Loading AI tools
The Newark Supergroup, also known as the Newark Group, is an assemblage of Upper Triassic and Lower Jurassic sedimentary and volcanic rocks which outcrop intermittently along the east coast of North America. They were deposited in a series of Triassic basins, the Eastern North American rift basins, approximately 220–190 million years ago.[1][2] The basins are characterized as aborted rifts, with half-graben geometry, developing parallel to the main rift of the Atlantic Ocean which formed as North America began to separate from Africa. Exposures of the Newark Supergroup extend from South Carolina north to Nova Scotia. Related basins are also found underwater in the Bay of Fundy. The group is named for the city of Newark, New Jersey.
| Newark Supergroup | |
|---|---|
| Stratigraphic range: Triassic - Jurassic | |
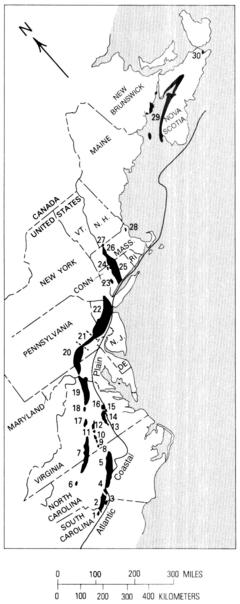 Exposed basins of the Newark Supergroup | |
| Type | Supergroup |
| Sub-units | see text |
| Location | |
| Region | East Coast, The Maritime Provinces |
| Country | |
| Extent | Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, Massachusetts, Connecticut, New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, and South Carolina |
| Type section | |
| Named for | Newark, New Jersey |
The Newark Supergroup consists largely of poorly sorted nonmarine sediments; typical rocks are breccia, conglomerate, arkose sandstone, siltstone, and shale.[3][4] Most of the strata are red beds that feature ripple marks, mud cracks, and even rain drop prints; dinosaur footprints are common, though actual body fossils are very rare.[4] Some of the strata are detailed to the level of varves, with indications of Milankovitch cycles.[5] In preserved lake sediments, Semionotus fossils are especially common.[5]
The Newark sediments are extremely thick (up to 6 kilometers); they were deposited in a series of half-grabens that were themselves faulted into block mountains.[6] The beds dip to the east, while the faults dip westward.[6] The beds are intruded by numerous dikes and sills, indicative of considerable igneous activity; a superb example is the New Jersey Palisades sill.[6]
The Newark Supergroup's lithologies and structure are the classic hallmarks of a rift valley; the fault-blocking illustrates the crustal extension forces in play during the breakup of Pangea during the late Triassic Period.[3] The Appalachian Mountains had already been nearly eroded flat by the end of the period; the uplift and faulting that was the first part of the rifting provided new sources of sediment for the vast thicknesses deposited in the Newark Supergroup; the igneous intrusions are similarly diagnostic of a rift valley.[3][6] Coarse sediments were deposited near the eastern mountain front, while progressively finer ones were deposited farther west.[7]
Evidence suggests the climate at the time was subtropical and rainy, though divided between wet and dry months.[7] A few organic-rich deposits suggest patchy or intermittent swamps and lakes.[8]
Accumulation of Newark sediments within the rift basins continued from the late Triassic into the early Jurassic.[2][3]










The separate basins and sub-basins of the Newark Supergroup have historically been given their own geological formations by local paleontologists. However, a study by Weems, Tanner, and Lucas (2016) proposed that the formations of the Newark Supergroup should be defined on a regional scale due to their geological uniformity over eastern North America. From youngest to oldest, the regional formations proposed by this study are:[9]
- Longmeadow Sandstone of the Portland Group (Early Jurassic semi-arid fluvial deposits)
- Mount Toby Conglomerate of the Portland Group (Early Jurassic semi-arid alluvial conglomerate)
- Boonton Formation of the Portland Group (Early Jurassic lacustrine deposits)
- Hampden Formation of the Meriden Group (Early Jurassic basalts)
- East Berlin Formation of the Meriden Group (Early Jurassic semi-arid lacustrine and alluvial deposits)
- Holyoke Formation of the Meriden Group (Early Jurassic basalts and rare sediments)
- Shuttle Meadow Formation of the Meriden Group (latest Triassic-earliest Jurassic lacustrine and freshwater limestone deposits)
- Talcott Formation of the Meriden Group (latest Triassic (Rhaetian) basalts and rare sediments)
- Passaic Formation of the Chatham Group (Norian-Rhaetian? semi-arid fluvial and deltaic deposits)
- Lockatong Formation of the Chatham Group (Norian?[10] Humid lacustrine deposits)
- Stockton Formation of the Chatham Group (Carnian? Humid fluvial and deltaic deposits)
- Doswell Formation of the Chatham Group (Early Carnian? Humid fluvial, lacustrine, and coal deposits)
- Evangeline Formation of the Acadia Group (Ladinian? semi-arid fluvial deposits)[11]
- Economy Formation of the Acadia Group (Anisian-Ladinian? arid fluvial deposits and aeolian sandstone)[11]
- Chedabucto Formation of the Acadia Group (stratigraphically uncertain red beds at Chedabucto Bay)
- Honeycomb Point Formation of the Acadia Group (Late Permian? arid alluvial conglomerate and aeolian sandstone)[12]
