Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
2-Bromopropane
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
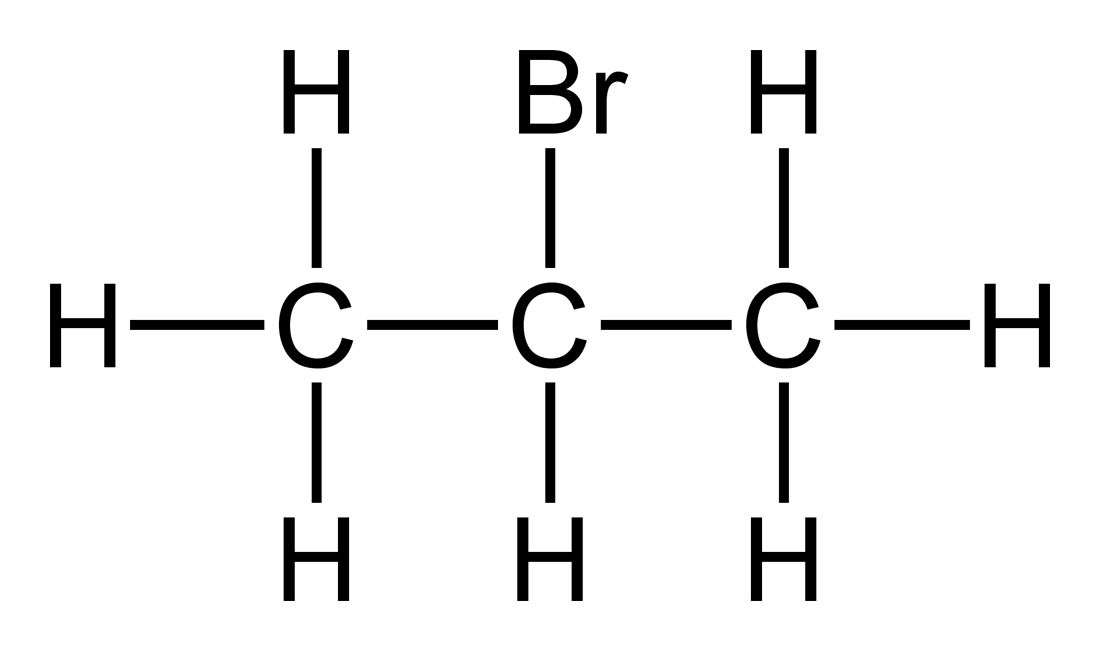
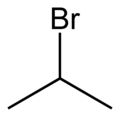
2-Bromopropane, also known as isopropyl bromide and 2-propyl bromide, is the halogenated hydrocarbon with the formula CH3CHBrCH3. It is a colorless liquid. It is used for introducing the isopropyl functional group in organic synthesis. 2-Bromopropane is prepared by heating isopropanol with hydrobromic acid.[3]
Remove ads
Preparation
2-Bromopropane is commercially available. It may be prepared in the ordinary manner of alkyl bromides, by reacting isopropanol with phosphorus and bromine,[4] or with phosphorus tribromide.[5]
Safety
Short-chain alkyl halides are often carcinogenic.
The bromine atom is at the secondary position, which allows the molecule to undergo dehydrohalogenation easily to give propene, which escapes as a gas and can rupture closed reaction vessels. When this reagent is used in base catalyzed reactions, potassium carbonate should be used in place of sodium or potassium hydroxide.
Further reading
- Max Gergel, “Excuse Me Sir, Would You Like to Buy a Kilo of Isopropyl Bromide?” Pierce Chemical Co. (1979). (story of start-up chemical company).
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads