Loading AI tools
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
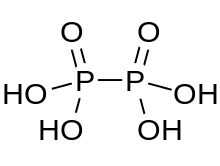
Hypophosphoric acid is a mineral acid with the formula H4P2O6, with phosphorus in a formal oxidation state of +4. In the solid state it is present as the dihydrate, H4P2O6·2H2O. In hypophosphoric acid the phosphorus atoms are identical and joined directly with a P−P bond. Isohypophosphoric acid is a structural isomer of hypophosphoric acid in which one phosphorus has a hydrogen directedly bonded to it and that phosphorus atom is linked to the other one by an oxygen bridge to give a phosphorous acid/phosphoric acid mixed anhydride. The two phosphorus atoms are in the +3 and +5 oxidation states, respectively.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Hypodiphosphoric acid | |
| Other names
Diphosphoric acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| H4P2O6 | |
| Molar mass | 161.98 g/mol |
| Appearance | White solid (dihydrate) |
| Melting point | 54 °C (129 °F; 327 K) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.2, 2.8, 7.3, 10.0[1] |
| Conjugate base | Hypophosphate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Hypophosphoric acid can be prepared by the reaction of red phosphorus with sodium chlorite at room temperature.[2]
A mixture of hypophosphoric acid, phosphorous acid (H3PO3) and phosphoric acid (H3PO4) is produced when white phosphorus oxidises in air when partially immersed in water.[2]
The tetrasodium salt Na4P2O6·10H2O crystallises at pH 10 and the disodium salt, Na2H2PO6·6H2O at pH 5.2.[1] The disodium salt can be passed through an ion exchange column to form the acid dihydrate, H4P2O6·2H2O.[2]
The anhydrous acid can be formed by vacuum dehydration over P4O10 or by the reaction of H2S on lead hypophosphate, Pb2P2O6.[1]
Hypophosphoric acid is tetraprotic with dissociation constants pKa1 = 2.2, pKa2 = 2.8, pKa3 = 7.3 and pKa4 = 10.0.[1]
On standing the anhydrous acid undergoes rearrangement and disproportionation to form a mixture of isohypophosphoric acid, HPO(OH)-O-PO2(OH); pyrophosphoric acid H2P2O7 and pyrophosphorous acid.[1]
Hypophosphoric acid is unstable in hot hydrochloric acid, in 4 M HCl it hydrolyses to give H3PO3 + H3PO4.[1]
Hypophosphorus acid contains oxonium ions and is best formulated [H3O+]2 [H2P2O6]2−. The acid is isostructural with the diammonium salt which contains the [HOPO2PO2OH]2− anion with a P−P bond length of 219 pm.[2]
The HOPO2PO2OH2− anion in Na2H2P2O6·6H2O has a symmetric, staggered ethane-like structure with a P−P bond of length 219 pm. Each phosphorus atom has two P−O bonds with length 151 pm, and a P−OH bond length of 159 pm.[3]
Many hypophosphate salts are known, for example, K4P2O6·8H2O, Ca2P2O6·2H2O, K3HP2O6·3H2O, K2H2P2O6·2H2O, KH3P2O6.
On standing in air, hypophosphates tend to oxidise to pyrophosphates containing the P
2O4−
7 ion where P has a formal oxidation state of +5. Hypophosphates are stable to alkali hydroxides. In fused sodium hydroxide they convert rapidly to the orthophosphate containing PO3−
4.[2]
Polyhypophosphates are known containing linear anions, for example Na5P3O8 containing O(PO2)3O5− with a P−P−P chain and Na6P4O10·2H2O containing O(PO2)4O6−, with a P−P−P−P chain. The cyclic anion (PO
2)6−
6, (hypohexametaphosphate[4]) where each phosphorus atom has an oxidation state of +3 is formed when a suspension of red phosphorus in KOH is oxidised with bromine.[2]
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.