Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
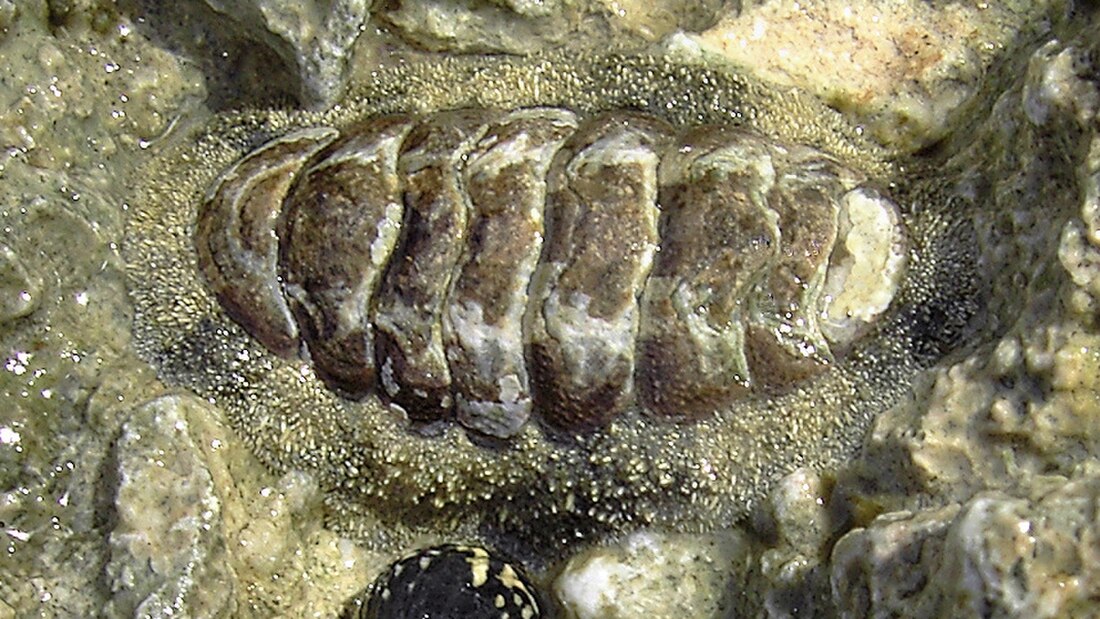
Acanthopleura granulata
Species of chiton From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Acanthopleura granulata, common name the West Indian fuzzy chiton (also known as Curbs or Sea Cradles),[1] is a medium-sized tropical species of chiton. This type of chiton's activity does not depend on spring-neap oscillations leading to lower locomotion loss.[2] Its morphology is different from usual chitons as it has a fifth valve, which is split into halves.[3]
This species is common within its range in the tropical Western Atlantic, but it is often not noticed, because its color and texture are similar to the rocks on which it lives. With not many predators the West Indian fuzzy chiton can live up to 40 years.[1]
In countries that used to be part of the British West Indies, these and other common intertidal chitons are known as "curb"; the foot of the animal is eaten by people and is also used as bait for fishing.

Remove ads
Description
This species of chiton grows to be about 7 cm (2.8 in) in length.[4] The girdle is densely spiky and usually has a few black bands.
The surface of the valves (or plates) in this species is almost always heavily eroded in adults, but when not eroded, the valve surface is granulated. The valves are thick and heavy. The morphology of the West Indian Fuzzy Chiton contains a fifth valve, split into two symmetrical half valves that are independent to each other and other valves. A griddle-like tissue splits the valves.[3]
This specific type of chiton displays hundreds of shell eyes (< 100 μm) embedded in their dorsal shell. These eyes provide special vision, containing a retina, layer of screening pigment and a lens.[5]
Remove ads
Distribution
This chiton occurs from southern Florida to Mexico, south to Panama, and in the West Indies.[4][6]
They orient themselves, maintaining a constant zonal level, according to the exposure to wave action along the coastal shore line. This organization is due to their foraging behavior, which is limited to the nocturnal low tides.[2]
Ecology
This species lives on rocks very high in the intertidal zone.[7] It can tolerate a lot of sun. Feeding is primarily nocturnal as there are increased levels of Hsp70, heat shock proteins which protects the organisms from environmental stressors including high temperatures, in the foot muscle under natural night time conditions .[8] During the day, levels decrease again as the stress level protein follows the daily air temperature curve.[9] It feeds on several species of algae.[10]
Gallery
- Two valves of A. granulata, an intermediate plate (32 mm) and a tail plate (21 mm)
- Two individuals of A. granulata in their natural habitat on a rock in Guadeloupe
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads