List of early Slavic peoples
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This is a list of early Slavic peoples reported in Late Antiquity and in the Middle Ages, that is, before the year AD 1500.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (February 2011) |
Ancestors

- Proto-Indo-Europeans (Proto-Indo-European speakers)
- Proto-Balto-Slavs (common ancestors of Balts and Slavs) (Proto-Balto-Slavic speakers)
- Proto-Slavs (Proto-Slavic speakers)
- Proto-Balto-Slavs (common ancestors of Balts and Slavs) (Proto-Balto-Slavic speakers)
Antiquity

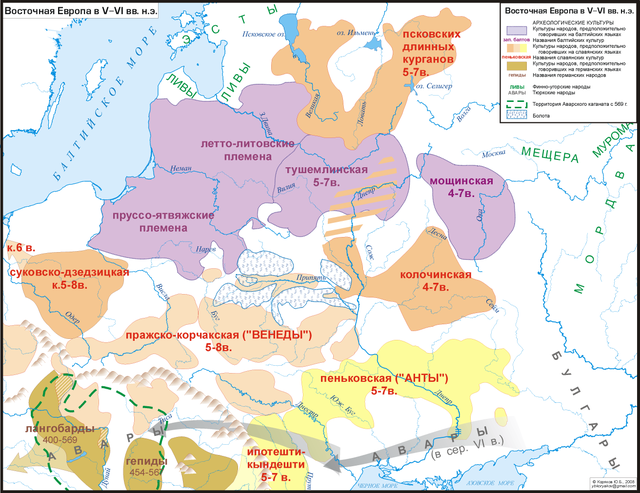
- Sporoi (also known as Vistula Veneti): common ancestors of all Slavs, Proto-Slavs, and the West-Slavic Veneti. It is hypothesized that Proto-Slavs had their origin in the area of present-day western Ukraine - west of the Dnieper, east of the Vistula, south of the Pripyat Marshes and north of the Carpathian Mountains and the Dniester, to the northwest of the Pontic Eurasian Steppes and south of the Baltic peoples, especially West Baltic peoples, with whom they have common ancestors, the Balto-Slavs.[1][2][3] Proto-Slavs are mainly associated with the Zarubintsy culture[4][5][6][need quotation to verify] that had possible links to the ancient peoples of the Vistula basin (Przeworsk culture). Proto and Early Slavs, who were closely related to the Balts, were more influenced by the ancient Celts (La Tène culture) and by the Scythians and Sarmatians (Western Eurasian Steppe Iranian peoples from the northeast group who were nomads or seminomads).[7][8] According to Marija Gimbutas, the people named "Scythian Farmers", mentioned by Herodotus, were the Proto-Slavs or Early Slavs, who bordered and lived south of the Balts, and not Scythians.[9]
- Antes: common ancestors of the East Slavs and most Eastern South Slavs. Also contributed to the West Slavs
- Veneti: common ancestors of the West Slavs. Also contributed to the Western South Slavs and the East Slavs
- Sclaveni: ancestors of the Western South Slavs. Their name was adopted by the Byzantines in the 600s as a catch-all for all Balkan Slavs, regardless of origin
Middle Ages
Summarize
Perspective

This section needs additional citations for verification. (August 2022) |
East Slavs

- Antes (common ancestors of the East Slavs; some were also the ancestors of part of West Slavs and South Slavs)
- Western-Northern groups
- Western Russian group / Western Ruthenian group / Western Old East Slavs ("Russians" or "Russian group" in the broad sense means Old East Slavic peoples, the common group from where modern ethnic groups or peoples of the Rusinians, Ukrainians, Belarusians and Russians descend and not only Russians in the narrow sense)
- Southwestern group (roughly in a large part of the hypothesized region of Proto-Slavs origin)
- Dulebes (Dulebi), ancestors of Ukrainians, Belarusians, part of Czechs and Poles. Assimilated into several East Slavic tribes or were the ancestors of them: the Volhynians, Drevlians, Polans, Dregoviches, and possibly Buzhans, eventually to become part of the Kievan Rus'.
