Loading AI tools
British railway union From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The South Eastern and Chatham Railway Companies Joint Management Committee (SE&CRCJMC),[2] known as the South Eastern and Chatham Railway (SE&CR), was a working union of two neighbouring rival railways, the South Eastern Railway (SER) and London, Chatham and Dover Railway (LC&DR), which operated between London and south-east England. Between 1899 and 1923, the SE&CR had a monopoly of railway services in Kent and to the main Channel ports for ferries to France and Belgium.
 | |
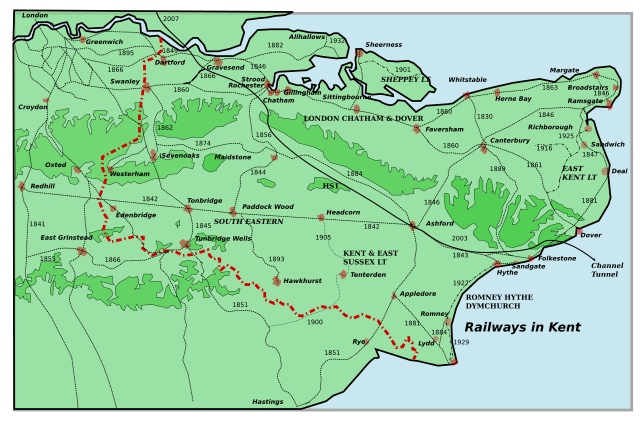
 1920 map of the railway | |
| Technical | |
|---|---|
| Track gauge | 4 ft 8+1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) |
| Length | 637 miles 61 chains (1,026.4 km) (1919)[1] |
| Track length | 1,302 miles 24 chains (2,095.8 km) (1919)[1] |
The companies had competed extensively, with some of the bitterest conflicts between British railway companies. Competing routes to the same destinations were built, so several towns in Kent had been served with a similar frequency service by both companies. In places, unfettered competition allowed two stations and services to multiple London termini.
It would be a constituent of the Southern Railway as part of the 1923 Grouping.
By the end of the 19th century, the SER and LC&DR had fought over a small and not particularly lucrative territory for 40 years. Both were notorious for the poor punctuality of their services and the decrepitude of their rolling stock, and the struggles had driven both companies to the verge of bankruptcy. It became inevitable that they must combine or succumb.
The SE&CR was formed on 1 January 1899, when the SER and LC&DR formed a "management committee" comprising the directors of both companies. This merged the two companies' operations, although they remained legally separate, with receipts split 59% to SER and 41% LC&DR until the Grouping, to avoid the costs and risks of a formal merger.
| South Eastern and London, Chatham and Dover Railways Act 1899 | |
|---|---|
| Act of Parliament | |
 | |
| Long title | An Act to provide for the working union of the South Eastern and London Chatham and Dover Railway Companies and for other purposes. |
| Citation | 62 & 63 Vict. c. clxviii |
| Dates | |
| Royal assent | 1 August 1899 |
On 5 August 1899 the South Eastern and London, Chatham and Dover Railways Act 1899 (62 & 63 Vict. c. clxviii) was passed.

The SE&CR began connecting the two networks and new services were introduced, reaping the benefits of joint working. A significant step was the construction of a junction in 1902-4 between the SER and LC&DR main lines where they crossed near Bickley and St Mary Cray, east of Bromley; the LC&DR's line via Maidstone to Ashford was connected to the SER station at Ashford; and the SER branch from Strood to Chatham alongside the LC&DR's main line to Chatham was closed prior to World War I. The overlapping networks on the Isle of Thanet (Margate-Broadstairs-Ramsgate) were rationalised by the Southern Railway. Service cuts under BR saw Gravesend lose its second station.

After the formation of the SE&CR, three minor lines were built before the formation of the Southern Railway in 1923. They were:


