Loading AI tools
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Balmuildy is the site of a Roman fort on the Antonine Wall in Scotland.[1] It is one of only two forts on the Antonine Wall to have been found with stone ramparts; the other is Castlecary.[2] A digital reconstruction of the fort has been created.[3]
| Balmuildy | |
|---|---|
 Balmuildy Bridge, modern road bridge near the Glaswegian section of the Antonine Wall | |
| Place in the Roman world | |
| Province | Britannia |
| Structure | |
| — Stone structure — | |
| Location | |
| Town | Glasgow |
| Country | |
| Site notes | |
| Condition | Ruined |

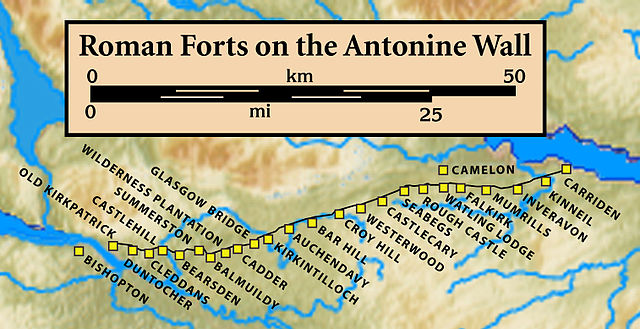
The fort is located in Glasgow, west of Bishopbriggs and east of Bearsden, south of the River Kelvin and north of the Forth and Clyde Canal. The fort was just south of the River Kelvin and north-west of Easter Balmuildy Farm which locates it within Glasgow City Council's borders, close to East Dunbartonshire to the east.[4] Its neighbouring forts are Bearsden to the west and Cadder to the east although there are intermediate fortlets at Summerston to the west and Wilderness Plantation to the east.[5] See map below for details.

Balmuildy Castro was constructed between 142 and 154 AD at the order of Roman Emperor Antoninus Pius.[7] Quintus Lollius Urbicus, governor of Roman Britain at the time, initially supervised the effort. It was one of sixteen forts built to support the Antonine Wall, with small fortlets between them; troop movement was facilitated by a road linking all the sites known as the Military Way. Antoninus Pius never visited Britain, whereas his predecessor Hadrian did. Pressure from the Caledonians may have led Antoninus to send the empire's troops further north. The wall, and Balmuildy, was abandoned only eight years after completion, and the garrisons relocated back to Hadrian's Wall. In 208 Emperor Septimius Severus re-established legions at the wall and ordered repairs; this has led to the wall being referred to as the Severan Wall. The occupation ended a few years later, and the wall was not occupied again.[8]
Most Roman forts along the wall held garrisons of around 500 men.[9] Larger forts like Castlecary and Birrens had a nominal cohort of 1,000 men[10] but probably sheltered women and children[11] as well, although the troops were not allowed to marry.[12] It is likely that there were large communities of civilians around the site.[13]

The site was excavated by Steuart Napier Miller who wrote about it in his 1922 volume: The Roman fort at Balmuildy (Summerston, near Glasgow) on the Antonine Wall.[19] Sir George Macdonald also described the site in the 1934 in The Roman wall in Scotland.[20] The related site of Summerston was written about by J. M. Davidson in 1937.[21]
An altar to Fortuna was found in one of the fort's bath houses similar to the one found at Castlecary.[22] There was also an altar dedicated to Mars found along with some statues.[23] A dedication to a building by the Second Legion was found although the stone had been repurposed by farmers.[24] Fragments of another stone by the same legion were also discovered.[25] Part has been scanned and a video produced.[26] All of these finds are now in the Hunterian Museum in Glasgow.[27] Other discoveries include: a door hinge plate,[28] a terracotta bath house drainpipe,[29] a holdfast to stick tiles to the bath house wall,[30] a perfume pot,[31] an unguent pot,[32] a Samian ware platter,[33] and a clay cheese press.[34] An oil lamp[35] and a surgical probe[36] have also been scanned to video.
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.