- Buzhans / Bugans (Bugane > Buzhane; [g] > [ʒ]; zh = [ʒ]) (in the regions of the Southern Bug and Western Bug rivers)
- Southern Bug Buzhans (Southern Bug Slavs) (Buzhane). Ancestors of Ukrainians and Russians.[11][12]
- Western Bug Buzhans (Western Bug Slavs) / Volhynians (Volynyane). Ancestors of Ukrainians, part of Czechs, and Poles.
- Dregoviches / Dregovichians (Dregovichi), they lived along the lower Pripyat River and the northern parts of the right bank of the Dnieper River. Ancestors of Belarusians.
- Drevlyans (Drevlyane), they lived in Polesia and right-bank Ukraine. Ancestors of Ukrainians and Belarusians.
- Polans (eastern) (Polyane), in Dnieper right (western) bank, Kyiv region. Ancestors of Ukrainians.
- Buzhans / Bugans (Bugane > Buzhane; [g] > [ʒ]; zh = [ʒ]) (in the regions of the Southern Bug and Western Bug rivers)
- Teverians (Tivertsi / Tyvertsi) / Stadici / Stadichi (Stadychi)?,[13] lived around Bessarabia. Ancestors of Ukrainians, and part of Romanians (especially Moldovans).
- White Croats, in Prykarpattia and Zakarpattia. Ancestors of Rusyns, Ukrainians, Poles, Slovaks, Czechs and Croats.
- Dulebes (Dulebi), ancestors of Ukrainians, Belarusians, part of Czechs and Poles. Assimilated into several East Slavic tribes or were the ancestors of them: the Volhynians, Drevlians, Polans, Dregoviches, and possibly Buzhans, eventually to become part of the Kievan Rus'.
- Southern group
- Don Slavs
- Ulichians (Ulichi), lived around lived around Southern Ukraine and Bessarabia. Ancestors of Ukrainians, and part of Romanians (especially Moldovans).
- Central group
- Radimichians / Radimichs (Radimichi). Ancestors of Belarusians and part of Russians. Mentioned as being a Lyakh tribes.
- Severians (Severyane), some migrated south into the Eastern Balkans. Ancestors of Ukrainians, Russians and part of Slavic Bulgarians.
- Southwestern group (roughly in a large part of the hypothesized region of Proto-Slavs origin)
- Old Russian group / Northern Russian group / Northern Ruthenian group / Northern Old East Slavs
- Northeastern group (Krivichian-Vyatichian group) (Krivichians and Vyatichians played a large part in the formation of Proto-Russians)
- Krivichians (Krivichi), originally native to the area around Pskov. Ancestors of Belarusians and Russians (Kievan Rus' Principalities roughly corresponded to older tribal lands)
- Polochans (Polochane) / Polotskian Krivichians, in Polotsk Land (Polotskaya Zemlya) (later Polotsk Principality). Ancestors of Belarusians.
- Pskovians / Pskovian Krivichians, in Pskov Land (Pskovskaya Zemlya). Ancestors of Russians.
- Smolenians / Smolenian Krivichians, in Smolensk Land (Smolenskaya Zemlya) (later Smolensk Principality). Ancestors of Russians.
- Tverians / Tverian Krivichians, in Tver Land (Tver'skaya Zemlya) (later Tver Principality). Ancestors of Russians.
- Zalessians / Zalessian Krivichians, in Zalessa Land or Zalesye (Zalesskaya Zemlya) / Opolyans / Opolyan Krivichians, in Opolye Land or Opolye (Opolskaya Zemlya) (later Rostov-Suzdal Principality or Vladimir-Suzdal Principality, that gradually evolved into the Grand Duchy of Moscow also called Muscovite Russia or Muscovite Rus') (this political entity is traditionally perceived as a cradle of the Great Russian language and Great Russian people, i.e. the Russians as a distinct Slavic people) (originally Moscow region was an enclave inhabited by a remnant of the Dniepr-Oka Baltic peoples, the Eastern Galindians or Goliad', which were conquered in the middle of 11th century by Rostov-Suzdal).
- Vyatichians (Vyatichi) also Oka Slavs, described as a Lyakh tribe(s). Ancestors of Russians[14] (Kievan Rus' Principalities roughly corresponded to older tribal lands).
