Kanchanaburi province
Province of Thailand From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Province of Thailand From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Kanchanaburi (Thai: กาญจนบุรี, pronounced [kāːn.t͡ɕā.ná(ʔ).bū.rīː]) is the largest of the western provinces (changwat) of Thailand. The neighboring provinces are (clockwise, from the north) Tak, Uthai Thani, Suphan Buri, Nakhon Pathom, and Ratchaburi. In the west it borders Kayin State, Mon State, and the Tanintharyi Region of Myanmar.
Kanchanaburi
กาญจนบุรี | |
|---|---|
From left to right, top to bottom : Kanchanaburi City Gate, Erawan National Park, Kanchanaburi Road, Burma Railway, Kanchanaburi War Cemetery | |
| Nickname: Mueang Kan (Thai: เมืองกาญจน์) | |
| Motto(s): แคว้นโบราณ ด่านเจดีย์ มณีเมืองกาญจน์ สะพานข้ามแม่น้ำแคว แหล่งแร่น้ำตก ("The ancient province. The (Three) Pagodas Pass Checkpoint, Gems of Mueang Kan, Bridge on the River Kwai. Source of minerals and waterfalls.") | |
 Map of Thailand highlighting Kanchanaburi province | |
| Country | Thailand |
| Capital | Kanchanaburi |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Thanaporn Prommahit |
| Area | |
| • Total | 19,483 km2 (7,522 sq mi) |
| • Rank | Ranked 3rd |
| Population (2018)[2] | |
| • Total | 893,151 |
| • Rank | Ranked 26th |
| • Density | 46/km2 (120/sq mi) |
| • Rank | Ranked 74th |
| Human Achievement Index | |
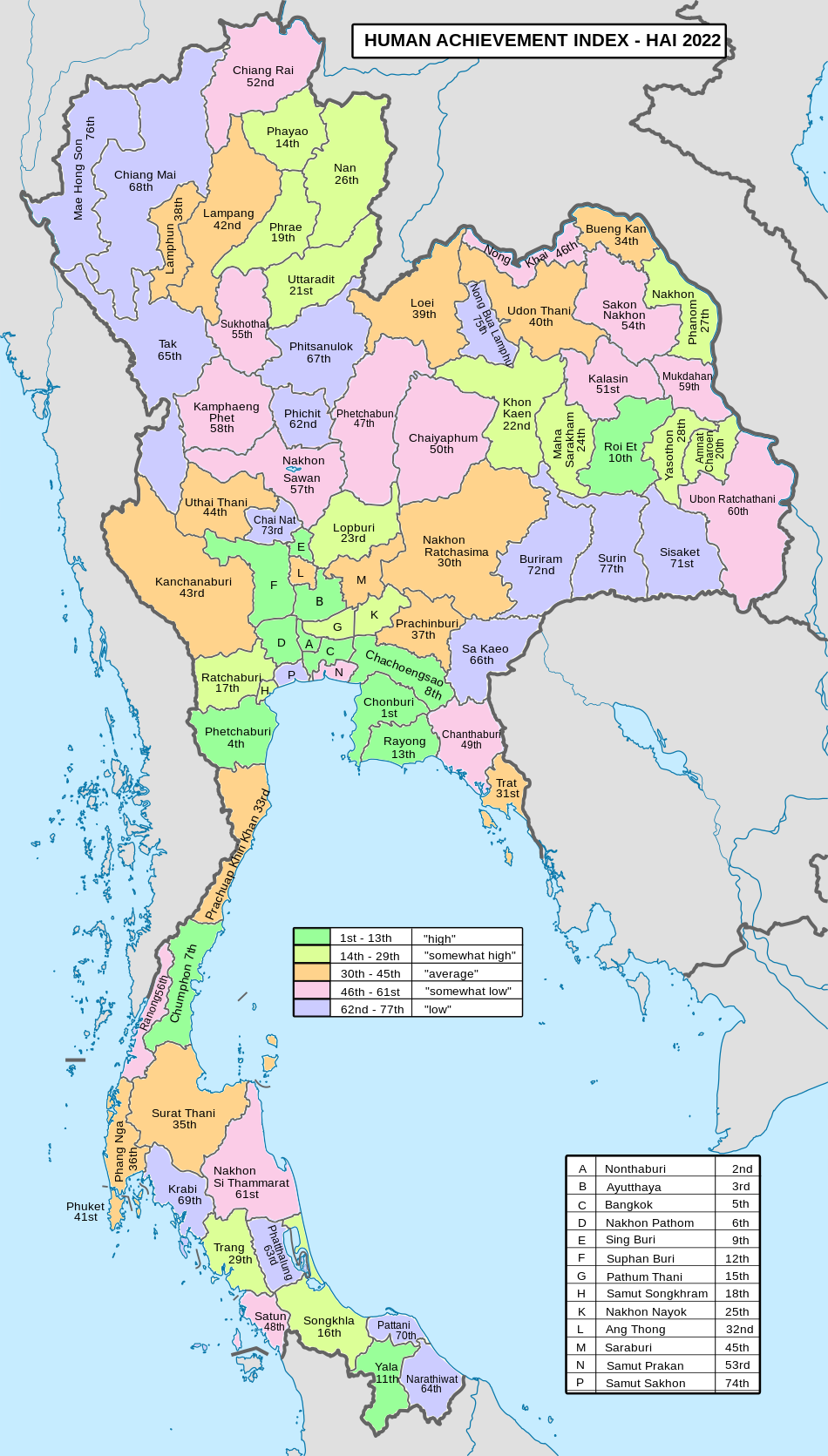
| • HAI (2022) | 0.6372 "average" Ranked 43rd |
| GDP | |
| • Total | baht 97 billion (US$3.5 billion) (2019) |
| Time zone | UTC+7 (ICT) |
| Postal code | 71xxx |
| Calling code | 034 |
| ISO 3166 code | TH-71 |
| Vehicle registration | กาญจนบุรี |
| Website | www |
Tourists are attracted by the history of its ancient civilization and the World War II Bridge over the River Kwai, originally spelt "Khwae" but officially changed to Kwai to accommodate the expectations of tourists.

