Loading AI tools
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
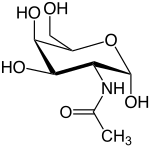
N-Acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc), is an amino sugar derivative of galactose.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-(Acetylamino)-2-deoxy-D-galactose | |
| Other names
GalNAc; 2-Acetamido-2-deoxy-D-galactose; N-Acetylchondrosamine; 2-Acetamido-2-deoxy-D-galactopyranose; N-Acetyl-D-galactosamine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H15NO6 | |
| Molar mass | 221.21 g/mol |
| Melting point | 172 to 173 °C (342 to 343 °F; 445 to 446 K) |
| Related compounds | |
Related monosaccharides |
N-Acetylglucosamine Galactosamine Galactose |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
In humans it is the terminal carbohydrate forming the antigen of blood group A.[1]
It is typically the first monosaccharide that connects serine or threonine in particular forms of protein O-glycosylation.
N-Acetylgalactosamine is necessary for intercellular communication, and is concentrated in sensory nerve structures of both humans and animals.
GalNAc is also used as a targeting ligand in investigational antisense oligonucleotides and siRNA therapies targeted to the liver, where it binds to the asialoglycoprotein receptors on hepatocytes. [2]
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.