Loading AI tools
Soviet ultraviolet space telescope (1983–1991) From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Astron was a Soviet space telescope launched on 23 March 1983 at 12:45:06 UTC, using the Proton-K rocket.[5] Based on the 4MV spacecraft design and operational for six years, Astron was the largest ultraviolet space telescope of its time.
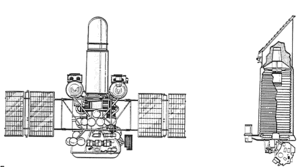 Diagram of the Astron observatory | |
| Mission type | Astrophysics |
|---|---|
| Operator | Soviet space program CNES |
| COSPAR ID | 1983-020A |
| SATCAT no. | 13901 |
| Mission duration | 8 years |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Bus | 4MV[1] |
| Manufacturer | NPO Lavochkin |
| Launch mass | 3,250 kg (7,170 lb)[2] |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 23 March 1983 12:45 UTC |
| Rocket | Proton-K/D-1 |
| Launch site | Baikonur 200/39 |
| End of mission | |
| Disposal | Decommissioned |
| Deactivated | 23 March 1991 |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | High Earth |
| Semi-major axis | 108,531 km (67,438 mi)[3] |
| Eccentricity | 0.6575927[4] |
| Perigee altitude | 30,791 km (19,133 mi)[3] |
| Apogee altitude | 173,530.2 km (107,826.7 mi)[3] |
| Inclination | 48.4°[3] |
| Period | 5,930.5 minutes[3] |
| Mean motion | 0.24281115 rev/day[4] |
| Epoch | 19 July 2017 07:25:15 UTC |
| Main telescope | |
| Collecting area | 0.17 m2 (1.8 sq ft)[1] |
| Wavelengths | X-ray: 2–25 keV[1] Ultraviolet: 150–350 nm |
The project was headed by Alexandr Boyarchuk.[6][7][8] The spacecraft was designed and constructed by the Crimean Astrophysical Observatory and NPO Lavochkin. A group of scientists from these institutions was awarded the USSR State Prize for their work.[9]
The payload consisted of an 80 cm ultraviolet telescope, which was jointly designed by the USSR and France, and an X-ray spectroscope.[10] It could take UV spectra 150-350 nm.[11]
Placed into an orbit with an apogee of 185,000 kilometres (115,000 mi), Astron was capable of making observations outside the Earth's umbra and radiation belt.
Among the most important observations made by Astron were those of SN 1987A supernova from March 4 to March 12, 1987,[12] and of Halley's Comet in December 1985, the latter of which enabled a group of Soviet scientists to develop a model of the comet's coma.[11]
Operation of the observatory ended on 23 March 1991.[13]
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.