Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Neptunium(IV) oxide
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Neptunium(IV) oxide, or neptunium dioxide, is a radioactive, olive green[5] cubic[6] crystalline solid with the formula NpO2. It is one of two stable oxides of neptunium, the other being neptunium(V) oxide.[7] It emits both α- and γ-particles.[4]
Remove ads
Production
Industrially, neptunium dioxide is formed by precipitation of neptunium(IV) oxalate, followed by calcination to neptunium dioxide.[8]
Production starts with a nitric acid feed solution containing neptunium ions in various oxidation states. First, a hydrazine inhibitor is added to slow any oxidation from standing in air. Then ascorbic acid reduces the feed solution to predominantly neptunium(IV):
- 2Np5+ + C6H8O6 → 2Np4+ + C6H6O6 + 2H+
- Np6+ + C6H8O6 → Np4+ + C6H6O6 + 2H+
Addition of oxalic acid precipitates hydrated neptunium oxalate...
- Np4+ + 2H2C2O4 + 6H2O → Np(C2O4)2.6H2O(v) + 4H+
...which pyrolyzes when heated:[8]
- Np(C2O4)2.6H2O Δ
→ Np(C2O4)2 Δ
→ NpO2 + 2CO(g)
Neptunium dioxide can also be formed from precipitation of neptunium(IV) peroxide, but the process is much more sensitive.[8]
Remove ads
Purification
As a byproduct of nuclear fission reactors, neptunium dioxide can be purified by fluorination, followed by reduction with excess calcium in the presence of iodine.[4] However, the aforementioned synthesis yields a quite pure solid, with less than 0.3% mass fraction of impurities. Generally, further purification is unnecessary.[8]
Structure
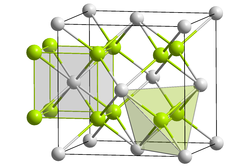
Due to neptunium's large size, neptunium dioxide has a fluorite structure, with lattice constant a=5.43 Å. Like all fluorite structure materials, it has a space group of Fm3m. Neptunium is eight-coordinate, with a cubic coordination geometry, and oxygen is four-coordinate, with a tetrahedral coordinate geometry.[9][10]
Other properties
Neptunium dioxide contributes to the α-decay of 241Am, reducing its usual half-life by an untested but appreciable amount.[11] The compound has a low specific heat capacity (900 K, compared with uranium dioxide's specific heat capacity of 1400 K), an abnormality theorized to stem from its 5f electron count.[12] Another unique trait of neptunium dioxide is its "mysterious low-temperature ordered phase". Mentioned above, it references an abnormal level of order for an actinide dioxide complex at low temperature.[13] Further discussion of such topics could indicate useful physical trends in the actinides.
Remove ads
Uses
The neptunium dioxide complex is used as a means of stabilizing, and decreasing the "long term environmental burden" of neptunium as a nuclear fission byproduct. Actinide-containing spent nuclear fuel will commonly be treated so that various AnO2 (where An = U, Np, Pu, etc.) complexes form. In neptunium dioxide, neptunium is of reduced radiotoxicity compared with elemental neptunium and is thus more desirable for storage and disposal.[14]
Neptunium dioxide is also used experimentally for research into nuclear chemistry and physics, and it is speculated that it could be used to make efficient nuclear weapons. In nuclear reactors, neptunium dioxide can also be used as the target for plutonium bombardment.[14]
Furthermore, a patent for a rocket powered by neptunium dioxide is held by Shirakawa Toshihisa,[15] but there is little information available into research and production associated with such a product.
Remove ads
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads