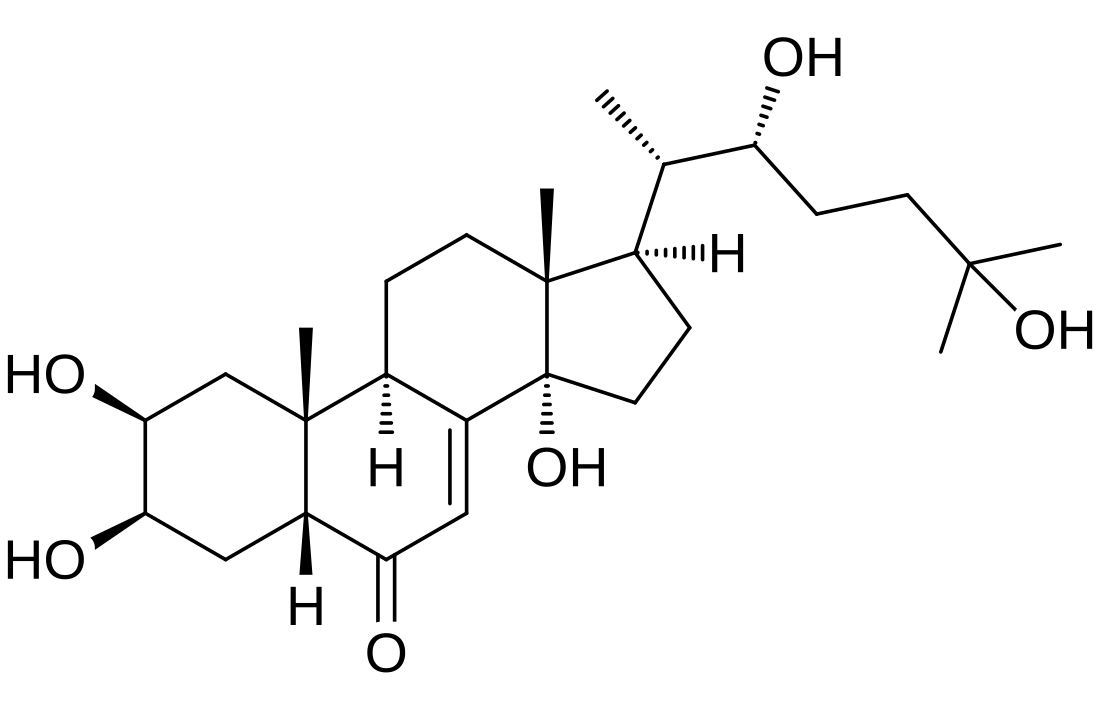
Ecdysone
Precursor of an insect hormone From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Ecdysone is a[clarification needed] prohormone of the major insect molting hormone 20-hydroxyecdysone, secreted from the prothoracic glands. It is of steroidal structure. Insect molting hormones (ecdysone and its homologues) are generally called ecdysteroids. Ecdysteroids act as moulting hormones of arthropods but also occur in other related phyla where they can play different roles.[1][2] In Drosophila melanogaster, an increase in ecdysone concentration induces the expression of genes coding for proteins that the larva requires. It causes chromosome puffs (sites of high expression) to form in polytene chromosomes. Recent findings in the laboratory of Chris Q. Doe have found a novel role of this hormone in regulating temporal gene transitions within neural stem cells of the fruit fly.[3]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(22R)-2β,3β,14α,22,25-Pentahydroxy-5β-cholest-7-en-6-one | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(1R,3aS,5aR,7R,8S,9aR,9bR,11aR)-1-[(2S,3R)-3,6-Dihydroxy-6-methylheptan-2-yl]-3a,7,8-trihydroxy-9a,11a-dimethyl-1,2,3,3a,5a,6,7,8,9,9a,9b,10,11,11a-tetradecahydro-5H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-5-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.020.692 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C27H44O6 | |
| Molar mass | 464.63 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Ecdysone and other ecdysteroids also appear in many plants mostly as a protection agent (toxins or antifeedants) against herbivorous insects.[4] These phytoecdysteroids have been reputed to have medicinal value. They are part of herbal adaptogenic remedies like Cordyceps, yet an ecdysteroid precursor in plants has been shown to have cytotoxic properties[5] as well as antioxidant properties on lipid peroxidation.[6]
Tebufenozide, sold under the Bayer trademark MIMIC,[7] has ecdysteroid activity although its chemical structure has little resemblance to the ecdysteroids.[8]
See also
- Ecdysone receptor
- PTTH - Metamorphosis Initiator hormone
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.