Geography of the Dominican Republic
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
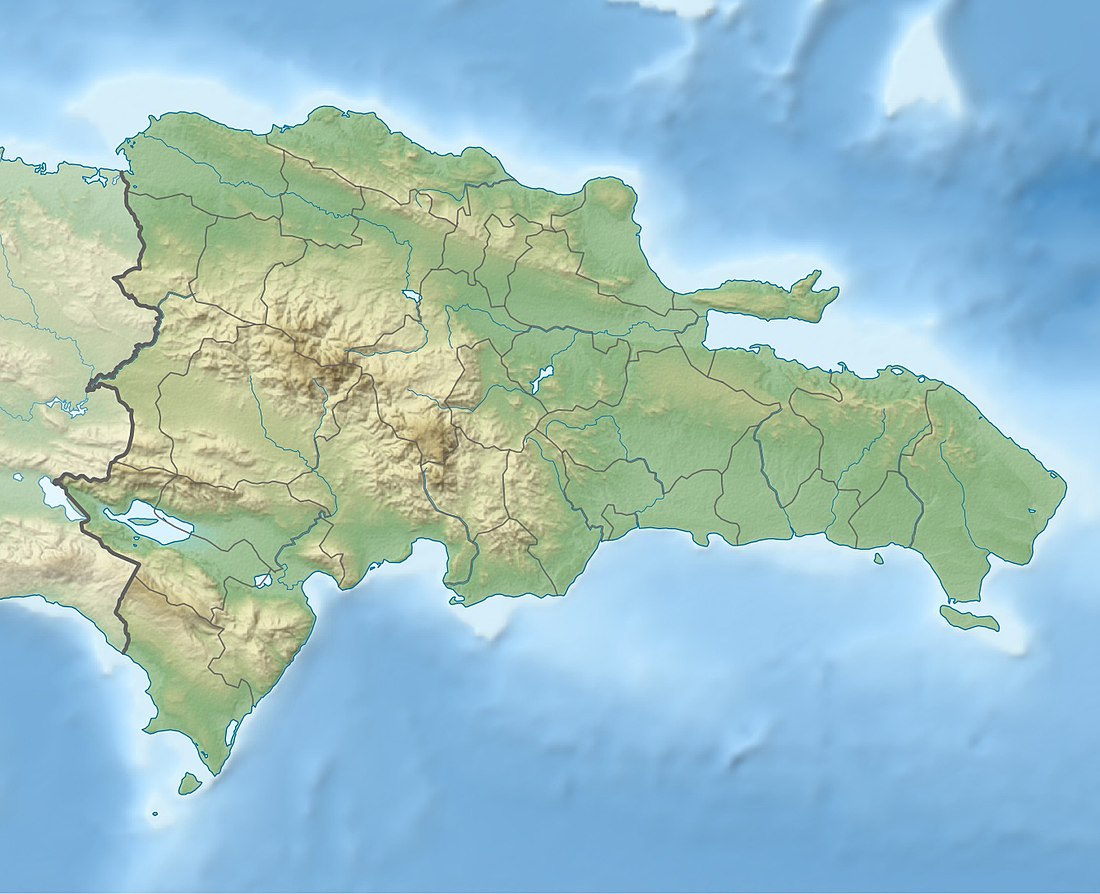
The Dominican Republic (Spanish: República Dominicana) is a country in the West Indies that occupies the eastern five-eighths of Hispaniola. It has an area of 48,670 km2, including offshore islands. The land border shared with Haiti, which occupies the western three-eighths of the island,[1][2] is 376 km long.[3] The maximum length, east to west, is 390 km from Punta de Agua to Las Lajas, on the border with Haiti. The maximum width, north to south, is 265 km from Cape Isabela to Cape Beata.[4] The capital, Santo Domingo, is located on the south coast.
 | |
| Continent | North America |
|---|---|
| Region | Caribbean Greater Antilles |
| Coordinates | 19°00' N 70°40' W |
| Area | Ranked 131st |
| • Total | 48,670 km2 (18,790 sq mi) |
| • Land | 99.2% |
| • Water | 0.8% |
| Coastline | 1,288 km (800 mi) |
| Borders | Total land borders: 275 km |
| Highest point | Pico Duarte 3,098 m |
| Lowest point | Lake Enriquillo -46 m |
| Longest river | Yaque del Norte River |
| Largest lake | Lake Enriquillo |
| Exclusive economic zone | 255,898 km2 (98,803 sq mi) |
The Dominican Republic's shores are washed by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and the Caribbean Sea to the south. The Mona Passage, a channel about 130 km wide, separates the country (and Hispaniola) from Puerto Rico.[5]
Physical features
Summarize
Perspective