- Kozelians / Kozelian Vyatichians, in Kozelsk Land (roughly in today's Kozelsk town and Kaluga and Tula regions, later part of the Chernigov Principality by conquest).
- Ryazanians / Ryazanian Vyatichians, in Ryazan' Land (later Ryazan Principality or Murom-Ryazan).
- Krivichians (Krivichi), originally native to the area around Pskov. Ancestors of Belarusians and Russians (Kievan Rus' Principalities roughly corresponded to older tribal lands)
- Northwestern group (possible Northern Slavic group?) (they played a large part in the formation of Proto-Russians)
- Ilmen Slavs / Ilmen Slovenians (Slovene), also known as Novgorod Slovenes, Novgorod Slavs (Slovene). Ancestors of Russians.
- Bezhetians / Bezhetian Ilmen Slovenians (in Bezhetsk Land - Begetskaja Zemlja) (later part of the Novgorod Land - Novgorodskaja Zemlja, and the Novgorod Republic).
- Derevians / Derevian Ilmen Slovenians (in Dereva Land - Derevskaja Zemlja) (later part of the Novgorod Land - Novgorodskaja Zemlja, and the Novgorod Republic).
- Obonegians / Obonegian Ilmen Slovenians (in Obonego Land - Obonegskaja Zemlja) (later part of the Novgorod Land - Novgorodskaja Zemlja, and the Novgorod Republic).
- Shelonians / Shelonian Ilmen Slovenians (in Shelona Land - Shelonskaja Zemlja) (later part of the Novgorod Land - Novgorodskaja Zemlja, and the Novgorod Republic).
- Ilmen Slavs / Ilmen Slovenians (Slovene), also known as Novgorod Slovenes, Novgorod Slavs (Slovene). Ancestors of Russians.
- Northeastern group (Krivichian-Vyatichian group) (Krivichians and Vyatichians played a large part in the formation of Proto-Russians)
- Western Russian group / Western Ruthenian group / Western Old East Slavs ("Russians" or "Russian group" in the broad sense means Old East Slavic peoples, the common group from where modern ethnic groups or peoples of the Rusinians, Ukrainians, Belarusians and Russians descend and not only Russians in the narrow sense)
- Western-Northern groups
West Slavs


- Veneti / Wends Lechitic ancestors of West Slavs; some were also the ancestors of part of South Slavs
- Czech–Moravian-Slovak group
- Bohemians (Čechové), tribal confederation, in Bohemia, Czech Republic. Ancestors of Czechs.
- Berunzani (a Slavic Bohemian tribe, Chekhove, of West Bohemia).
- Chekhove proper / Čechové (Bohemian Slavs proper), also known as Pragani (Fraganeo), the tribe that lived in the Prague and Central Bohemian regions
- Děčané, in Děčín region, Czech Republic.
- Dudlebi (Doudlebi / Doudlebové) (Bohemian Dulebes), a group of Dulebes assimilated as a Slavic Bohemian or Czech tribe. (they lived in most of the southern half of Bohemia).
- Khébané (Chébané / Hbané).
- Khodove (Chodové) ("Walkers", "Patrollers" or "Rangers") (formed from recruited people originating in the western Carpathian Mountains) (in Tuhošt' Land).
- Litoměřici or Lutomerizi, in the Czech lands from the sixth century (they lived in the Litoměřice region).
- Luchane / Luchani / Lutsane (Lučané)
- Lemuzi
- Lupiglai
- Pshovane (Pšované) / Besunzane (Bežunčani)
- Sedlichane (Sedličané / Sedlčané)
- Volynyane, a group of Volhynians (Volhynian Buzhans) assimilated as a Slavic Bohemian or Czech tribe. Volhynians are ancestors of Poles, Czechs and modern-day Ukrainians.
- Zlicans (Zlitsans) / Zlichane (Zličané), in Bohemia (Czech). Ancestors of Czechs and possibly Poles.
- White Croats, in Northeastern Bohemia and Southern Poland by the 10th century, ancestors of Czechs, Slovaks, Poles and Croats.
- Moravians / Northern Merehani (Moravane), tribal confederation, in Záhorie (Slovakia) and Moravia. Ancestors of (modern) Moravians and part of the Slovaks. The Morava river of Moravia was in their lands. Ancestors of the South Moravians (Merehani), in Morava river valley, east Serbia, that migrated south of the Danube and were assimilated by South Slavs.
