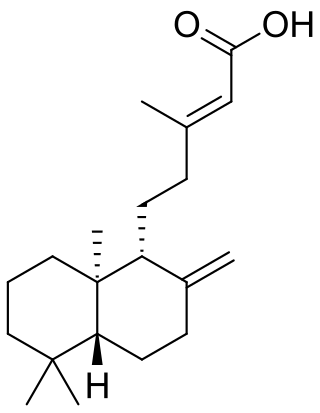
Copalic acid
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Copalic acid is a chemical compound that is a constituent of copaiba oil, an oleoresin extracted from trees in the genus Copaifera.[1] It is a diterpenoid of the labdane class.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(E)-5-[(1R,4aR,8aR)-5,5,8a-Trimethyl-2-methylidene-3,4,4a,6,7,8-hexahydro-1H-naphthalen-1-yl]-3-methylpent-2-enoic acid | |
| Other names
(-)-Copalic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H32O2 | |
| Molar mass | 304.474 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Because copaiba oil has some uses in traditional herbal medicine, there has been scientific interest in investigating the potential pharmacology of its constituents, including copalic acid.[2][3] In addition, synthetic derivatives of copalic acid have been investigated for their potential pharmacology as well.[4]
Several laboratory syntheses of copalic acid have been reported.[5][6]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.