Autonomous regions of China
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The autonomous regions (Chinese: 自治区; pinyin: Zìzhìqū) are one of four types of province-level divisions of the People's Republic of China. Like Chinese provinces, an autonomous region has its own local government, but under the law of the People's Republic of China, an autonomous region has more legislative rights, such as the right to "formulate self-government regulations and other separate regulations."[1] An autonomous region is the highest level of minority autonomous entity in China, which has a comparably higher population of a particular minority ethnic group.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (October 2018) |
| Autonomous regions 自治区 Zìzhìqū | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Category | Unitary state |
| Location | China |
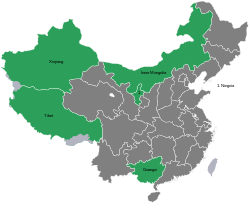
| Number | 5 (Guangxi, Inner Mongolia, Ningxia, Tibet, and Xinjiang) |
| Populations | 110,879,058[a] |
| Areas | 4,380,000 km2 (1,690,000 sq mi)[b] |
| Government |
|
| Subdivisions | |
There are five autonomous regions in China: Guangxi, Inner Mongolia (Nei Menggu), Ningxia, Tibet (Xizang), and Xinjiang.
History
Established in 1947, the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region became the first autonomous region in the Chinese liberated zone. Xinjiang was made autonomous in 1955 after the PRC's founding, and Guangxi and Ningxia were made autonomous in 1958. Tibet was annexed by the People's Republic of China in 1951, and was declared an autonomous region in 1965. The designation of Guangxi and Ningxia as Zhuang and Hui autonomous areas, respectively, was protested by the local Han Chinese, who made up two-thirds of the population of each region.[citation needed] Although Mongols made up an even smaller percentage of Inner Mongolia than either of these, the ensuing Chinese Civil War gave little opportunity for protest.[2]
Legal rights
Autonomous regions in China have no legal right to secede, unlike in the Soviet Union – the Law of the People's Republic of China on Regional Ethnic Autonomy, written in 1984, states that "each and every ethnic autonomous region is an inseparable part of the People's Republic of China," and that "any form of ... separatism ... is absolutely prohibited."[3][4][5]
Public goods and services
In general, China's minority regions have some of the highest per capita government spending on education, among other public goods and services.[6]: 366 Providing public goods and services in these areas is part of a government effort to reduce regional inequalities, reduce the risk of separatism, and stimulate economic development.[6]: 366
List of autonomous regions
| Name in English | Simplified Chinese Pinyin |
Abbreviation | Local name SASM/GNC romanization (Language) |
Capital | Designated minority |
Language | Flag | Pre-1949 ROC subdivision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region | 内蒙古自治区 Nèi Měnggǔ Zìzhìqū |
蒙 Měng (IMAR) |
ᠦᠪᠦᠷ ᠮᠣᠩᠭᠤᠯ ᠤᠨ ᠥᠪᠡᠷᠲᠡᠭᠡᠨ ᠵᠠᠰᠠᠬᠣ ᠣᠷᠣᠨ Öbür mongüol-un öbertegen zasaqu orun (Mongolian) |
Hohhot (呼和浩特; ᠬᠥᠬᠡᠬᠣᠲᠠ) |
Mongol | Mongolian |  |
Suiyuan, Chahar, Rehe, Liaobei, Xing'an, Gansu and Ningxia. |
| Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region | 广西壮族自治区 Guǎngxī Zhuàngzú Zìzhìqū |
桂 Guì (GZAR) |
Gvangjsih Bouxcuengh Swcigih (Standard Zhuang/Zhuang) | Nanning (南宁; Nanzningz) |
Zhuang | Zhuang, Standard Zhuang language (Vahcuengh) | Guangxi (province) | |
| Tibet Autonomous Region | 西藏自治区 Xīzàng Zìzhìqū |
藏 Zàng (TAR) |
བོད་རང་སྐྱོང་ལྗོངས། Poi Ranggyong Jong (Standard Tibetan) |
Lhasa (拉萨; ལྷ་ས།) |
Tibetan | Standard Tibetan |  |
Tibet Area, Xikang |
| Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region | 宁夏回族自治区 Níngxià Huízú Zìzhìqū |
宁 Níng (NHAR) |
The Hui speak Chinese | Yinchuan (银川) |
Hui | Dungan, Chinese | Ningxia (province) | |
| Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region | 新疆维吾尔自治区 Xīnjiāng Wéiwú'ěr Zìzhìqū |
新 Xīn (XUAR) |
شىنجاڭ ئۇيغۇر ئاپتونوم رايونى Shinjang Uyghur Aptonom Rayoni (Uyghur) |
Ürümqi (乌鲁木齐; ئۈرۈمچی) |
Uyghur | Uyghur |  |
Xinjiang (province) |
Statistics
Population
| Administrative Division | National Share (%) | 2020 Census[7] | 2010 Census[8] | 2000 Census[9] | 1990 Census[10] | 1982 Census[11] | 1964 Census[12] | 1954 Census[13] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangxi | 3.55 | 50,126,804 | 46,026,629 | 43,854,538 | 42,245,765 | 36,420,960 | 20,845,017 | 19,560,822 |
| Inner Mongolia | 1.70 | 24,049,155 | 24,706,321 | 23,323,347 | 21,456,798 | 19,274,279 | 12,348,638 | 6,100,104 |
| Ningxia | 0.51 | 7,202,654 | 6,176,900 | 5,486,393 | 4,655,451 | 3,895,578 | * | * |
| Tibet Autonomous Region | 0.26 | 3,648,100 | 3,002,166 | 2,616,329 | 2,196,010 | 1,892,393 | 1,251,225 | 1,273,969 |
| Xinjiang | 1.83 | 25,852,345 | 21,813,334 | 18,459,511 | 15,155,778 | 13,081,681 | 7,270,067 | 4,873,608 |
| Total | 7.85 | 110,879,058 | 101,725,350 | 93,740,118 | 85,709,802 | 74,561,891 | 41,714,947 | 31,808,503 |
Ethnic
| Administrative Division | Titular Ethnic Group | Han Chinese | Other ethnic minorities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Xinjiang (Uyghur) | 45.0% | 42.2% | 12.8% |
| Tibet (Tibetan) | 86.0% | 12.2% | 1.8% |
| Inner Mongolia (Mongol) | 17.7% | 78.7% | 3.6% |
| Ningxia (Hui) | 35.0% | 64.1 % | 0.9% |
| Guangxi (Zhuang) | 31.4% | 62.5 % | 6.1% |
See also
Notes
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
