Loading AI tools
Protests in Kyiv, 2014 From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In response to anti-protest laws in Ukraine (announced on 16 January 2014[14] and enacted on 21 January 2014), a standoff between protesters and police began on 19 January 2014 that was precipitated by a series of riots in central Kyiv on Hrushevsky Street, outside Dynamo Stadium and adjacent to the ongoing Euromaidan protests.
| 2014 Hrushevsky Street protests | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Part of Euromaidan and Revolution of Dignity | |||
 Hrushevsky street protests in January 2014 | |||
| Date | 19–22 January 2014 (protests)[1][2][3] 23 January – 17 February 2014 (standoff) 18–23 February 2014 (escalation) (1 month) | ||
| Location | Hrushevsky Street, Kyiv, Ukraine 50.450417°N 30.529586°E | ||
| Caused by |
| ||
| Goals |
| ||
| Methods | Protesting, riot, civil disobedience | ||
| Status | Protesters dispersed, escalation into the Revolution of Dignity | ||
| Parties | |||
| |||
| Lead figures | |||
Andriy Parubiy (MP, Euromaidan commandant)[7] | |||
| Number | |||
| |||
| Casualties and losses | |||
During a Euromaidan rally which gathered up to 200,000 protesters, participants marched on the Verkhovna Rada and were met by police cordons. Following a tense stand-off, violence started as police confronted protesters. Protesters erected barricades to prevent the movement of government forces. Four protesters were confirmed dead in clashes with police, three of them shot.
On 28 January 2014, 9 of the 12 anti-protest laws were repealed and Prime Minister Mykola Azarov tendered his resignation and a bill offering amnesty to arrested and charged protesters was issued.[15][16] On 14 February 2014, groups responsible for organizing the standoff agreed to partially unblock the street to restore traffic, but maintain the barricades and ongoing protests. Following the amnesty of protesters on 16 February 2014, police and protesters both retreated while allowing a corridor for traffic. This lasted until 18 February 2014, when thousands marched on parliament once again, reestablishing Hrushevsky Street and related streets in a new standoff with police. By 19 February 2014, all barricades had been cleared from the streets and the protesters pushed back, though violent clashes elsewhere in Kyiv continued to grow in intensity, resulting in the Revolution of Dignity.



On 19 January, a Sunday mass protest, the ninth in a row, took place gathering up to 200,000 in central Kyiv to protest the new anti-protest laws, dubbed the "Dictatorship laws".[17][18] The rally was attended by opposition leaders, but was also the first public appearance of Tetiana Chornovol since her alleged attack by the authorities.[19] Many protesters ignored the face concealment ban by wearing party masks, while others wore hard hats and gas masks.[19] AutoMaidan leader Dmytro Bulatov demanded a single oppositional candidate be named, and the crowd also chanted against leaders to comply with this action.[19] Batkivshchyna leaders Arseniy Yatsenyuk and Oleksandr Turchynov declared that a new, alternative parliament would be created.[19]

Euromaidan activists appealed to the military for its "solemn allegiance to the Ukrainian people" rather than the "criminal regime", and for members of the military and police to not carry out "criminal orders", most notably in the use of force against civilians; they promised those who would be fired for refusing orders of violence would be reinstated once a new government for Ukraine was installed.[19] Former Ukrainian Navy chief, Rear Admiral Ihor Tenyukh, who was removed by President Yanukovych in 2010, warned of the dangers posed by the "coup d'état planned by the current authorities" and called for members of the armed forces to defy "illegal" orders from those in power.[20] "Tomorrow the regime will enslave you too. Therefore we are calling on you to fulfil your military oath of loyalty to the Ukrainian people and not to the authorities who have gone off the rails," he was quoted as saying.[20]
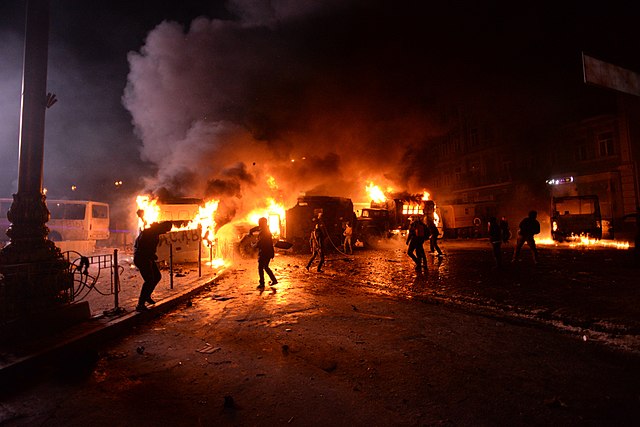
Clashes began as thousands descended upon parliament via Hrushevsky Street, and were met by police cordons, and a blockade of military cars, mini-vans and buses.[19][20] Police warned over loudspeaker, stating, "Dear citizens, your actions are illegal and are against the state." They also warned that advancing within three meters of police would be considered a threat to police officers' rights and will prompt a response.[19] Tensions eventually developed, and the sides exchanged projectiles as protesters attacked the police barricade armed with sticks, pipes, helmets, and gas masks. They were met with stun and smoke grenades.[21][22]

