Loading AI tools
Bony groove in the maxilla of the skull From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The infraorbital groove (or sulcus) is located in the middle of the posterior part of the orbital surface of the maxilla. Its function is to act as the passage of the infraorbital artery, the infraorbital vein, and the infraorbital nerve.
| Infraorbital groove | |
|---|---|
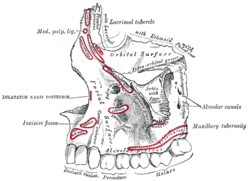 Left maxilla. Outer surface. (Infra-orbital groove labeled at upper right.) | |
 1 Foramen ethmoidale, 2 Canalis opticus, 3 Fissura orbitalis superior, 4 Fossa sacci lacrimalis, 5 Sulcus infraorbitalis, 6 Fissura orbitalis inferior, 7 Foramen infraorbitale | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Maxilla of skull |
| System | Skeletal |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | sulcus infraorbitalis maxillae |
| TA98 | A02.1.12.005 |
| TA2 | 760 |
| FMA | 57746 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
The infraorbital groove begins at the middle of the posterior border of the maxilla (with which it is continuous).[1] This is near the upper edge of the infratemporal surface of the maxilla. It passes forward, and ends in a canal which subdivides into two branches.
The infraorbital groove has an average length of 16.7 mm, with a small amount of variation between people.[1] It is similar in men and women.[1]
The infraorbital groove creates space that allows for passage of the infraorbital artery, the infraorbital vein, and the infraorbital nerve.
The infraorbital groove is an important surgical landmark for local anaesthesia of the infraorbital nerve.[1]
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.