- Ganátsi / Hanátsi (Hanáci)
- Golasitsi / Holasitsi (Holasici)
- Gorátsi / Horátsi (Horáci)
- (Podyjští Moravané)
- Slovaks* (more appropriately Sloveni[15] for time period of this article), also called Nitran Slavs / Váh Slavs / Hungarian Slavs / Moravian Slovenes[16] / Sloväni / Slověniny), tribal confederation, in Slovakia and northern parts of Hungary, possibly western Hungary as well. Ancestors of Slovaks, mayhaps were part of broader Slavic group sharing the same name (notice similarities with the south Slavic Slovenians). Sometimes referred to as Slovieni,[17] although this word is generally incorrect, being a contracted term from 19th century.[18] Note: While today the male member of Slovak nation is called Slovák, the original name for such person would be approx. Sloven.[19] This is evident from the endonym of the country (Slovensko), and also the name for Slovak female (Slovenka) or language (slovenský jazyk). This change, purely linguistical, occurred starting in 14th century, applying the newer suffix -ák/-ak/-iak to the stem word Slov. This change most likely originated in neighbouring Bohemia, which is probably the reason why it never completely permeated Slovak language (compared to the Moravian region of Slovácko, so called Moravian Slovakia).
- Bohemians (Čechové), tribal confederation, in Bohemia, Czech Republic. Ancestors of Czechs.
- Lechites (Lechitic group) Lechitic tribes are ancestors of Poles/Polish people, Lechia was the pre-Christian name of Poland.
- Polish tribes- also known as Lechitic tribes.
- Lendians, in east Lesser Poland and Red Ruthenia (Poland and Ukraine). Ancestors of Poles.
- Masovians, tribal confederation, in Mazovia, Poland. Ancestors of Poles.
- Polans (western), tribal confederation, in Greater Poland, Poland. Ancestors of Poles.
- Silesians / Silezane / Slezane (Ślężanie) Lechitic tribe, Poland. Ancestors of Poles.
- Besunzane / Bezunchane (Bieżuńczanie)
- Bobryane (Bobrzanie)
- Dyedoshane (Dziadoszanie) / Dadosesani
- Golensizi (Golęszyce)
- Lubushane (Lubuszanie)
- Lupiglaa (in today's Głubczyce region)
- Opolans / Opolini (Opolanie Lechitic tribe
- Silesians Slezane/(Ślężanie)
- Tryebovane (Trzebowianie)
- Vistulans, in Lesser Poland, tribal confederation, Poland. Ancestors of Poles. Likely the same people as the White Croats.
- Pomeranians, tribal confederation, in Pomerania, Lechitic tribes living at the Baltic Sea regions. Ancestors of Poles, Kashubians, Slovincians, and modern-day Germans.
- Kashubians, in Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland. Ancestors of the modern-day Kashubians.
- Prissani / Pyritzans (Pyrzyczanie), in Pomerania, Poland. Ancestors of Poles.
- Slovincians, a West Slavic tribe that lived between lakes Gardno and Łebsko near Słupsk in Pomerania. Ancestors of modern-day Slovincians.
- Wolinians / Uelunzani, on Wolin island, Pomerania, Poland. Ancestors of Poles
- Goplans, in Kuyavian-Pomeranian, Poland. Ancestors of Poles.
- Polish tribes- also known as Lechitic tribes.
- Wends also spelled as Wenedi, Veneti, Vendi, Vindi, Vinden, includes Northern Polabian and Southern Polabian tribes. The former are linguistically grouped with Lechitic, while the latter with Sorbian languages. See also Bavaria Slavica where Wends some Christian Wends settled in largely modern-day Bavaria.
- Veleti (Wilzi) (Northern Polabians), tribes in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, modern-day Germany.
- Lutici, Lechitic tribal confederation, northeastern region of modern-day Germany.
- Bethenici (Bethenzi or Bechelenzi)
- Doshane
- Lutici
- Circipane, in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, modern-day Germany.
- Kessinians, in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern.
- Redarians, in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern.
- Tollensians, in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern.
