Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
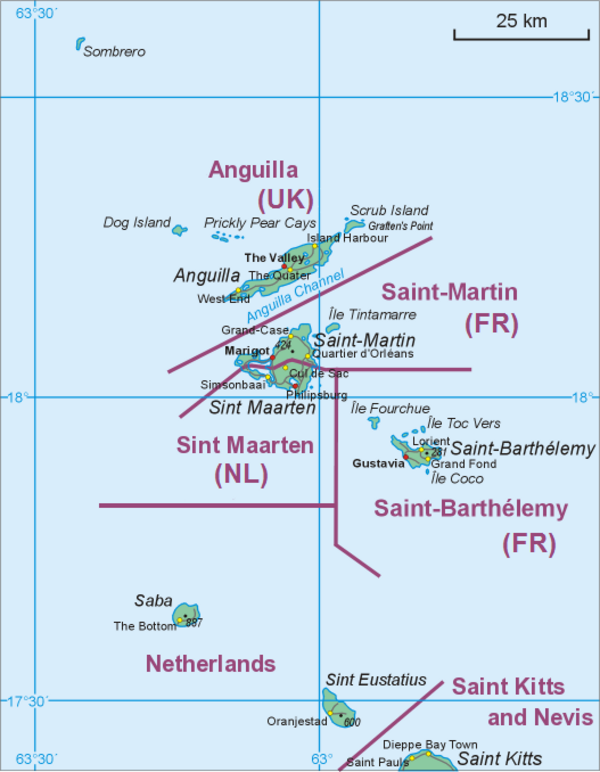
Saba National Marine Park
Marine life protection zone around the island of Saba From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The Saba National Marine Park encompasses the waters and sea bed encircling the Caribbean island of Saba, Caribbean Netherlands, from the high water mark to 200 feet (61 m) deep.[2] In total, the marine park covers approximately 5 square miles (13 km2).[2] At the time of its creation in 1987, the government passed the Marine Environment Ordinance to protect the coral reefs and other marine life within the park.[2][3][4] The Saba Conservation Foundation manages the Saba National Marine Park,[5] as well as the island's hyperbaric facility,[6][7] and natural sites on land (e.g., the Saba Trail network).[2][8][5]
Remove ads
Protection
A number of regulations ensure that the park's thriving aquatic life remains healthy.[9] Zones divide the area according to acceptable uses.[10] Commercial fishing is forbidden in certain places to prevent overfishing.[9] The reefs are protected from damage by 36 permanently anchored buoys where boats can moor.[11] Scuba divers are not permitted to dive by themselves; they must dive with guides from one of Saba's dive shops.[12]
Protecting the Saba National Marine Park is not only an environmental consideration, it is also an economic concern. Tourism currently brings in more money to the island than any other industry,[13] and the Saba National Marine Park is the biggest tourist draw.
Remove ads
Geography
In addition to the fact that Saba's reefs are still flourishing, unlike many others in the region, several unusual natural formations attract divers. Some of these features were formed through volcanic activity,[14][15] such as the Pinnacles: these peaks rise up to 100 feet (30 m) from the ocean floor,[16] and are covered with corals, sponges, and other invertebrate animals. In the Ladder Bay area, a natural labyrinth was created by flowing lava.[17] Other attractions include underwater caves, tunnels, and rock walls.
Remove ads
Fauna

Many different species of life inhabit Saba National Marine Park, includes varieties of coral, fish, and other marine life.
Soft corals are located throughout the marine park, on all sides of the island.[12] Hard corals live mostly in the waters on the island's east side.[18] Porites coral, Star coral (Astreopora),Brain coral, and Gorgonian (Alcyonacea) coral can be at and around the Ladder Bay area.[19]
Types of fish found in the park include parrotfish, Atlantic blue tang, black durgon, and barracuda. Other fish varieties around the park include Burrfish, Chromis, Filefish, Glassy Sweepers, Goatfish, Horse-eye Jacks, Lancer Dragonets, Lizardfish, Peacock Flounders, Pikeblennies, Schoolmasters, Spotted Drums, Tarpons, Yellowfin Groupers, and Yellowhead Jawfish.[19][20][21][22][17][18]

Other marine life in the marine park include octopuses, sea turtles, and spiny lobsters. Stingrays and sharks (specifically nurse sharks and reef sharks)[18] frequent certain areas. On the west side of the island, Channel Clinging Crabs, Green Turtles, Hawksbill Turtles, Spotted Moray Eels, Squat Lobster, and Tigertail Sea Cucumber can be seen.[19][20][21][22]
Visiting
Saba's residents may access the park without charge.[2] Visitors pay $3 (US) per dive[2] (in addition to dive shop diving fees). The park fee supports maintenance of the park and its equipment.
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads