Loading AI tools
Intrinsic muscle of the tongue From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The inferior longitudinal muscle of tongue is an intrinsic muscle of the tongue.[1] It is situated on the under surface of the tongue between the genioglossus and hyoglossus.[citation needed] It is innervated by the hypoglossal nerve (cranial nerve XII). Its contraction shortens and thickens the tongue.
This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. (May 2015) |
| Inferior longitudinal muscle of tongue | |
|---|---|
 Coronal section of tongue, showing intrinsic muscles. | |
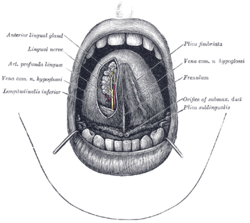 The mouth cavity. (Longitudinalis inferior labeled at bottom left.) | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Root of tongue |
| Insertion | Apex of tongue |
| Nerve | Hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) |
| Actions | Retracts tongue with superior longitudinal muscle, making tongue short and thick |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus longitudinalis inferior linguae |
| TA98 | A05.1.04.107 |
| TA2 | 2123 |
| FMA | 46694 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The inferior longitudinal muscle of the tongue is an intrinsic muscle of the tongue.[1] It is thin and oval in cross-section. It is situated between the paramedian septum, and the lateral septum.[2] It extends from the root to the apex of the tongue. Posteriorly, some of its fibers attach onto the body of the hyoid bone.[citation needed] Anteriorly, its fibres blend with those of the styloglossus, hyoglossus, and genioglossus to form the ventral area of the tip of the tongue.[2]
The inferior longitudinal muscle of the tongue is supplied by the hypoglossal nerve (CN XII).[3]
Contraciton of the inferior longitudinal muscle of the tongue shortens and thickens the tongue.[2]
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.