- Hevelli (Havolane), in Brandenburg, by river Havel.
- Morizani / Morichane
- Rani / Rujani, on Lechitic tribes on Rugia/Rügen island.
- Sprevane, by river Spree.
- Stodorane (Lutici Stodorane)
- Ukrani, in Uckermark and Vorpommern-Greifswald.
- Obotrites / Reragi (Northern Polabians)
- Belesem / Byelozem = "White Earth" or "White Earth Tribe", they lived scattered in Oster Walde / Osterwalde - "Eastern Woods" in the Old Mainland Saxon view, west banks of the Elbe river
- Drevani = "Wood" or "Wood Tribe", they lived scattered in Oster Walde / Osterwalde - "Eastern Woods" in the Old Mainland Saxon view, west banks of the Elbe river) (Osterwalde and Luneburg Heath also matched the land where the Langobards lived for a time before migrating towards South) (mostly in today's Lower Saxony, in the Hanoverian Wendland, Lechitic tribes in modern-day Germany).
- Linones, in the region around Lenzen.
- Lipani, tribe that lived scattered in the west banks of the Elbe river
- Obotrites proper / Northern Obotrites (Wismar Bay to Lake Schwerin).
- Polabians proper, in modern-day eastern Schleswig-Holstein area.
- Travjane east of the Trave.
- Wagri / Wagrians (the eastern Holstein as part of Saxony).
- Warnabi / Warnower in (the upper Warnow and Mildenitz).
- Lutici, Lechitic tribal confederation, northeastern region of modern-day Germany.
- Southern Polabians tribes in Saxony (Lusatia) and Thuringia.
- Sorbian tribal confederation in the narrow sense
- Proper Sorbs / White Serbs
- Chutici-Chudzicy-Khutices
- Citici-Żytyce-Zhitices
- Colodici-Koledycze-Koledices
- Glomacze-Daleminzi
- Neletici-Neletiches-Nieletycy-Nieletycze
- Nishans-Nishane
- Nizitsi-Niszanie-Nizchices
- Nudycze
- Plisny
- Siusler-Susłowie
- Szkudycze
- Zyrmunty-Yhirmunts
- Sorbian tribal confederation in the wider sense
- Lusatians, in Lower Lusatia. Ancestors of Sorbs in Lower Lusatia.
- Milchane (Milčané) / Milceni / Milzeni, in Upper Lusatia, and in an area of far north Bohemia. Ancestors of Sorbs in Upper Lusatia.
- Sorbian tribal confederation in the narrow sense
- Veleti (Wilzi) (Northern Polabians), tribes in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, modern-day Germany.
- Czech–Moravian-Slovak group
South Slavs

South Slavic tribes descend mainly from two Slavic tribal confederations, Sclaveni and Antes. To reach the Balkans, the two groups took two different paths. While the Sclaveni came from Central Europe north of the Danube and migrated south around the eastern edges of the Alps and across the western part of the Pannonian Plain, the Antes came from the steppe between the Dniester and the Dnieper, penetrating into the Balkans throuhgh Transylvania or, alternatively, the mouth of the Danube.[20]
A number of historians have attributed the early split between Eastern and Western South Slavs to the different origins of Sclaveni and Antes.[21] While Western South Slavs were closely linked to the Western Slavic Veneti, Eastern South Slavs originated from the Eastern Slavic Antes. This is confirmed by both historical records and the duplication of tribal names between West Slavs and Western South Slavs and East Slavs and Eastern South Slavs, respectively. For example, the Polabian White Serb confederation is generally thought to be the ancestor of both Western Slavic Sorbs and South Slavic Serbs, while the Dunabian Abodriti, also known as Praedenecenti, are generally associated with the Polabian Obotrites.[22]
The same is true for Antes and Eastern South Slavs. For example, part of the East Slavic Severians are known to have migrated to present-day northeastern Bulgaria, becoming foederati of the First Bulgarian Empire under the name Severi, while some Pripyat Dregoviches are assumed to have migrated to the valley of the Vardar, establishing themselves as the Drougoubitai.[23] The Seven Slavic tribes are also hypothesized to be Antes hailing from the lands of modern Ukraine, but missing records of their tribal names makes the hypothesis unverifiable.
