Loading AI tools
Military occupation by Russia From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Russian occupation of Kyiv Oblast was a military occupation that began on the first day of the Russian invasion of Ukraine on 24 February 2022. The capital, Kyiv, was extensively bombed during the invasion, but was never captured. However, many cities were captured near northern and western parts of the oblast.
| Part of the Russian invasion of Ukraine | |
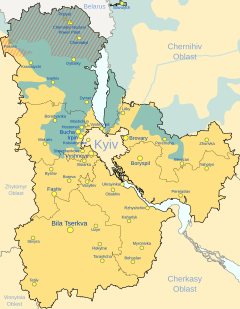 Kyiv Oblast: Ukrainian territory never occupied | |
| Date | 24 February 2022 – 3 April 2022 (1 month, 1 week and 3 days) |
|---|---|
| Location | Kyiv Oblast, Ukraine |

On 24 February 2022, Russian forces began invading Ukraine with their main target being the capital, Kyiv. Russian forces entered Kyiv Oblast and quickly captured Chernobyl and Pripyat in the Chernobyl Exclusion Zone.[2]
By 26 February 2022, Russian forces captured Hostomel, Borodianka, Vorzel and Bucha, and fought a gruesome battle for Antonov airport, which resulted in Russian victory, with battles and clashes ongoing near Irpin and Horenka.[3]
On the morning of 25 February, three Russian saboteurs, dressed as Ukrainian soldiers, entered Obolon District, 10 kilometres (6 mi) north of the Verkhovna Rada building, the seat of the parliament of Ukraine.[4][5] On 27 February, clashes between Ukrainian forces and Russian saboteurs continued. Meanwhile, local officials remained adamant that the city was still under full Ukrainian control.[6]
On 28 February, a fresh wave of Russian troops advanced towards Kyiv, but little direct combat occurred, and only three missiles were fired at the city that day.[7] Satellite images revealed the existence of a long column of Russian vehicles heading to Kyiv along a 64-kilometre-long (40 mi) highway approaching Kyiv from the north, and was approximately 39 km (24 mi) from the center of Kyiv.[8][9]
On the morning of 1 March, the Russian Ministry of Defense issued an evacuation notice to local civilians that they intended to target Ukrainian transmission facilities around Kyiv and that all nearby residents should leave the area.[10] Hours later, a Russian missile struck the Kyiv TV Tower, killing five people and injuring five others.[11][12] Vitaly Klitschko, mayor of Kyiv, banned the sales of alcohol in Kyiv while appealing to shop owners and pharmacy chains not to “take advantage” of the situation by raising the prices of "food, essential goods and medicines".[13][better source needed]
On 22 March, Ukrainian forces launched a counter-offensive to drive the Russians away from the city. Ukrainian forces evacuated thousands of people from nearby suburbs and settlements, including 20,000 people in Boryspil alone, and took back surrounding villages and towns.[14][15]
On 10 March, Russian armored vehicles were seen heading towards Brovary, shortly after capturing the town of Lukyanivka.[16][17]
On 28 March, Ukrainian forces recaptured Lukyanivka and pushed Russian forces out of Brovary. In Lukyanivka, most houses were destroyed and damaged Russian tanks were left on the streets.[18][19][20]
On 29 March, Russia started to shell the Brovary area. A warehouse was set ablaze and nearby villages sustained heavy damage.[21]
On 28 March, Ukrainian forces won the battle of Irpin, and started recapturing many settlements.[22][23][24]
By 2 April, the Ukrainian military recaptured all of Kyiv Oblast, ending the occupation.[25][26]
Russian troops scattered mines across areas from where they withdrew and demining operations began, with the United States planning to provide $89,000,000 for demining in Kyiv, Chernihiv, Zhytomyr and Sumy Oblasts.[27][28]
On 8 May, Yuliya Tymoshenko, people's deputy of Ukraine, announced that demining operations were complete in Kyiv Oblast.[29][30]
In Chernobyl, Russian soldiers stole dangerous radioactive dust and substances from the nuclear power plant's laboratory.[31][32][33]
Russian forces extensively bombed Borodianka, a town near Kyiv. Soldiers used cluster munitions to fire at residential building during the night. They also left mines in civilian areas.[34][35]
When Bucha was under Russian occupation, Russian soldiers raped, tied up and killed civilians in Bucha and left them to die on the streets. When Russian forces withdrew, they left countless tanks in destroyed civilian homes and left the dead bodies lying throughout the town, as well as mines.[36][37][38] The massacre was widely condemned and many officials, including the President of Ukraine, Volodymyr Zelensky, accused the Russian forces of committing genocide in Bucha.[39] According to local authorities, 458 bodies have been recovered from the town, including 9 children under the age of 18; among the victims, 419 people were killed with weapons and 39 appeared to have died of natural causes, possibly related to the occupation.[40]
On 6 March 2022, Russian forces shelled an intersection where residents of Irpin were fleeing to Kyiv, resulting in 8 deaths.[41]
| Name | Pop. | Raion | Held by | As of | More information |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bila Tserkva | 208,737 | Bila Tserkva | 24 Feb 2022 | ||
| Borodianka | 13,044 | Bucha | 1 Apr 2022 | See Bombing of Borodianka | |
| Brovary | 109,473 | Brovary | 1 Apr 2022 | See Battle of Brovary | |
| Bucha | 36,971 | Bucha | 1 Apr 2022 | See Battle of Bucha, Bucha massacre Captured by Recaptured by | |
| Buzova | 1,548 | Bucha | 1 Apr 2022 | ||
| Chernobyl | 2,500 | Vyshhorod | 2 Apr 2022 | See Capture of Chernobyl Captured by Recaptured by | |
| Dymer | 5,817 | Vyshhorod | 1 Apr 2022 | Captured by Recaptured by | |
| Fastiv | 44,841 | Fastiv | 17 Mar 2022 | ||
| Hornostaipil | 1,033 | Vyshhorod | 3 Apr 2022 | Captured by Recaptured by | |
| Hostomel | 17,534 | Bucha | 1 Apr 2022 | See Battle of Hostomel, Battle of Antonov Airport Captured by Recaptured by | |
| Irpin | 62,456 | Bucha | 1 Apr 2022 | See Battle of Irpin, Irpin refugee column shelling Partially captured by Recaptured by | |
| Ivankiv | 10,563 | Vyshhorod | 1 Apr 2022 | Captured by Recaptured by | |
| Klavdiievo-Tarasove | 5,019 | Bucha | 2 Apr 2022 | Captured by Recaptured by | |
| Kyiv | 2,962,180 | none[a] | 28 Feb 2022 | See Battle of Kyiv, Kyiv shopping centre bombing, Kyiv missile strikes | |
| Makariv | 9,589 | Bucha | 1 Apr 2022 | Captured by Recaptured by | |
| Nemishaieve | 7,841 | Bucha | 3 Mar 2022 | ||
| Obukhiv | 33,443 | Obukhiv | 24 Feb 2022 | ||
| Shevchenkove | 2,913 | Brovary | 1 Apr 2022 | ||
| Slavutych | 24,685 | Vyshhorod | 3 Apr 2022 | Geographically within Chernihiv Oblast See Battle of Slavutych Captured by Recaptured by | |
| Vasylkiv | 37,310 | Obukhiv | 26 Feb 2022 | ||
| Velyka Dymerka | 9,461 | Brovary | 1 Apr 2022 | Captured by Recaptured by | |
| Vorzel | 6,766 | Bucha | 1 Apr 2022 | ||
| Vyshhorod | 22,933 | Vyshhorod | 7 Mar 2022 |
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.