Lothrop Stoddard
American white supremacist author (1883–1950) From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Theodore Lothrop Stoddard (June 29, 1883 – May 1, 1950) was an American historian, journalist, political scientist and white supremacist. Stoddard wrote several books which advocated eugenics, white supremacy, Nordicism, and scientific racism, including The Rising Tide of Color Against White World-Supremacy (1920). He advocated a racial hierarchy which he believed needed to be preserved through anti-miscegenation laws. Stoddard's books were once widely read both inside and outside the United States.
Lothrop Stoddard | |
|---|---|
| Born | Theodore Lothrop Stoddard June 29, 1883 Brookline, Massachusetts, United States |
| Died | May 1, 1950 (aged 66) Washington, D.C., United States |
| Alma mater | |
| Organizations | |
| Notable work | The Rising Tide of Color Against White World-Supremacy (1920) |
| Other political affiliations | Ku Klux Klan |
| Board member of | American Birth Control League |
| Father | John Lawson Stoddard |
| Military career | |
| Allegiance | United States |
| Service | United States Army |
| Unit | Signal corps |
| Battles / wars | Philippine–American War |
He was a member of the Ku Klux Klan, where his books were recommended reading.[1][2][3][4] He was also a member of the American Eugenics Society[5] as well as a founding member and board member of the American Birth Control League, which would later become the Planned Parenthood Federation of America.[6]
Stoddard's work influenced the Nazi government of Germany. His book The Revolt Against Civilization: The Menace of the Under-man (1922) may have introduced the term Untermensch (the German translation of "Under-man") into Nazi discussions of race. He traveled as a journalist in Germany during the first months of World War II, during which he received preferential treatment for interviews with Nazi officials and met briefly with Adolf Hitler.[7] After the war, Stoddard's writing faded from popularity.
Early life and education
Stoddard was born in Brookline, Massachusetts, the son of John Lawson Stoddard, a prominent writer and lecturer, and his wife Mary H. Stoddard.[8] In 1900 he enlisted in the United States Army to fight in the Philippine–American War and was commissioned to the signal corps. Following his military stint, Stoddard attended Harvard College, graduating magna cum laude in 1905, and studied law at Boston University until 1908. Stoddard received a Ph.D. in History from Harvard University in 1914.[9]
Career
Stoddard was a member of the American Historical Association, the American Political Science Association, and the Academy of Political Science.[10]
In 1923, an exposé by Hearst's International revealed that Stoddard was a member of the Ku Klux Klan (KKK), and had been acting as a consultant to the organization. A letter from the KKK to members had praised The Rising Tide of Color Against White World-Supremacy in explicitly racial terms. Stoddard privately dismissed the Hearst magazine as a "radical-Jew outfit".[1]
Views
Summarize
Perspective
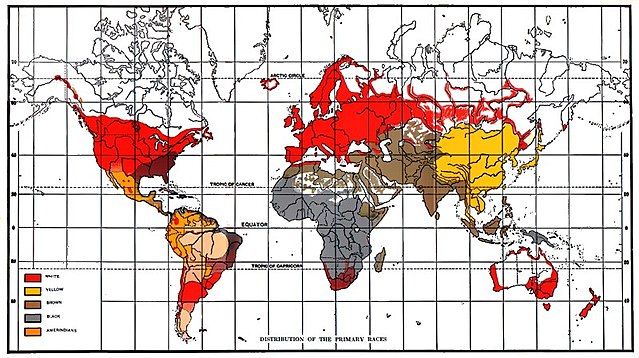
Stoddard wrote many books, most of them related to race and civilization. He wrote primarily on the alleged dangers posed by "colored" peoples to white civilization. Many of his books and articles were racialist and described what he saw as the peril of nonwhite immigration. He develops this theme in The Rising Tide of Color Against White World-Supremacy originally published in 1920[11][12] with an introduction by Madison Grant.[13] He presents a view of the world situation pertaining to race and focusing concern on the coming population explosion among the non-white peoples of the world and the way in which "white world-supremacy" was being lessened in the wake of World War I and the collapse of colonialism.[page needed] In the book, Stoddard blames the ethnocentrism of the German "Teutonic imperialists" for the outbreak of World War I.[11][non-primary source needed] President Warren G. Harding mentioned the book during a 1921 speech in Birmingham, Alabama, saying that America's race problem was only the beginning of what would soon become a worldwide race problem.[13]
Stoddard argued that race and heredity were the guiding factors of history and civilization and that the elimination or absorption of the "white" race by "colored" races would result in the destruction of Western civilization. Like Madison Grant in The Passing of the Great Race, Stoddard divided the white race into three main divisions: "Nordic", "Alpine", and "Mediterranean". He considered all three to be of good stock and far above the quality of the colored races, but argued that the "Nordic" was the greatest of the three, and needed to be preserved by way of eugenics. He considered most Jews to be racially "Asiatic" and argued for restricting Jewish immigration because he considered them a threat to Nordic racial purity in the US. He warned that the United States was being "invaded by hordes of immigrant Alpines and Mediterraneans, not to mention Asiatic elements like Levantines and Jews."[14][15][16] Stoddard's racist beliefs were especially hostile to black people. He claimed that they were fundamentally different from other groups, they had no civilizations of their own, and had contributed nothing to the world. Stoddard opposed miscegenation, and said that "crossings with the negro are uniformly fatal".[1]