The province is in the west of Thailand, 129 km from Bangkok, and covers a total area of approximately 19,483 km2 (7,522 sq mi). It is the country's third largest province, after Nakhon Ratchasima and Chiang Mai. Topographically, it is covered with timber and evergreen forests. The total forest area is 12,002 km2 (4,634 sq mi) or 61.9 percent of provincial area.[5] The district covers the source valleys of the rivers Kwae Yai and Kwae Noi ("River Kwai"), which merge at Kanchanaburi city to form the Mae Klong River.
Bong Ti is a transnational border crossing point, which is expected to gain in importance if the planned Dawei deepwater port project goes ahead, along with a highway and a railway line between Bangkok and the port.[6]
There area seven national parks in the mountainous areas of the Tenasserim Hills, along with two other national parks, make up region 3 (Ban Pong) of Thailand's protected areas.
There are two wildlife sanctuaries, along with one other wildlife sanctuary, make up region 3 (Ban Pong) of Thailand's protected areas.
Archaeological remains found in Kanchanaburi date back to the 4th century, with evidence of trade with surrounding regions at that time. Very little is known about the historical Khmer influence in Kanchanaburi, but Prasat Muang Sing, one of the country's most well-known Khmer sites, provides evidence of their occupation.

Not much was historically recorded about Kanchanaburi province before the reign of King Rama I, but some historians believe that the province was of strategic importance during the Ayutthaya period, since it was on the invasion route from Burma.[9] In 1982, many human and elephant skeletons and swords were found in Phanom Thuan district, leading to speculation that this site might even have been the site of the famous battle of King Naresuan against the Burmese crown prince, most commonly assigned to the Don Chedi district in nearby Suphanburi province.

Most foreigners are mainly aware of Kanchanaburi's recent history with the Burma Railway. During the Japanese occupation of Thailand in 1942, both allied POWs and Asian labourers were ordered by the Japanese to build a Thailand-Burma railway. Eventually, more than 100,000 people (16,000 allied POWs and 90,000 local Asian labourers) died from horrific working conditions.[10]
The seal of the province shows the three stupas on Bantadthong Mountain. They give the name to the mountain pass to Myanmar, called "Three Pagodas Pass".[11]
The provincial flower is the night-flowering jasmine (Nyctanthes arbortristis). The provincial tree is the Moulmein lancewood (Homalium tomentosum). The provincial aquatic animal is the Jullien's golden carp (Probarbus jullieni).
The provincial motto is "The ancient province. The (Three) Pagodas Pass Checkpoint, Gems of Kan, Bridge on the River Kwai. Source of minerals and waterfalls."

Kanchanaburi is divided into 13 districts (amphoe). The districts are further divided into 98 subdistricts (tambon) and 887 villages (muban).
As of 26 November 2019 there are:[12] one Kanchanaburi Provincial Administration Organisation (ongkan borihan suan changwat) and 49 municipal (thesaban) areas in the province. Kanchanaburi and Tha Ruea Phra Thaen have town (thesaban mueang) status. Further 47 subdistrict municipalities (thesaban tambon). The non-municipal areas are administered by 72 Subdistrict Administrative Organisations – SAO (ongkan borihan suan tambon).[2]
Kanchanaburi's main railway station is Kanchanaburi railway station, served by the Southern Line Nam Tok Branch Line (Burma Railway).
Phaholpolpayuhasena Hospital is the main hospital of the province, operated by the MInistry of Public Health.
In 1918, alluvial sapphire deposits were discovered near Bo Ploi. It was a major source of sapphires in the 1980s and 1990s.[13][14][15]
Kanchanaburi province is the site of Klity Creek,[16] a waterway heavily polluted by the practices of the Lead Concentrate Company. The company was ordered by a Thai court to clean up its environmental damage in 2013. To date (2019) the court ordered clean-up has been halting and ineffectual.[17]
Most of the sights in Kanchanaburi itself are directly related to World War II. The museums are dusty and generally not worth it, except for the Thailand–Burma Railway Centre, which gives a good introduction of the Burma Railway and its history. There are also two war cemeteries, the most moving of which is the Kanchanaburi War Cemetery.
The War Museum is located near the Thailand–Burma Railway station of Kanchanaburi. Although it is called the War Museum, the museum also houses a historical art gallery with murals and statues of historical figures and events from that region. Moreover, aside from WWII artifacts, there is also a sanctuary for stray cats, a wildlife atrium, a Miss Thailand costume museum, an arhive library from the founder of the museum, the Chansiri family. The museum was inaugurated on May 11, 1987.[18]



Since 2003, United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) in Thailand has tracked progress on human development at sub-national level using the Human achievement index (HAI), a composite index covering all the eight key areas of human development. National Economic and Social Development Board (NESDB) has taken over this task since 2017.[3]
| Rank | Classification |
| 1–13 | "High" |
| 14–29 | "Somewhat high" |
| 30–45 | "Average" |
| 46–61 | "Somewhat low" |
| 62–77 | "Low" |
| Map with provinces and HAI 2022 rankings |
 |
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.