The Dominican Republic is a country with many mountains, and the highest peaks of the West Indies are found here. The chains of mountains show a direction northwest–southeast, except in the Southern peninsula (in Haiti) where they have a direction west–east. The mountains are separated by valleys with the same general direction.
From north to south, the mountain ranges and valleys are:[6]
- Cordillera Septentrional (in English, "Northern Range"). It runs parallel to the north coast, with extensions to the northwest, the Tortuga Island, and to the southeast, the Samaná Peninsula (with its Sierra de Samaná). Its highest mountain is Diego de Ocampo, close to Santiago, with 1,249 m. There are several small plains between this range and the Atlantic Ocean. Rivers are short and most of them flow to the north.
- The Cibao Valley (Dominican Republic) is the largest and the most important valley of the country. This long valley stretches from North Haiti, where is called Plaine du Nord, to Samaná Bay. It can be divided in two sections: the northwestern part is the Yaque del Norte Valley (or Línea Noroeste) and the eastern Yuna Valley (or Vega Real, English: Royal Valley). The Vega Real is the most fertile area in the country, with a high population density.
- The Cordillera Central (also called Sierra del Cibao) is the island's most rugged and imposing feature and is known in Haiti as the Massif du Nord ("Northern Massif"). The highest mountains of the West Indies are in this range: Pico Duarte, 3,098 m, and others above 3,000 m. Near the center of the island, this range turns southward and is called Sierra de Ocoa, finishing near the city of Azua de Compostela, on the Caribbean coast. Another branch, Cordillera Oriental or Sierra del Seibo, is separated from the main chain by a karstic region (Los Haitises) and with a west–east direction; it is located south of Samaná Bay.

- The San Juan Valley and Plain of Azua are big valleys south of the Cordillera Central with altitude from 0 to 600 m.
- The Sierra de Neiba, with Mount Neiba the highest mountain with 2,279 m. An extension to the southeast of Sierra de Neiba is the Sierra Martín García (Loma Busú, 1,350 m).
- The Hoya de Enriquillo or Neiba Valley is a remarkable valley, with a west–east direction, of low altitude (on average 50 m with some points below sea level) and with a great salt lake: the Enriquillo Lake.
- The Sierra de Bahoruco, called Massif de la Selle in Haiti. This southern group of mountains have a geology very different from the rest of the island.
- Llano Costero del Caribe (in English, "Caribbean Coastal Plain") is in the southeast of the island (and of the Dominican Republic). It is a large savanna east of Santo Domingo.

Climate
Summarize
Perspective

The Dominican Republic is a tropical, maritime nation. Owing to its diverse mountainous topography, the country's climate shows considerable variation for its size, and has the most diverse climate zones of all the Caribbean islands, including subtropical highland climates (Cwb), oceanic climates (Cfb) and hot semi-arid climates (BSh) along the usual tropical savanna (Aw), monsoon (Am), and rainforest (Af) climates typical of a Caribbean nation. Conditions are ameliorated in many areas by elevation and by the northeast trade winds, which blow steadily from the Atlantic all year long. The annual mean temperature is 25 °C (77 °F); regional mean temperatures range from 18 °C (64.4 °F) in the heart of the Cordillera Central (Constanza) to as high as 27 °C (80.6 °F) in arid regions. Temperatures rarely rise above 32 °C (89.6 °F), and freezing temperatures only occur in winter in the highest mountains. The average temperature in Santo Domingo in January is 24 °C (75.2 °F), and 27 °C (80.6 °F) in July.
The rain season for the northern coast is from November to January. For the rest of the country, the rain season is from May to November. The average annual rainfall is 1,346 mm (53.0 in), with extremes of 2,500 mm (98.4 in) or more in the mountainous northeast (the windward side of the island) and 500 mm (19.7 in) in the southwestern valleys. The western valleys, along the Haitian border, remain relatively dry, with less than 760 mm (29.9 in) of annual precipitation, due to the rain shadow effect caused by the central and northern mountain ranges. The northwestern and southeastern extremes of the country are also arid.
The Dominican Republic is occasionally damaged by tropical storms and hurricanes, which originate in the mid-Atlantic and southeastern Caribbean from June until November (mainly from August to October) each year.
- Tropical rainforest climate in Samana.
- Frosted alpine forest in Constanza.
- Semi-arid climate in Pedernales.
- Desert sand dunes of Bani.
Islands
There are several smaller islands and cays that are part of Dominican territory. The largest islands are:
- Saona, close to the southeastern coast of Hispaniola, in the Caribbean Sea. It has an area of 117 km2.[4] Its Taíno name was Iai [7] or Adamanay. Columbus named this island as Savona, after the Italian city of the same name, but the use during years has eliminated the letter v.
- Beata, also on the southern coast. It has an area of 27 km2.[4] Its Taíno name is unknown. Columbus named this island Madama Beata.
- Catalina, very close to the southeastern coast. It has an area of 9.6 km2.[4] Its Taíno name was Iabanea[7] but some writers, including poets, say that it was called Toeya or Toella.
Rivers and lakes
Summarize
Perspective


