Liquiritigenin
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
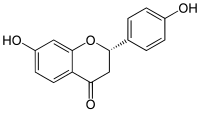
Liquiritigenin is a flavanone that was isolated from Glycyrrhiza uralensis, and is found in a variety of plants of the Glycyrrhiza genus, including Glycyrrhiza glabra (licorice).[1] It is an estrogenic compound which acts as a selective agonist of the ERβ subtype of the estrogen receptor (ER),[2] though it is also reported to act as an ERα partial agonist at sufficient concentrations.[3] It also has a choleretic effect.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2S)-4′,7-Dihydroxyflavan-4-one | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2S)-7-Hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2,3-dihydro-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H12O4 | |
| Molar mass | 256.257 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Liquiritigenin,NADPH:oxygen oxidoreductase (hydroxylating, aryl migration) is an enzyme that uses liquiritigenin, O2, NADPH and H+ to produce 2,7,4'-trihydroxyisoflavanone, H2O, and NADP+.
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.