Opposition leader Vitali Klitschko (who attempted to bring calm)[nb 1] was sprayed with a fire extinguisher by a protester from the crowd, and shouted down as a traitor. Following this, live TV pictures showed protesters attempting to overturn a bus used by police, which was later set on fire after petrol bombs were thrown.[20] At least three buses were overtaken by demonstrators.[19] Water cannons used to douse the flames were also directed at protesters; an illegal use of force due to freezing temperatures.[19] Later, rubber bullets were used against protesters as more police vehicles were set ablaze.[19][24][non-primary source needed] Up to 10,000 protestors remained near the Valeriy Lobanovskyi Dynamo Stadium by 10 p.m. as clashes continued with smoke filling the air from the burning vehicles.[19] The entire line of police buses used in the blockade was set on fire,[25] and as midnight approached, nearly everything in the square by the Dynamo Stadium was burning.[26] Commenting on the situation, opposition MP Lesya Orobets stated, "War has finally started, laws don't apply anymore."[26] Reports from Lviv indicated that demonstrators in Lviv, Kalush, and Ivano-Frankivsk blocked military units from deploying to Kyiv;[19][27][non-primary source needed][28] with a similar situation occurring in Rivne, blocking Berkut troops.[29][non-primary source needed] Lviv troops later thanked protesters for blocking their deployment.[30] Automaidan activists by 3 a.m. blocked all roads exiting Yanukovych's Mezhyhyria mansion.[19] In the early morning, protesters in central Kyiv continued supplying molotov cocktails and advanced on police cordons while fortifying barricades to their rear as police continuously used water cannons, fired rubber bullets, and jammed cell phone signals.[31]

By the evening, Vitali Klitschko had arranged a night-time meeting with President Viktor Yanukovych at his presidential mansion Mezhyhirya in an attempt to argue for snap elections to defuse the situation from escalating into further violence.[19] The meeting ended with Yanukovych promising to resolve the crisis with a 'special commission' that included representatives of the administration (including the president), Cabinet of Ministers, and political opposition.[19][32] Arseniy Yatseniuk took to the Euromaidan stage at about 9:30 p.m. to say that he had received a telephone call from the president telling him the administration wanted to start negotiations to end the political crisis.[19] On Monday, 20 January, the commission was announced by Party of Regions MP Hanna Herman, but that it would convene without the President and be led by National Security and Defense Council secretary Andriy Klyuyev.[33][34][35][nb 2] Opposition leaders refused to take part in the government's proposed commission provided the president abstained from them himself.[37]



Clashes continued into the second day, with thousands remaining on Hrushevskoho Street, continuing to exchange explosives and rocks with police.[31] Of the 5,000 protesters present in the conflict area at the gates of the Dynamo Stadium near Mariinskyi Park, 200 were seen engaging the 500 riot police without stopping by the afternoon.[31] Berkut riot police were filmed by Radio Liberty throwing rocks at protesters while making obscene gestures towards them.[38] Later in the day, a group of protesters assembled an 8-foot high trebuchet to hurl rocks and other projectiles at police ranks.[39] In retaliation, police lobbed flash grenades, rocks, and Molotov cocktails at protesters. Police snipers scattered over the rooftops in the area but were exposed with fireworks and lasers.[31] By 10:45 p.m., the protestors near Dynamo Stadium numbered 10,000 and they continued to skirmish with thousands of police.[31] According to the Ukrainian Interior Ministry, representatives of the opposition in the Ukrainian parliament were providing weapons to attack the police.[40]
In the twilight hours of 21 January, after the anti-protest laws had taken legal effect, President Yanukovych ordered a 'bloody crackdown',[41] with police warning over loudspeakers that they might use weapons.[42] Interior Minister Vitaliy Zakharchenko signed an executive order authorizing the use of physical force, special devices, and firearms.[43][44][nb 3]

