Species in mammal superfamily Lorisoidea From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Lorisoidea is a superfamily of nocturnal primates. Members of this superfamily are called lorisoids, and include lorises, angwantibos, pottos, galagos, and bushbabies. Lorisoidea is one of two superfamilies that form the suborder Strepsirrhini, itself one of two suborders in the order Primates. They are found in Asia and Africa, generally in forests, though some species can be found in shrublands and savannas. They range in size from the Prince Demidoff's bushbaby, at 10 cm (4 in) plus a 15 cm (6 in) tail, to the West African potto, at 39 cm (15 in) plus a 10 cm (4 in) tail. Lorisoids primarily eat fruit, insects, and tree gums and resins. Most lorisoids do not have population estimates, but the ones that do range from 40 mature individuals to 500,000. Six species are categorized as endangered: the Bengal, pygmy, Sumatran, and Sunda slow lorises, the red slender loris, and the Rondo dwarf galago. A further two species are categorized as critically endangered: the Bangka slow loris and the Javan slow loris.
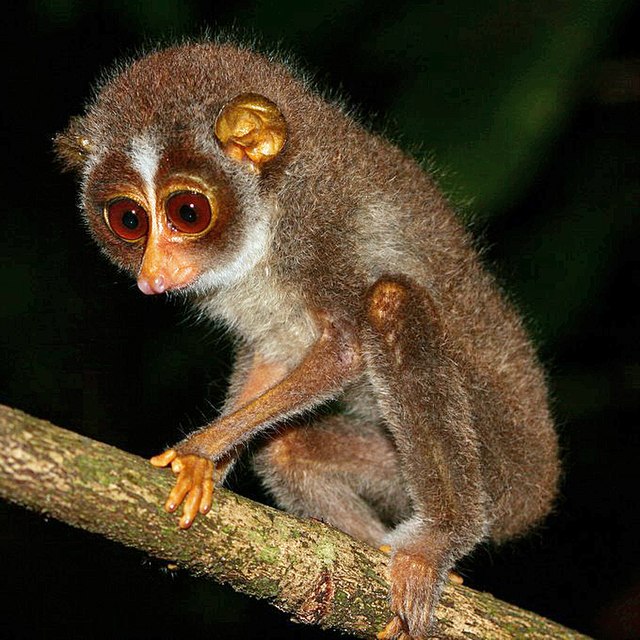

The thirty-five extant species of Lorisoidea are divided into two families: Galagidae, containing nineteen bushbaby and galago species divided between six genera, and Lorisidae, containing sixteen species divided between the three genera in the loris subfamily Lorisinae and the two genera of the angwantibo and potto subfamily Perodicticinae. Several extinct prehistoric lorisoid species have been discovered, though due to ongoing research and discoveries the exact number and categorization is not fixed.[1]
| Conservation status | |
|---|---|
| EX | Extinct (0 species) |
| EW | Extinct in the wild (0 species) |
| CR | Critically endangered (2 species) |
| EN | Endangered (6 species) |
| VU | Vulnerable (4 species) |
| NT | Near threatened (7 species) |
| LC | Least concern (15 species) |
| Other categories | |
| DD | Data deficient (1 species) |
| NE | Not evaluated (0 species) |
Conservation status codes listed follow the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species. Range maps are provided wherever possible; if a range map is not available, a description of the lorisoid's range is provided. Ranges are based on the IUCN Red List for that species unless otherwise noted. All extinct genera, species, or subspecies listed alongside extant species went extinct after 1500 CE, and are indicated by a dagger symbol "†".
The superfamily Lorisoidea consists of two extant families: Galagidae and Lorisidae. Galagidae contains nineteen species in six genera, while Lorisidae is divided into two subfamilies: Lorisinae, containing eleven species divided between three genera, and Perodicticinae, containing five species divided between two genera.
Family Galagidae
Family Lorisidae
The following classification is based on the taxonomy described by the reference work Mammal Species of the World (2005), with augmentation by generally accepted proposals made since using molecular phylogenetic analysis, as supported by both the IUCN and the American Society of Mammalogists.[4]
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northern needle-clawed bushbaby | E. pallidus (Gray, 1863) Two subspecies
|
Western equatorial Africa |
Size: 18–33 cm (7–13 in) long, plus 28–31 cm (11–12 in) tail[5] Habitat: Forest[6] Diet: Tree gums and resins[6] |
NT
|
| Southern needle-clawed bushbaby | E. elegantulus (Conte, 1857) |
Western equatorial Africa |
Size: 21–24 cm (8–9 in) long, plus 28–32 cm (11–13 in) tail[7] Habitat: Forest[8] Diet: Tree and liana gums and resins, as well as invertebrates[8] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dusky bushbaby
|
G. matschiei Liburnau, 1917 |
Central Africa |
Size: 14–19 cm (6–7 in) long, plus 24–28 cm (9–11 in) tail[9] Habitat: Forest[10] Diet: Insects, fruit, flowers, and gum[9] |
LC
|
| Mohol bushbaby | G. moholi Smith, 1836 |
Central and southern Africa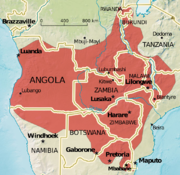 |
Size: 14–17 cm (6–7 in) long, plus 11–28 cm (4–11 in) tail[11] Habitat: Savanna[12] Diet: Arthropods, as well as tree gum and resin[11] |
LC
|
| Senegal bushbaby | G. senegalensis É Geoffroy, 1796 Four subspecies
|
Equatorial Africa (possible additional range in red) |
Size: 13–21 cm (5–8 in) long, plus 19–30 cm (7–12 in) tail[5] Habitat: Forest and savanna[13] Diet: Insects, as well as small birds, eggs, fruits, seeds, flowers, and tree gum[14] |
LC
|
| Somali bushbaby | G. gallarum Thomas, 1901 |
Eastern Africa |
Size: 13–20 cm (5–8 in) long, plus 20–30 cm (8–12 in) tail[5] Habitat: Savanna[15] Diet: Gum and invertebrates[5] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Angolan dwarf galago
|
G. kumbirensis Svensson et al., 2017 |
Angola in southwestern Africa |
Size: 14–18 cm (6–7 in) long, plus 17–21 cm (7–8 in) tail[16] Habitat: Forest and shrubland[17] Diet: Unknown[16] |
NT
|
| Prince Demidoff's bushbaby | G. demidoff Fischer von Waldheim, 1806 |
Western and central equatorial Africa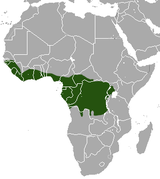 |
Size: 10–13 cm (4–5 in) long, plus 15–21 cm (6–8 in) tail[18] Habitat: Forest[19] Diet: Insects, as well as fruit and gum[18] |
LC
|
| Thomas's bushbaby
|
G. thomasi Elliot, 1907 |
Western and central equatorial Africa |
Size: 12–17 cm (5–7 in) long, plus 15–24 cm (6–9 in) tail[20] Habitat: Forest[21] Diet: Insects, as well as small vertebrates, fruit, and tree buds, leaves, and gum[20] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brown greater galago | O. crassicaudatus É Geoffroy, 1812 Three subspecies
|
Southern Africa |
Size: 29–38 cm (11–15 in) long, plus 41–48 cm (16–19 in) tail[22] Habitat: Forest, savanna, and shrubland[23] Diet: Gum and sap, as well as fruit and insects[22] |
LC
|
| Northern greater galago | O. garnettii (Ogilby, 1838) Four subspecies
|
Eastern Africa |
Size: 23–34 cm (9–13 in) long, plus about 36 cm (14 in) tail[24] Habitat: Forest[25] Diet: Fruit and insects[24] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grant's bushbaby | P. granti (Thomas & Wroughton, 1907) |
Southeastern Africa |
Size: 14–19 cm (6–7 in) long, plus 20–27 cm (8–11 in) tail[5] Habitat: Forest[26] Diet: Invertebrates, fruit, gum, and flowers, as well as small birds[26] |
LC
|
| Kenya coast galago | P. cocos Heller, 1912 |
Southeastern Africa |
Size: 14–19 cm (6–7 in) long, plus 18–23 cm (7–9 in) tail[5] Habitat: Forest[27] Diet: Insects and fruit[28] |
LC
|
| Rondo dwarf galago
|
P. rondoensis Honess, 1997 |
Scattered Tanzania in southeastern Africa |
Size: 10–13 cm (4–5 in) long, plus 17–18 cm (7 in) tail[28] Habitat: Forest[29] Diet: Insects, as well as fruit and gum[28] |
EN
|
| Uluguru bushbaby
|
P. orinus Lawrence & Washburn, 1936 |
Southeastern Africa |
Size: 12–14 cm (5–6 in) long, plus 16–20 cm (6–8 in) tail[5] Habitat: Forest[30] Diet: Gum, nectar, invertebrates, and small vertebrates[5] |
VU
|
| Zanzibar bushbaby
|
P. zanzibaricus (Matschie, 1893) Two subspecies
|
Scattered Tanzania |
Size: 14–15 cm (6–6 in) long, plus 12–15 cm (5–6 in) tail[31] Habitat: Forest[32] Diet: Fruit, insects, and gum[31] |
NT
