Gasa District
District of Bhutan From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Gasa District (Dzongkha: དགའ་ས་རྫོང་ཁག; Wylie: dgav-sa rdzong-khag, also མགར་ས་རྫོང་ཁག) is one of the 20 dzongkhags (districts) comprising Bhutan. The capital of Gasa District is Gasa Dzong near Gasa. It is located in the far north of the county and spans the Middle and High regions of the Tibetan Himalayas. The dominant language of the district is Dzongkha, which is the national language. Related languages, Layakha and Lunanakha, are spoken by semi-nomadic communities in the north of the district. The People's Republic of China claims the northern part of Gasa District.
Gasa District
དགའ་ས་རྫོང་ཁག | |
|---|---|
| Gasa District | |
| Coordinates: 28°0′N 90°0′E | |
| Country | Bhutan |
| Capital | Gasa Dzong |
| Area | |
• Total | 3,117.74 km2 (1,203.77 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 4,500 m (14,800 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 1,500 m (4,900 ft) |
| Population (2005)[1] | |
• Total | 3,116 |
• Estimate (2010) | 3,396 |
| • Rank | 20th |
| • Density | 1.00/km2 (2.6/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+6 (BTT) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+6 (not observed) |
| HDI (2019) | 0.536[2] low · 20th of 20 |
| Website | www |

Gasa has an area of 3,117.74 km2 (1,203.77 sq mi) as of 2010[update],[1] formerly 4,409.30 km2 (1,702.44 sq mi) as of 2002[update].[3] It had a population of 3,116 as of the 2005 census,[1] making it the largest, least populated, and thus least densely populated of all the dzongkhags; it is also the least developed district of Bhutan.
History
Gasa was formerly a drungkhag (sub-district) of the Punakha dzongkhag (district). It became a separate dzongkhag in 1992, the start of 7th Five Year Plan.[1]
Administrative divisions

Gasa District is divided into four village blocks (or gewogs):[1][4]
- Khamaed Gewog,[4] formerly known as ⋅Goenkhamae[1]
- Khatoed Gewog,[4] formerly known as Goenkaatoe[1]
- Laya Gewog[1][4]
- Lunana Gewog[1][4]
Geography
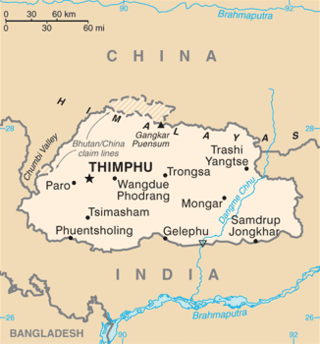
Gasa is bordered to the north by Tibet Autonomous Region of the People's Republic of China and by Thimphu, Punakha, and Wangdue Phodrang dzongkhags to the south.
Economy
Gasa has become a tourist destination because of its pristine forests and the exceptionally scenic location of its Dzong. In 2008 a massive flood on the Mo Chhu (Female River) destroyed a popular hot spring complex, which is under restoration and was to re-open in late 2011. The high altitude makes farming difficult, although government programs seek to establish mustard and summer vegetable planting programs. Residents herd yaks and dzos, and a small number benefit from the nascent tourism industry. A narrow road from Punakha, which is mostly unpaved, reaches up to the Dzong and is now being extended up to Laya. The majority of the known herds of wild Takin occur in Gasa. Electricity is also being supplied to some of the gewogs and all electrification programs are expected to be completed by 2012.
Gasa is most famous for its Layap people and the Snowman Trek, one of the most challenging treks in the Himalayas.
Environment
All of Gasa is an environmentally protected area of Bhutan. Most parts of the dzongkhag lie within Jigme Dorji National Park (Khamaed, Khatoed, Laya, Lunana Gewogs), although the northeast reaches of Gasa are part of Wangchuck Centennial Park (Lunana Gewog).[5][6] Several of Bhutan's glaciers are located in Gasa, namely in Lunana Gewog, which borders Tibet.
Tourism
Sabhi Goenpa
Tshechu Dra is a sacred cliff of longevity is located in the Panikong village where Guru Rinpoche is said to have extracted longevity water from a cliff to benefit sentient beings.[7]
Zabsel Drubdey Rawai Drubdey
Gasa Tshachu
Bjagay Menchu
Festival
- Annual Gasa Tshechu
- Royal Highland Festival
- Laya Run
Climate
| Climate data for Gasa, elevation 2,760 m (9,060 ft), (2003–2017 normals) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 18.5 (65.3) |
17.0 (62.6) |
23.5 (74.3) |
27.0 (80.6) |
26.0 (78.8) |
25.5 (77.9) |
30.0 (86.0) |
26.0 (78.8) |
25.0 (77.0) |
25.0 (77.0) |
21.0 (69.8) |
19.0 (66.2) |
30.0 (86.0) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 9.9 (49.8) |
10.3 (50.5) |
13.3 (55.9) |
15.7 (60.3) |
17.7 (63.9) |
19.6 (67.3) |
21.0 (69.8) |
20.7 (69.3) |
19.9 (67.8) |
17.8 (64.0) |
13.2 (55.8) |
11.4 (52.5) |
15.9 (60.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 4.4 (39.9) |
4.9 (40.8) |
7.0 (44.6) |
11.0 (51.8) |
12.9 (55.2) |
15.2 (59.4) |
16.5 (61.7) |
16.4 (61.5) |
15.7 (60.3) |
13.3 (55.9) |
7.8 (46.0) |
5.8 (42.4) |
10.9 (51.6) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −1.1 (30.0) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
2.6 (36.7) |
6.3 (43.3) |
8.1 (46.6) |
10.8 (51.4) |
12.0 (53.6) |
12.0 (53.6) |
11.4 (52.5) |
8.8 (47.8) |
2.4 (36.3) |
0.1 (32.2) |
6.1 (42.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −7.0 (19.4) |
−6.0 (21.2) |
−5.0 (23.0) |
−6.0 (21.2) |
−6.0 (21.2) |
2.0 (35.6) |
4.0 (39.2) |
3.0 (37.4) |
6.0 (42.8) |
−5.0 (23.0) |
−6.0 (21.2) |
−5.0 (23.0) |
−7.0 (19.4) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 19.1 (0.75) |
27.9 (1.10) |
86.7 (3.41) |
99.7 (3.93) |
164.8 (6.49) |
294.5 (11.59) |
371.1 (14.61) |
324.1 (12.76) |
194.5 (7.66) |
115.5 (4.55) |
35.7 (1.41) |
10.7 (0.42) |
1,744.3 (68.68) |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 71.7 | 71.3 | 74.0 | 73.3 | 75.3 | 83.7 | 85.2 | 83.5 | 81.2 | 73.3 | 73.5 | 71.5 | 76.5 |
| Source: National Center for Hydrology and Meteorology[8] | |||||||||||||
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.