Therefore, it has been suggested that the ancestors of medieval Bosnians, Serbs and Croatians were the Sclaveni, wereas the progenitors of the Bulgarian Slavs were the Antes.[24] Nevertheless, there must have been substantial overlap between Sclaveni and Antes, especially in contact zones. For example, the exact origin of White Croats is still shrouded in mystery. Some scholars consider them be an Antes tribal polity that migrated to Galicia in the 3rd–4th century,[25][26][27] while others regard them as early Sclaveni or as a mixture of both Antes and Sclaveni.[28]
Nevertheless, South Slavs over time evolved into a new Slavic ethnolinguistic group. This phenomenon was accentuated by the Bavarian expansion east (as an element in the Ostsiedlung) and by the Magyar settlement and expansion in the Pannonian Plain, which severed the contiguous land or territory between West and South Slavs (in the Middle Danube river basin) and contact between both of them, contributing to greater differentiation.
- Sclaveni / Slavini (common ancestors of most Western South Slavs)
- West South Slavic group
- Bošnjani, inhabited central parts of early medieval Bosnia, between the rivers of Upper Neretva on the south, Middle Bosna and the Krivaja (Bosna) on the north, Upper Drina on the east and Upper Vrbas on the west.[29] Ancestors of Bosniaks and Bosnians. Theories of them being descended from the Buzhans exist.[30]
- Braničevci / Braniches, in eastern Serbia.
- Carantanians / Carniolan Slavs / Old Slovenes / Southern Slovene (Sloventsi), tribal confederation, in Austria and Slovenia. Ancestors of Slovenes (particularly Carinthian Slovenes). They descend in part from Nitran Slavs (Northern Slovenes) that were also partial ancestors of modern Slovaks.
- Dudleipa, they may have been a branch of the Dulebes.
- Duliebi, they may have been a branch of the Dulebes.
- Stodorane (Caranthanian Stodorane)
- Susili
- Docleani / Diokletlians, in southern Montenegro (see also Tribes of Montenegro)
- Guduscani, in Lika, Croatia.
- Kanalites, in southern Dalmatia.
- Merehani / Southern Merehani / Southern Moravians (Moravci / Moravtsi), in (South) Morava river, eastern Serbia. They descend from Moravian / Merehani tribal groups that migrated south of the Danube and over time differentiate themselves and were assimilated into South Slavs.
- Narentines / Neretvians, in southern Dalmatia.
- Pannonian Slavs, in west Pannonian Plain, west of the Danube river, roughly in today's west Hungary. They were assimilated by Magyars after they settled in Hungary.
- Pannonian Dulebes, a group of Dulebes.
- Sava Slavs, roughly in the plain between the Sava and Mura rivers. Ancestors of part of Croats.
- Praedenecenti / Eastern Abodriti / Eastern Obotrites, in Banat. They descend from Abodriti / Obotrites tribal groups that migrated south of the Danube and over time differentiate themselves and were assimilated into South Slavs.
- Timočani, in eastern Serbia.
- Travunians / Terbunians, in Herzegovina and western Montenegro
- White Croats, in Western Ukraine, Lesser Poland and Bohemia. Ancestors of Croats and other Slavic peoples.
- White Serbs / Sorbs, in Lower Lusatia, Germany. Ancestors of Sorbs and Serbs.
- Zachumliani / Zachlumians, in southern Dalmatia.
- West South Slavic group
- Antes (common ancestors of most Eastern South Slavs)
- East South Slavic group
- Berziti / Bersites, in Ohrid, North Macedonia.
- Drougoubitai / Draguvites, in North Macedonia and Greek Macedonia.
- Moratsi, or Marvatsi, in the western Rhodopes, along the Mesta river and around Dospat.
- Milcovci / Miltsovtsi
- Seven Slavic tribes (or Seven Slavic Clans) (Heptaradici / Eptaradici - "Seven Roots"?), tribal confederation, in northern Bulgaria and Southern Romania that formed the basis of the Slavic Bulgarians (after later being conquered by the Turkic origin Bulgars that formed much of the Aristocracy and led to the name change of the people and language).
