Reuters reporters Asif Shahzad, Abu Arqam Naqash reported that the structure and its vicinity (of the bomb site) to be intact from the rear,[68] however on 8 March 2019, the Reuters media team was prevented for third time from climbing hill to the closely guarded madrasa site in Balakot.[70]
Some diplomats and analysts have raised doubts about the efficacy of the strike, stating that the terrorist groups along the border would have vacated the area, after the Indian Prime Minister vowed to retaliate against the Pulwama attack.[71] The local people varied as to the purpose of the facility.[69] Whilst some stated it being an active Jaish training camp, others stated it to have been a mere school for the local kids and that such militant camps had used to exist far earlier.[68][69] Satellite-data analysis by Nathan Ruser, from the Australian Strategic Policy Institute said there was an absence of any apparent evidence to verify Indian statements.[61][72][73] Michael Sheldon, a digital forensics analyst at the Atlantic Council, did an independent investigation on the issue, in which he said that no damage was caused to any infrastructure around the target site. He concluded that "something appears to have gone wrong in the targeting process", which was mysterious in light of the autonomous nature of the missiles reportedly used.[74][75][24][76] However, Pakistan had to close the site for one and a half month or 43 days before opened to foreign delegates and media.[77][78][79]
The Indian officials stated that synthetic aperture radar showed that four buildings had been destroyed.[73] Vice-Marshal RGK Kapoor of the Indian Air Force said on 28 February 2019 that though it was "premature" to provide details about the casualties, they had "fairly credible evidence" of the damage inflicted on the camp by the air strikes.[68]
In April 2019, Indian External Affairs Minister Sushma Swaraj officially revealed that no Pakistani soldier or civilian was hurt in Balakot air raids.[80][81]
Border skirmishes
Heavy skirmishes between Pakistani and Indian forces occurred along the Line of Control on 26 February, with small arms and mortar fire being exchanged.[82] Pakistani officials reported that at least four civilians were killed, and eleven were wounded.[83][84] A 55-year-old woman and her two children were killed in the Nakyal sector. In the Khuiratta sector, a 40-year-old woman was killed.[83]
Throughout 27 February, heavy exchanges of fire between Indian and Pakistani forces continued along the Line of Control.[85] Ten Indian soldiers were injured along with two residential houses being destroyed in the skirmishes.[6] The Pakistani Army stated that on 1 March, two of its soldiers were killed by firing from the Indian Army at the Line of Control.[86] Shelling across the Line of Control reportedly killed a Kashmiri woman and her two sons after a shell landed on their home, with another civilian being critically wounded.[87] On 6 and 7 March, Pakistani and Indian forces exchanged heavy artillery fire along the line of control, with Pakistani forces using 130 mm and 105 mm artillery and 120 mm mortars.[88] In response to the Pakistani artillery fire, the Indian army began utilizing 155mm FH77B Bofors cannons against Pakistani positions.[88]
Retaliatory airstrikes, capture and release of pilot, and friendly fire

On 27 February, Pakistani military officials announced that Pakistan had carried out an airstrike against multiple targets in Jammu and Kashmir. A military spokesman claimed that the Pakistan Air Force (PAF) was able to lock onto Indian military installations, but opted to drop weapons into open areas instead, "to avoid human loss and collateral damage.[unbalanced opinion?][89] Pakistan's Prime Minister Imran Khan said that the airstrikes only aimed to "send a message" and appealed for negotiations to avoid a full-blown war.[90] The spokesman further said that the Pakistan Air Force had shot down two Indian aircraft after they encroached on Pakistan's airspace, one of which fell in Pakistan administered Kashmir while the other fell in Indian administered Kashmir.[91][92] It was also stated that Pakistan Army had captured two Indian pilots, one of whom was said to be injured and taken to the Combined Military Hospital.