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bioko Allen's bushbaby | S. alleni (Waterhouse, 1838) Two subspecies
|
Western equatorial Africa |
Size: 15–24 cm (6–9 in) long, plus 20–30 cm (8–12 in) tail[5] Habitat: Forest[33] Diet: Fruit, as well as insects and small mammals[34] |
NT
|
| Gabon bushbaby
|
S. gabonensis Gray, 1863 |
Western equatorial Africa |
Size: 18–21 cm (7–8 in) long, plus 23–28 cm (9–11 in) tail[28] Habitat: Forest[35] Diet: Arthropods, insects, fruit, and gum[36] |
LC
|
| Makandé squirrel galago
|
S. makandensis Ambrose, 2013 |
Gabon in western equatorial Africa |
Size: Unknown[28] Habitat: Forest[37] Diet: Unknown[28] |
DD
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gray slender loris | L. lydekkerianus A. Cabrera, 1908 Four subspecies
|
Southern India and Sri Lanka |
Size: 18–22 cm (7–9 in) long, with no tail[38] Habitat: Forest[39] Diet: Insects[40] |
NT
|
| Red slender loris | L. tardigradus (Linnaeus, 1758) |
Sri Lanka |
Size: 18–26 cm (7–10 in) long, with no tail[41] Habitat: Forest[42] Diet: Insects, as well as tree frogs, geckos, small birds, eggs, and fruit[41] |
EN
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bangka slow loris
|
N. bancanus (Lyon, 1906) |
Borneo and Bangka Islands in southeastern Asia | Size: About 26 cm (10 in) long, with no tail[43] Habitat: Forest[44] Diet: Insects, gum, nectar, and fruit[45] |
CR
|
| Bengal slow loris | N. bengalensis (Lacépède, 1800) |
Southeastern Asia |
Size: 26–38 cm (10–15 in) long, with vestigial tail[46] Habitat: Forest[47] Diet: Resin and gum, as well as nectar, fruit, invertebrates, bark, and bird eggs[46] |
EN
|
| Bornean slow loris | N. borneanus (Lyon, 1906) |
Borneo | Size: About 26 cm (10 in) long, with no tail[43] Habitat: Forest[48] Diet: Insects, gum, nectar, and fruit[49] |
VU
|
| Javan slow loris | N. javanicus É Geoffroy, 1812 |
Java in southeastern Asia |
Size: 28–31 cm (11–12 in) long, with vestigial tail[50] Habitat: Forest[51] Diet: Nectar, gum, insects, fruit, lizards, and eggs[50] |
CR
|
| Kayan River slow loris | N. kayan Munds, Nekaris, Ford, 2013 |
Borneo | Size: About 27 cm (11 in) long, with no tail[43] Habitat: Forest[52] Diet: Unknown[53] |
VU
|
| Philippine slow loris | N. menagensis Lydekker, 1893 |
Borneo and nearby islands |
Size: About 27 cm (11 in) long, with no tail[43] Habitat: Forest[54] Diet: Insects, nectar, gum, and fruit[55] |
VU
|
| Sumatran slow loris
|
N. hilleri (Stone and Rehn, 1902) |
Sumatra in southeastern Asia | Size: 26–30 cm (10–12 in) long, with no tail[56] Habitat: Forest[57] Diet: Insects, nectar, gum, and fruit[57] |
EN
|
| Sunda slow loris | N. coucang (Boddaert, 1785) |
Southeastern Asia |
Size: 27–38 cm (11–15 in) long, with no tail[58] Habitat: Forest[59] Diet: Sap, gum, nectar, stems, and fruit, as well as arthropods and insects[58] |
EN
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pygmy slow loris | X. pygmaeus (Bonhote, 1907) |
Southeastern Asia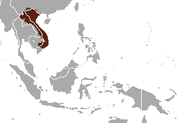 |
Size: 15–25 cm (6–10 in) long, with no tail[60] Habitat: Forest[61] Diet: Insects, gum, resin, fruit, and bamboo[60] |
EN
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calabar angwantibo | A. calabarensis (Smith, 1860) |
Western equatorial Africa |
Size: 22–31 cm (9–12 in) long, plus 4–10 cm (2–4 in) tail[62] Habitat: Forest[63] Diet: Insects, as well as fruit and gum[62] |
NT
|
| Golden angwantibo
|
A. aureus de Winton, 1902 |
Western equatorial Africa |
Size: 22–26 cm (9–10 in) long, plus vestigial tail[64] Habitat: Forest[65] Diet: Insects and fruit[65] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central African potto | P. edwarsi Bouvier, 1879 |
Central Africa | Size: 30–37 cm (12–15 in) long, plus 3–7 cm (1–3 in) tail[66] Habitat: Forest[67] Diet: Gum, insects, snails and fruit[67] |
LC
|
| East African potto | P. ibeanus Thomas, 1910 Two subspecies
|
East central Africa | Size: 29–37 cm (11–15 in) long, plus 4–10 cm (2–4 in) tail[66] Habitat: Forest[68] Diet: Fruit, gum, nectar, and invertebrates, as well as moss, frogs, and eggs[68] |
LC
|
| West African potto | P. potto (Müller, 1766) |
Western equatorial Africa | Size: 30–39 cm (12–15 in) long, plus 3–10 cm (1–4 in) tail[69] Habitat: Forest[70] Diet: Fruit, arthropods, insects, and eggs, as well as small vertebrates[69] |
NT
|
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.