The 8 longest rivers of the Dominican Republic are:[8]
- Yaque del Norte. At 296 km, it is the longest river in the Dominican Republic. Its sources are in the Cordillera Central and flows to the Atlantic Ocean. Its watershed has an area of 7,044 km2.
- Yuna. It is 185 km long. Its sources are in the Cordillera Central and flows to the east into Samaná Bay. Its watershed has an area of 5,498 km2.
- Yaque del Sur. It is 183 km long and its sources are in the Cordillera Central. It flows to the south into the Caribbean Sea. Its watershed has an area of 4,972 km2.
- Ozama. It is 148 km long. Its sources are in Sierra de Yamasá (a branch of the Cordillera Central). It flows into the Caribbean Sea. Its watershed has an area of 2,685 km2.
- Camú. It is 137 km long. Its sources are in the Cordillera Central and flows into the Yuna River. Its watershed has 2,655 km2.
- Nizao. It is 133 km long. Its sources are in the Cordillera Central and flows to the south into the Caribbean Sea. Its watershed has an area of 974 km2.
- San Juan. It is 121 km long. Its sources are in the Cordillera Central and flows to the south into the Yaque del Sur River. Its watershed has an area of 2,005 km2.
- Mao. It is 105 km long. Its sources are in the Cordillera Central and flows to the north into the Yaque del Norte River. Its watershed has an area of 864 km2.
The Artibonite River is the longest river of the island, but only 68 km flows through the Dominican Republic.
The largest lake of Hispaniola, and of the Caribbean, is Lake Enriquillo. It is located in the Hoya de Enriquillo with an area of 265 km2. There are three small islands within the lake. It is around 40 meters below sea level, and is a hypersaline lake, with a higher concentration of salt than seawater.
Other lakes are Rincón (fresh water, area of 28.2 km2), Oviedo (brackish water, area of 28 km2), Redonda, and Limón.
Statistics

- Location
- Caribbean, it occupies five-eighths of the island of Hispaniola, between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, east of Haiti
- Geographic coordinates
- 19°00′N 70°40′W
- Area
-
- Total: 48,670 km²
- Land: 48,320 km²
- Water: 350 km²
- Land boundaries
- Coastline
- 1,288 km
- Maritime claims
-
- Territorial sea: 6 nmi (11.1 km; 6.9 mi)
- Contiguous zone: 24 nmi (44.4 km; 27.6 mi)
- Exclusive economic zone: 255,898 km2 (98,803 sq mi) with 200 nmi (370.4 km; 230.2 mi)
- Continental shelf: 200 nmi (370.4 km; 230.2 mi) or to the edge of the continental margin
- Climate
- Tropical maritime; little seasonal temperature variation; seasonal variation in rainfall
- Rivers
- Significant rivers include the Jimani River, Río Yaque del Norte, Río Jamao del Norte, Río Isabela and the Ozama River
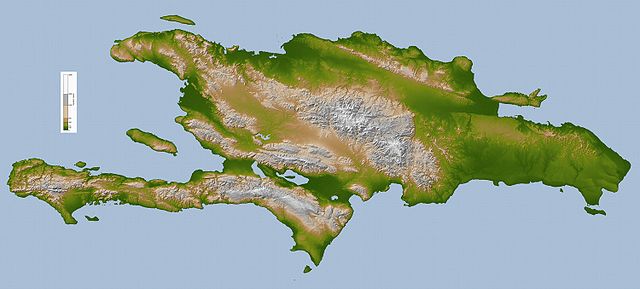
- Terrain
- Rugged highlands and mountains with fertile valleys interspersed
- Geographical extremes
- Northernmost point – Cabo Isabela
- Southernmost point – Alto Velo Island, Jaragua National Park
- Southernmost point (mainland) – south of Oviedo, Pedernales in Jaragua National Park
- Westernmost point – Las Lajas, border with Haiti, Independencia Province
- Easternmost point – Punta de Agua, La Altagracia Province
- Elevation extremes
- Lowest point – Lago Enriquillo: -46 m
- Highest point – Pico Duarte: 3,098 m
- Natural resources
- Nickel, bauxite, gold, silver
- Land use
-
- Arable land: 16.56%
- Permanent crops: 10.35%
- Other: 73.10% (2012 est.)
- Irrigated land
- 3,241 km² (2018)
- Total renewable water resources
- 21 km3 (2011)
- Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural)
-
- total: 5.47 km3/yr (26%/1%/72%)
- per capita: 574.2 m3/yr (2005)
- Natural hazards
- Lies in the middle of the hurricane belt and subject to severe storms from June to October; occasional flooding; periodic droughts
- Environment - current issues
- Water shortages; soil eroding into the sea damages coral reefs; deforestation; damage caused by Hurricane Georges
- Environment - international agreements
-
- Party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
- Signed, but not ratified: Law of the Sea
- Geography - note
- Shares island of Hispaniola with Haiti (eastern five-eighths is the Dominican Republic, western three-eighths is Haiti)[1][2]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.