Basin-specific formations are given below:
Deep River Basin, Sanford/Durham/Wadesboro Sub-Basins (North Carolina)
- Sanford Formation (equivalent to the Passaic Formation)
- Cumnock Formation (Cumnock Member of the Lockatong Formation)
- Pekin Formation (equivalent to the Stockton Formation)
Danville/Dan River Basin (North Carolina, Virginia)
- Stoneville Formation (equivalent to the Passaic Formation)
- Cow Branch Formation (equivalent to the Lockatong Formation)
- Dry Fork Formation (Dry Fork Member of the Stockton Formation)
- Walnut Cove Formation (Walnut Cove Member of the Stockton Formation)
- Pine Hall Formation (Pine Hall Member of the Stockton Formation)
Richmond Basin (Virginia)
- Otterdale sandstone (equivalent to the Stockton Formation)
- "Vinita Beds" (Vinita Member of the Doswell Formation)
- "Coal Measures" (equivalent to the Vinita Member of the Doswell Formation)
- "Barren Beds" (equivalent to the Stagg Creek Member of the Doswell Formation)
Taylorsville Basin (Virginia)
- Leedstown Formation (equivalent to the Passaic Formation)
- Port Royal Formation (equivalent to the Lockatong Formation)
- Newfound Formation (equivalent to the Stockton Formation)
- Falling Creek Formation (equivalent to the Vinita Member of the Doswell Formation)
- South Anna Formation (equivalent to the Stagg Creek Member of the Doswell Formation)
Culpeper Basin (Virginia, Maryland)
- Waterfall Formation (equivalent to the East Berlin Formation)
- Sander Basalt (equivalent to the Deerfield Basalt Member of the Holyoke Formation)
- Turkey Run Formation (Turkey Run Member of the Holyoke Formation)
- Hickory Grove Basalt (Hickory Grove Member of the Holyoke Formation)
- Midland Formation (equivalent to the Shuttle Meadow Formation)
- Mount Zion Church Basalt (equivalent to the Talcott Formation)
- Catharpin Creek Formation (Catharpin Creek Member of the Passaic Formation)
- Bull Run Formation (Groveton/Leesburg, Balls Bluff Members of the Passaic Formation)
- Manassas Formation (Manassas, Rapidan/Reston/Tuscarora Creek Members of the Passaic Formation)
Gettysburg Basin (Maryland, Pennsylvania)
- Bendersville Formation (equivalent to the Shuttle Meadow Formation)
- Aspers Basalt (equivalent to the Talcott Formation)
- Gettysburg Formation (Fairfield, Heidlersburg, Plum Rum, and Hammer Creek Members of the Passaic and Lockatong Formations)
- New Oxford Formation (equivalent to the Stockton Formation)
- Irishtown Beds (Irishtown Member of the Doswell Formation)
Newark Basin (Pennsylvania, New Jersey, New York)
- Boonton Formation
- Hook Mountain Basalt (equivalent to the Hampden Formation)
- Towaco Formation (equivalent to the East Berlin Formation)
- Preakness Basalt (equivalent to the Holyoke Formation)
- Feltville Formation (equivalent to the Shuttle Meadow Formation)
- Orange Mountain Basalt (equivalent to the Talcott Formation)
- Passaic Formation
- Lockatong Formation
- Stockton Formation
Hartford Basin (Connecticut, Massachusetts)
- Portland Formation (equivalent to the Boonton Formation, Longmeadow Sandstone and Mount Toby Conglomerate)
- Hampden Basalt/Formation
- East Berlin Formation
- Holyoke Basalt/Formation
- Shuttle Meadow Formation
- Talcott Formation
- New Haven Arkose (equivalent to the Sugarloaf Member of the Passaic Formation)
Pomperaug Basin (Connecticut)
- South Brook Basalt (equivalent to the Hampden Formation)
- White Oaks Formation (equivalent to the East Berlin Formation)
- Orenaug Basalt (equivalent to the Holyoke Formation)
- Cass Formation (equivalent to the Shuttle Meadow Formation)
- East Hill Basalt (equivalent to the Talcott Formation)
- South Britain Arkose (equivalent to the Sugarloaf Member of the Passaic Formation)
Deerfield Basin (Massachusetts)
- Mount Toby Formation
- Turners Falls Sandstone (equivalent to the East Berlin Formation)
- Deerfield Basalt (Deerfield Basalt Member of the Holyoke Formation)
- Fall River Beds (equivalent to the Shuttle Meadow Formation)
- Sugarloaf Arkose (Sugarloaf Member of the Passaic Formation)
Fundy Basin (New Brunswick, Nova Scotia)
- McCoy Brook Formation (McCoy Brook Member of the Shuttle Meadow Formation)
- North Mountain Basalt (equivalent to the Talcott Formation)
- Blomidon Formation (Blomidon, Red Head, and Wolfville Members of the Passaic Formation)
- Wolfville Formation (Evangeline, Economy, and Chedabucto Formations)
- Honeycomb Point Formation
Minor basins
Minor basins crop out in South Carolina (Crowburg, Wadesboro basins), North Carolina (Ellerbe, Davie County basins), Virginia (Scottsburg, Randolph, Roanoke Creek, Briery Creek, Farmville, Flat Branch, Deep Run, Scottsville, Barboursville basins), Connecticut (Cherry Brook Outlier), Massachusetts (Northfield and Middleton basins), and Nova Scotia (Chedabucto Basin).
Until the late 1970s, the entire Newark Supergroup was assumed to be Triassic in age. A 1977 study of fossil pollen argued that the sediments actually range from the Ladinian to the Lower Jurassic.[13] Under this hypothesis, the Supergroup was deposited over the course of 50 million years.[1]
Wikiwand in your browser!
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.