Protesters received text messages from their service providers stating "Dear subscriber, you've been registered as participant in the mass disturbances."[45] Responsibility for the messages was denied by the providers, 2 of which were owned by Russian companies. Experts suggested the government was behind the cell network actions.[46][47]
Hundreds of armed "titushky" were reported by eyewitnesses in the vicinity, attacking protesters and passers-by, as well as smashing vehicles; some were reportedly transported into the city on the back of large trucks showing no license plates.[48][49] Soon thereafter, they occupied many of the streets of downtown Kyiv.[50][non-primary source needed] In one incident, Vitali Klitschko appeared on Franko Street: upon seeing him, the titushky fled.[51][non-primary source needed] Klitschko then disarmed 2 of them who confessed to him that they were brought into the city from Kherson and ordered to smash cars and bring chaos to the city.[43][52] Automaidan activists detained other titushky in downtown Kyiv who admitted they were promised a payment of UAH 220 ($27) to vandalize the city.[53][non-primary source needed] A number of the titushky, who were apprehended by the protestors, were joined by political opposition leaders and brought to the opposition's headquarters at the Trades Union Building. They were questioned on live television, confessing their actions and job for the government to incite violence and anarchy. The rounding up of titushky was referred to as the titushky safari.[54]
Berkut troops continued to throw molotov cocktails at protesters.[43][55] Nearing 4 a.m., the bells of St. Michael's Cathedral sounded its bells in alarm, as it did on the night of 30 November police crackdown on the Maidan.[43][56][non-primary source needed] Meanwhile, the standoff continued with police until noon, when a ceasefire began between roughly 500 police officers and 1,000 protesters and priests standing within the buffer.[43]



At 6 a.m. local time on Unity Day, police shot and killed two protesters with live ammunition.[57] Following news of the deaths, protesters retreated and dispersed from the vicinity of Dynamo Stadium. This allowed police to advance and retake the area for a brief period, before being pushed back once more by protesters.

In response to the escalating violence, police were permitted by the government to increase measures to stopping the riots and protests. Police were now able to block roads to restrict access to the city, and allowed the use of water cannons against rioters regardless of air temperature (−10 C at the time of the announcement).[58]
Police fired rubber rounds against journalists and cameramen that were present, and continued to throw molotov cocktails at protesters.[59] Eyewitnesses said police were firing indiscriminately with rubber and regular bullets into the crowd periodically throughout the day, striking an unknown number of people.[60] Hundreds were injured, and significant damage was done to cars on the scene that were set ablaze as in previous days. Journalists found numerous ammunition shells on the ground. Police and medics confirmed live rounds were used in the shooting deaths of two protesters earlier in the day.[57][59][61] The prime minister denied that the police carried live ammunition. The co-ordinator of the protesters' medical corps said that five people had been killed, four from gunshot wounds and one in a fall.[61] About 100 meters behind the front line, protesters erected a secondary barricade using cement planters and steel ripped from massive billboards, to slow police if they tried to chase protesters back to the square again.[62] By evening 300 were injured and 4 dead by police gunfire.[63]

The truce between the two sides from the opposition's ultimatum to the government held, which expired at 8 p.m. Fire from the conflict zone spread and a shop was burned down on the first floor of the seven-story building, 40 square meters in area (at 2 Museum Alley).[64] The fire was caused by the burning rubber tires that blocked the vulytsia Hrushevskoho.[64] The burning tires were set to provide smoke screen for protesters.[64]
Euromaidan activists documented police brutality with instances of sadism on multiple occasions from Berkut and servicemen of the Internal Troops of Ukraine, wherein officers assaulted activists and even random people and would humiliate them using excessive foul language, and force them to undress.[65][66] In a video leaked to YouTube, Interior Ministry troops tortured and humiliated a Euromaidan activist on Hrushevsky street; he was stripped naked in the cold after being beaten, and photographed by officers.[67][68] The video was in close proximity, indicating that it was leaked by an officer, a sign of discontent within police ranks.[67] BBC News interviewed another protester who was photographing the Hrushevskoho Street protests, and then beaten and stabbed by police.[69] On 23 January reports surfaced that riot police were engaging in the use of improvised grenades, taping nails and other shrapnel to conventional stun grenades.[70] On 23 January 2014, Ministry of Internal Affairs of Ukraine officially apologized for the "unacceptable actions of people in police uniform" in the scandalous video filming a naked detainee.[71]
Following peace talks with president Yanukovych, opposition leaders Klitschko and Tyahnybok addressed the crowd on Hrushevsky Street to announce a proposed truce with the government in exchange for the release of all arrested or detained protesters. The news was poorly received by the crowd, who chanted "liar!" and "Freedom or death!" and booed the leaders.[72] Tyahnybok, who favored the truce, warned that the president stated his intentions to arrest 1,000 activists over the coming five days, and that repressions were ahead should a deal not be reached.[73] Klitschko then called for a national strike, stating he was ready to sacrifice himself. A vote was then held with the crowd which resulted in cutting off talks with Yanukovych and enlarging the area of Euromaidan in Kyiv to include Hrushevsky Street.[74][non-primary source needed][75]

