Scinaiaceae
Family of algae From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Scinaiaceae is a family of red algae (Rhodophyta) in the order Nemaliales.[2][3]
| Scinaiaceae | |
|---|---|
 | |
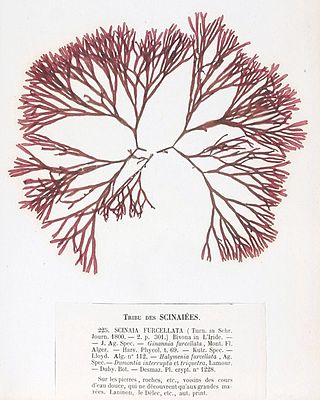
| Scinaia furcellata | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Clade: | Archaeplastida |
| Division: | Rhodophyta |
| Class: | Florideophyceae |
| Order: | Nemaliales |
| Suborder: | Galaxaurineae |
| Family: | Scinaiaceae J.M. Huisman, J.T. Harper & G.W. Saunders 2004[1] |
| Genera | |
|
See text | |
Huisman had placed former members of Galaxauraceae family, that were lacking lime into his new family of Scinaiaceae.[4]
Distribution
The family has cosmopolitan distribution.[5] Including being found in India,[6][7] Arabian Sea,[8] Brazil,[9] North America (including Alaska, British Columbia, Washington, and Oregon[10]) Chile, New Zealand (Tasmania and Campbell Island) and the Falkland Islands.[3]
Notes
Molecular analyses of DNA on species of Nothogenia has been carried out to determine species relationships.[3]
Most Scinaiaceae species produce mucilage (thick, gluey substance) mainly in the cortical layer.[11]
Several species in the Scinaiaceae family (including Nothogenia fastigiata and Scinaia hatei) have been screened for anti-viral activity (against herpes, Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), Influenzavirus A, Influenzavirus B and simian immunodeficiency viruses). Sulfated polysaccharides (xylomannans) from the red alga, have inhibitory effects.[12][13]
List of genera
According to the AlgaeBase (amount of species per genus);[14]
- Gloiophloea J.Agardh - 3 spp.
- Nothogenia Montagne[3] - 10 spp.
- Scinaia Bivona-Bernardi - 45 spp.
- Whidbeyella Setchell & N.L.Gardner - 1 sp. Whidbeyella cartilaginea[15]
Former genera; Ginannia Montagne, Haloderma Ruprecht, Myelomium Kützing, Pseudogloiophloea Levring and Rhodosaccion (J.Agardh) Montagne.[14]
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.