The LC&DR's works at Longhedge, Battersea closed in 1911 and production was concentrated at Ashford. Harry Wainwright was replaced by Richard Maunsell as Locomotive Superintendent in 1913.
With the development and implementation of electrification by the L&SWR, the LB&SCR, the "Tube" companies and tram operators in the early twentieth century, the SE&CR planned to start electrifying its lines. The proposed method would have used four rails, with one of the two additional rails energised at +1500 V DC and the other at −1500 V DC. Current would have been collected by side-contact, with the conductor rails protected by wooden boarding on top and at the sides. Trains would have consisted of multiple-units, each including two motor coaches, each motor coach having two traction motors: one motor coach would have been supplied by the positive conductor rail, the other by the negative.[8][9] This very high voltage for rail track level systems was used in Britain only on the L&YR's 1200 V DC side-contact third-rail line from Manchester Victoria to Bury. Grouping in 1923 led to the Southern Railway adopting the L&SWR's standard of 660 V DC third rail on the SE&CR's network.
The SE&CR operated ships on cross-channel services.
| Ship | Launched | Tonnage (GRT) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Albert Victor | 1880[11] | 814[11] | Scrapped 1899.[11] |
| Boulogne | 1878[11] | 407[11] | Sold in 1903 to British Central Africa Co Ltd.[11] |
| Duchess of York | 1895[11] | 996[11] | Scrapped in 1904[11] |
| Folkestone | 1878[11] | 398[11] | Scrapped in 1903.[11] |
| Louise Dagmar | 1880[11] | 818[11] | Scrapped in 1899.[11] |
| Mary Beatrice | 1882[11] | 803[11] | Scrapped in 1900[11] |
| Princess of Wales | 1898[11] | 1,009[11] | Sold in 1910 to Argentina, renamed Río Uruguay.[11] |
| Ship | Launched | Tonnage (GRT) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Breeze | 1863[12] | 385[12] | Scrapped in 1899.[12] |
| Calais | 1896[12] | 979[12] | Sold in 1911 to Hattemer, Boulogne, renamed Au Revoir.[12] |
| Calais-Douvres | 1889[12] | 1,212[12] | Sold in 1900 to Liverpool & Douglas Steamers.[12] |
| Dover | 1896[12] | 979[12] | Scrapped in 1911.[12] |
| Empress | 1887[12] | 1,213[12] | Scrapped in 1906[12] |
| Foam | 1862[12] | 495[12] | Scrapped in 1901.[12] |
| France | 1864[12] | 365[12] | Scrapped in 1899.[12] |
| Invicta | 1882[12] | 1,282[12] | Scrapped in 1899.[12] |
| Lord Warden | 1896[12] | 979[12] | Scrapped in 1911.[12] |
| Petrel | 1862[12] | 503[12] | Scrapped in 1899.[12] |
| Prince | 1864[12] | 338[12] | Scrapped in 1899.[12] |
| Samphire | 1861[12] | 336[12] | Scrapped in 1899.[12] |
| Victoria | 1886[12] | 1,042[12] | Scrapped in 1904[12] |
| Wave | 1863[12] | 385[12] | Scrapped in 1899[12] |
| Ship | Launched | Tonnage (GRT) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biarritz | 1914[13] | 2,495[13] | Scrapped in 1949 at Dover.[14] |
| Canterbury | 1900[15] | 561[15] | Sold in 1926 to W E Guinness, renamed Arpha. Sold in 1938 to Sark Motorships Ltd. Requisitioned by the Royal Navy in 1939 as HMS Arpha. Sold in 1946 to Shell Caribbean Petroleum Ltd, renamed Coriano. Sold in 1951 to J M Perez Hernandez. Scrapped after 1955.[15] |
| Empress | 1907[13] | 1,689[13] | Requisitioned by Royal Navy in 1914, sold to France in 1923. Scrapped at Dunkirk in 1933.[16] |
| Engadine | 1911[13] | 1,676[13] | Requisitioned by Royal Navy in 1914, returned in 1920. Sold in 1933 to Philippines and renamed Corregidor. Struck a mine and sank on 17 December 1941.[17] |
| Invicta | 1905[13] | 1,680[13] | Sold in 1923 to France. Scrapped in 1932.[18] |
| Mabel Grace | 1899[11] | 1,289[11] | Scrapped in 1909.[11] |
| Maid of Orleans | 1918[13] | 2,384[13] | Torpedoed on 28 June 1944 and sunk.[19] |
| Onward | 1905[13] | 1,671[13] | Caught fire in 1918 at Folkestone and sank. Salvaged in 1920, sold to Isle of Man Steam Packet Company and rebuilt as Mona's Isle, the fourth IoMSPCo ship to carry that name. Scrapped in November 1948 at Milford Haven, Pembrokeshire.[20] |
| Riviera | 1911[13] | 1,674[13] | Requisitioned by Royal Navy in 1914, returned in 1920. Sold in 1932 to Burns & Laird Lines Ltd, renamed Laird's Isle. Scrapped in October 1957 at Troon, Ayrshire.[21] |
| The Queen | 1903[13] | 1,676[13] | Captured on 26 October 1916 by German destroyer S-60 and sunk.[22] |
| Victoria | 1907[23] | 1,689[13] | Sold in 1928 to the IoMSPCo. Scrapped in January 1957 at Barrow in Furness.[23] |
| Ship | Launched | Tonnage (displacement) |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gannet | 1878 | 1,130 | Used as an accommodation ship at Port Victoria in 1900–03. |
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.