In The Revolt Against Civilization (1922), Stoddard put forward the idea that civilization places a growing burden on individuals, which leads to a growing underclass of individuals who cannot keep up and a "ground-swell of revolt".[17] Stoddard advocated immigration restriction and birth control legislation to reduce the numbers of the underclass and promoted the reproduction of members of the middle and upper classes. Stoddard was one of several eugenicists who sat on the board of the American Birth Control League.[18]
The Nazi Party's chief racial theorist Alfred Rosenberg appropriated the racial term Untermensch from the German version of Stoddard's 1922 book The Revolt Against Civilization: The Menace of the Under-man. The German title was Der Kulturumsturz: Die Drohung des Untermenschen (1925).[19]
Debate with W.E.B. Du Bois
In 1929, Stoddard debated African American historian W.E.B. Du Bois on white supremacy and its assertion of the natural inferiority of colored races.[20][21] The debate, organized by the Chicago Forum Council, was billed as "One of the greatest debates ever held".[13] Du Bois argued in the affirmative to the question "Shall the Negro be encouraged to seek cultural equality? Has the Negro the same intellectual possibilities as other races?"[22] Du Bois knew the racism would be unintentionally funny onstage; as he wrote to Fred Atkins Moore, the event's organizer, Senator J. Thomas Heflin "would be a scream" in a debate.[13]
The transcript records Stoddard saying: "'The more enlightened men of southern white America ... are doing their best to see that separation shall not mean discrimination; that if the Negroes have separate schools, they shall be good schools; that if they have separate train accommodations, they shall have good accommodations.' [laughter]."
Du Bois, in responding to Stoddard, said the reason for the audience laughter was that he had never journeyed under Jim Crow restrictions. "We have," Du Bois told him and the mixed audience.[13]
This moment was reported in The Chicago Defender's headline: "DuBois Shatters Stoddard’s Cultural Theories in Debate; Thousands Jam Hall ... Cheered As He Proves Race Equality." The Afro-American reported: "5,000 Cheer W.E.B. DuBois, Laugh at Lothrop Stoddard."[13]
Reports from Nazi Germany
Between 1939 and 1940, Stoddard spent four months as a journalist for the North American Newspaper Alliance in Nazi Germany. He received preferential treatment from Nazi officials compared to other journalists. An example was the Reich Ministry of Public Enlightenment and Propaganda's insisting that NBC's Max Jordan and CBS's William Shirer use Stoddard to interview the captain of the Bremen.[7][23]
Stoddard wrote a memoir, Into the Darkness: Nazi Germany Today (1940), about his experiences in Germany. Among other events, the book describes interviews with such figures as Heinrich Himmler, Robert Ley and Fritz Sauckel, as well as a brief meeting with Adolf Hitler.[7] Stoddard visited the Hereditary Health Court in Charlottenburg, an appeals court that decided whether Germans would be sterilized. After observing several dysgenics trials at the court, Stoddard asserted that the eugenics legislation was "being administered with strict regard for its provisions and that, if anything, judgments were almost too conservative" and that the law was "weeding out the worst strains in the Germanic stock in a scientific and truly humanitarian way."[7][24]
Postwar
After World War II, Stoddard's theories were deemed too closely aligned with those of the Nazis and therefore he suffered a large drop in popularity.[25] His death from cancer in 1950 went almost entirely unreported despite his previously broad readership and influence.[26]
Bibliography
Summarize
Perspective
Books
- The French Revolution in San Domingo, Houghton Mifflin Company, 1914.
- Present-day Europe, its National States of Mind, The Century Co., 1917.
- Stakes of the War, with Glenn Frank, The Century Co., 1918.[27]
- The Rising Tide of Color Against White World-Supremacy Charles Scribner's Sons, 1921 [1st Pub. 1920]. ISBN 4-87187-849-X
- The New World of Islam, Charles Scribner's Sons, 1922 [1st Pub. 1921].
- The Revolt Against Civilization: The Menace of the Under Man, Charles Scribner's Sons, 1922.
- Racial Realities in Europe, Charles Scribner's Sons, 1924.
- Social Classes in Post-War Europe. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons, 1925.
- Scientific Humanism. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons, 1926.
- Re-forging America: The Story of Our Nationhood. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons, 1927.
- The Story of Youth. New York: Cosmopolitan Book Corporation, 1928.
- Luck, Your Silent Partner. New York: H. Liveright, 1929.
- Master of Manhattan, the life of Richard Croker. Londton: Longmans, Green and Co., 1931.
- Europe and Our Money, The Macmillan Co., 1932
- Lonely America. Garden City, NY: Doubleday, Doran, and Co., 1932.
- Clashing Tides of Color. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons, 1935.
- A Caravan Tour to Ireland and Canada, World Caravan Guild, 1938.
- Into the Darkness: Nazi Germany Today, Duell, Sloan & Pearce, Inc., 1940.[28]
Selected articles
|
|
|
Additionally, Stoddard wrote several articles for The Saturday Evening Post.[29][30][31]
See also
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.