- Unknown tribes (unknown names)
- Severians, in Dobrudja, / Severes / Severi (Balkan Severians), northeast Bulgaria and Southeastern Romania, the Severians were an East Slavic tribe, part of the tribal groups that migrated southward and southwestward and formed a union with the Seven Slavic tribes (to form the Slavic Bulgarians) and over time differentiate themselves and were assimilated into South Slavs.
- Smolyani, in the Central and Western Rhodopes, the Mesta valley and the adjoining areas of northern Greece. They revolted against Byzantine rule in 837 and after receiving military aid by Khan Presian I of Bulgaria, their territory was annexed by the First Bulgarian Empire. Their name is not mentioned after the mid 800s, which suggests assimilation into Slavic Bulgarians.
- Strymonites, along the Struma river in southwestern Bulgaria and the adjoining part of northern Greece. Annexed by the First Bulgarian Empire in 840. They were last mentioned in 904 in connection with the Sack of Thessaloniki by the Arabs and were therefore most likely assimilated into Slavic Bulgarians.
- Sklavenoi / Sclaveni Proper (Slavic tribes of Greece, including Greek Macedonia).
- Baiounitai / Bainuites / Vajunites, originally in Macedonia, later migrated to Epirus/South Albania (Vagenetia).
- Belegezites / Velegezites, in Thessaly.
- Ezerites / Erezitai, in the Peloponnese.
- Melingoi, in the Peloponnese.
- Rynchines / Rhynchinoi, also Recchines, in Greek Macedonia. (Southern Macedonia), Northern Chalkidiki and southern slopes of the Rhodopes.
- Sagudates, in southern Greek Macedonia.
- East South Slavic group
Unclassified Slavs
Possible Slavs
Unclassified
Slavs or Balts
Slavs, Balts or Uralics
Slavs or Romance peoples
- Bolokhovians / Bolokhoveni / Bolokhovens (East Slavic tribe or Valachians? the similar name to Valachians could have been only coincidental)
Slavs or Turkics
Mixed
- Keramisians or, more likely, Sermesianoi, a mixed population of some 70,000 Bulgars, Pannonian Slavs and Byzantine Christians from Syrmia led by the Bulgar (khan) Kuber,[34][35] who unsuccessfully tried to seize Thessaloniki and then settled in the Keramisian field (a corruption of "Sermesian", i.e., of Sirmium), most likely the Pelagonia plain in North Macedonia, in 680. Since treasures attributed to them have been found at Vrap and Ersekë in Eastern Albania,[36] the Sermesianoi are hypothesized to have migrated west following Byzantine emperor Leo III the Isaurian's campaigns against them in the early 700s.
Unclassified peoples or tribes
Mentioned by Bavarian Geographer and possibly Baltic Indo-European
- Thafnezi / Athfenzi / (Y)athfengi? (possibly Yatvingians)[37]
Mentioned by Bavarian Geographer and possibly Iranian Indo-European
- Lucolane / Lucolani (possibly Alan Sarmatian Iranians)[38]
- Serauici / Seravici (possibly Alan Sarmatian Iranians)[39]
Mentioned by Bavarian Geographer and possibly Turkic
- Attorozi (possibly Turkic)[40]
- Aturezani (possibly Turkic)[41]
- Chozirozi / Caziri (possibly the Khazars)[42]
- Uuilerozi / Vilerozi / Bilerozi (possibly Turkic)[43]
Mentioned by Bavarian Geographer and possibly Uralic
Mentioned by Bavarian Geographer and Unknown
- Thadesi
See also
Sources
- Adams, Douglas Q. (1997). Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture. London: Fitzroy Dearborn Publishers. ISBN 978-1-884964-98-5
- Barford, Paul M (2001), The Early Slavs: Culture and Society in Early Medieval Eastern Europe, Cornell University Press, ISBN 0-8014-3977-9
- Gimbutas, Marija Alseikaitė (1971), The Slavs, Thames and Hudson, ISBN 0-500-02072-8
- Koncha, S. (2012). Bavarian Geographer On Slavic Tribes From Ukraine. http://ukrbulletin.univ.kiev.ua/Visnyk-16-en/Koncha.pdf Ukrainian Studies. 12. Bulletin of Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv. pp. 15–21.
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.