[93][94] But a subsequent statement revised the count down to one–Abhinandan Varthaman, a Wing Commander.[95] According to Indian media allegations, the other pilot the Pakistan Army claimed to have captured and taken to the Combined Military Hospital is claimed to be the downed F-16 pilot.[96][97][98] On the other hand, according to The National Bureau of Asian Research, such claims of an F-16 being shot down by India are said to be "debunked".[99] US count of PAF's F-16 fleet and Independent media reports confirmed that no F-16 was shot down during aerial dogfight between IAF and PAF.[100][41] The Indian claim of shooting down of a PAF F-16 was also rebutted by the prominent geo-political and military analyst Professor Christina Fair who stated while rejecting IAF claims "IAF narrative is not based on an empirical body of facts but dictated more by things deployed by politicians to win elections".[42]
India rejected this version of events and stated to have "successfully foiled" Pakistan's attempt to "target military installations".[101] An Indian Air Force (IAF) official statement hours after the airstrike stated that bombs had been dropped on Indian army formation compounds, but there was no damage to military installations.[102] The Indian military later stated that three Pakistan Air Force jets had crossed the Line of Control (LoC) from Nowshera, Jammu and Kashmir and had dropped bombs over Nadian, Laam Jhangar, Kerri in Rajouri District and Hamirpur area of Bhimber Galli in Poonch, before being pushed back by six Indian airforce jets.[103][104] There were no damage or casualties.[105] Raveesh Kumar from the Indian Ministry of External Affairs also stated that a Pakistani aircraft of the sortie was shot down by the Indian Air Force in the process.[106][66]
The Indian Ministry of External Affairs confirmed[106] that an Indian pilot was missing in action after a MiG-21 Bison fighter plane was lost while engaging with Pakistani jets.[107]
The retaliatory air strikes coupled with the capture of the Indian pilot led to a heightened state of military alert. Tanks were deployed to the border in the Pakistani side whilst several Kashmiri residents reportedly fled their homes and painted their homes with red-cross signs to avert air-strikes.[108]
Pakistan released the captured pilot on 1 March, describing the move as a gesture of peace.[8][109][non-primary source needed][110] The Indian Air Force though stated that the pilot's release was an obligation under the Geneva Conventions.[111] The Indian media also criticized Pakistan's release of his photographs and interrogation videos to be against the protocols of the convention.[112][113] A video published by the state just prior to his release that showed him praising Pakistani Army and condemning Indian media was criticized for being heavily edited.[114][115]
Friendly fire against Indian Air Force Mi-17 Helicopter
In the same hours of PAF retaliatory airstrikes in Jammu and Kashmir on 27 February 2019, IAF mistakenly shot down its own MI-17 helicopter, mistaking it an enemy aircraft.[26] Resultantly, six (6) IAF personnel who were serving as a crew of IAF MI-17 lost their lives including MI-17 pilots, namely, Squadron Leaders Siddharth Vashisht and Ninad Mandavgan.[116] IAF Chief RKS Bahaduria admitted IAF's negligence only a year latter in 2019, terming it "a big mistake".[27] IAF convened an enquiry commission in which Group Captain Suman Roy Choudhry Chief Operations Officers (COO) of Srinagar Air Force Station during PAF airstrikes, was dismissed from his service in 2023.[28]
Failed Indian naval intrusion
On 5 March, the Pakistani Navy claimed to have successfully warded off an intrusion attempt by an Indian submarine into its territorial waters and released a video of a surfaced submarine.[117][118][119] The Indian Navy subsequently rejected these statements as "false propaganda."[120]
Other incidents
Summarize
Perspective
Closure of Pakistani airspace
On 27 February, Pakistan cancelled all commercial flights and closed its airspace until the midnight of 28 February.[121][122] A NOTAM was issued by the Pakistan Civil Aviation Authority to close the airspace.[123][non-primary source needed] Airlines were required to reroute or cancel their flights with routes planned over Pakistan.[124] On 1 March, the NOTAM closing the airspace was extended until 8:00 AM (UTC) on 4 March with 23 exceptions listed.[125] Pakistan's airspace was closed for flights crossing the country's airspace except for arriving and departing flights at major airports in Pakistan.[126] The airspace closure was again repeatedly extended,.[127][128][129][130] The Pakistan finally opened its airspace for all civilian aircraft on 15 July 2019, after 140 days.[131][132]
India did not close down its civilian air traffic and only the Srinagar airspace was closed for 2–3 hours on the day of the skirmish.[133] However the Pakistani flights were allowed usage of Indian airspace only after 15 July when Pakistan opened up its airspace.[134]
The airspace closure led to a loss of US$100 Million for Pakistan due to the skipping of its airspace by an average of 400 aircraft daily.[135] Air India suffered loss of ₹491 Crore till 2 July, as it had to reroute its flights that were affected by the closure of Pakistani airspace. Similarly private Indian airlines SpiceJet lost ₹ 30.73 crore, IndiGo lost ₹ 25.1 crore and GoAir lost ₹ 2.1 crore.[136]
Suspension of Samjhauta Express
On 28 February, Samjhauta Express, a train that runs twice weekly between India and Pakistan, was suspended by the government of Pakistan.[137] It was scheduled to depart from Lahore with 16 passengers, who were stranded there.[138] On 4 March, Pakistan, and consequently India, resumed the operations of Samjhauta Express.[139]
Pakistan arrests suspected militants
On 5 March, Pakistan arrested 44 members of various groups, including the Jaish-e-Muhammad. Some of those arrested had been named by India in a dossier it gave to Pakistan in the aftermath of the Pulwama attack.[140] Pakistan said those arrested will be held for at least 14 days, and if India provided further evidence they would be prosecuted.[140] Among those arrested were relatives of JeM leader Masood Azhar, including his son Hamad Azhar and his brother Abdul Rauf.[140]
Peace offer
Both Prime Minister Imran Khan of Pakistan and Prime Minister of India Narendra Modi agreed on a peace offer on 22 March 2019 ending hostilities and vowed to fight against terrorism together.[141][142]
Aftermath and analysis
Revocation of special status and August border clashes
On 5 August 2019, the Government of India revoked the special status granted to Jammu and Kashmir[143]
On 15 August Pakistan and Indian forces exchanged fire over the disputed frontier in Kashmir, leaving 3 Pakistani soldiers dead and two civilians.[144]
On 21 August the Indian-administered Kasmir police informed about a gun battle that left a rebel and a police officer killed.[145] The deceased militant was a member of Lashkar-e-Taiba a terror organization.[145]
Artillery strike
The Statesman, an Indian newspaper, reported that 18 terrorists and 16 Pakistani soldiers were killed when Indian Army launched artillery strikes on terrorist camps in Neelum valley on 19 and 20 October.[146] Mohammad Faisal, however, said that five Pakistani civilians had died.
Legacy
In 2023, Mike Pompeo, who served as United States Secretary of State during the crisis, claimed that U.S. diplomacy prevented the dispute from sparking a nuclear war. According to Pompeo, he was informed by Sushma Swaraj in February 2019 that the Indian government believed Pakistan was preparing a nuclear attack, and that India was preparing an escalatory response. Pompeo claimed that he and then-national security advisor John Bolton spoke with then-Pakistani Army Chief Qamar Javed Bajwa in "the tiny secure communications facility in our hotel" to deescalate the dispute. Neither the Indian Ministry of External Affairs or Pakistani Foreign Office commented on Pompeo's claims.[147]
International reaction
A number of nations, including Australia,[148] Canada,[149] China,[150] Indonesia,[151] Malaysia,[152] Sri Lanka,[153] the United Arab Emirates,[154] and the United States,[155] expressed their concern, with some calling for restraint. Iran and Turkey have each offered to mediate the crisis.[156][157]
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