Anti-government protesters built three new barricades on Hrushevskoho Street to protect the Euromaidan protest camp on Independence Square.[76] Reports suggested a possible rift between the Euromaidan camp and the more radical participants on Hrushevsky Street.[77]
Verkhovna Rada chairman Volodymyr Rybak stated on Rada TV that the issue of introducing a state of emergency would not be raised at 28 January extraordinary session of parliament since "The only issue that will be raised at the special session will be the current situation. The situation is very difficult, and we will consider the peaceful solution to the political crisis in Ukraine".[78] Overnight, clashes flared at times but both sides held their positions and by 5 a.m. a temporary truce was made, and by morning the scene was relatively calm. However, by 10:30 a.m. fighting broke out. Fires from burning tires stretched 70 meters across the street, and flames five meters high divided the sides. Berkut police were reported to be firing on protesters once again blindly through the smoke, and using search lights to peer through.[77]
Closing in on midnight, word spread that Internal Troops were occupying nearby Ukrainian House, strategically between Maidan and the Hrushevskoho barricades, and that they intended to flank their position. Protesters launched a pre-emptive strike on the building, in order to wrest control of the position. Protesters stormed the building, smashing windows, and lighting parts of the premises on fire.[77][79] Protesters outside created a corridor for police to evacuate the building of their own volition, and the stand-off lasted for six hours until finally police surrendered the building after a peace was brokered by Vitali Klitschko.[77][80][non-primary source needed] Anti-government protesters who occupied the building claimed to have discovered spent cartridges on the roof, and alleged that police who occupied the building until that morning might have used the rooftop to shoot at demonstrators on 22 January.[81][82]

On 28 January, Prime Minister Mykola Azarov turned in his resignation to President Viktor Yanukovych, hours before a vote of no confidence could have removed Azarov from power. The resignation also removed the entire administration from power,[83] which President Yanukovych confirmed by signing a decree dismissing the rest of Azarov's cabinet.[16] However, Azarov and his government remained in office until a new election could be held.[15]
Pro-government lawmakers joined with the opposition in Parliament to repeal nine of the eleven anti-protest laws which had triggered the violence. Yanukovych also proposed offering amnesty to the protesters if they abandoned their positions and dispersed. In addition, he promised to form a committee to propose revisions to the Ukrainian constitution that would weaken the powers of the president. Most spectators did not expect these concessions to be sufficient to satisfy protesters,[16] many of whom were still demanding Yanukovych's resignation.[84]
On 2 February, 5,000 gathered on Hrushevskoho to support the standoff.[85] The faceoff was described by the Kyiv Post as "not likely to end soon."[86]
On 6 February thousands (according to an UNIAN correspondent about three to four thousand[87]) Ukrainian opposition activists, some carrying shields and baseball bats, marched from their camp on Maidan Nezalezhnosti to the Verkhovna Rada building (according to BBC News) in a show of force.[88] According to (commandant of Euromaidan) Andriy Parubiy the march had a warning character, and if authorities did not consider the demands of Euromaidan, the actions would have a more decisive character "the next time".[89]
On 14 February, Right Sector, in compliance with the amnesty law freeing protesters, agreed to restore traffic on Hrushevsky Street. All members of the UNSO left the scene.[90] At the same time, the Right Sector demanded the immediate closure of all criminal cases against protesters, saying "Unless this is done as soon as possible, we reserve the right to act at our own discretion."[91] The Maidan council also agreed to restore traffic; "This does not mean that we are surrendering the buildings, this does not mean that we are pulling down the barricades, this means that we will partially unblock Hrushevsky Street to restore traffic," Maidan activist of Andrew Dzyndzia said, and reiterated that protesters would remain on Hrushevskoho Street.[92]
On 17 February an activist was stabbed in the lung after he crossed into the police-controlled side the barricades.[93]

There have been a number of participants not directly involved in the conflict, such as journalists and medics. Medics have worked on a volunteer basis providing urgent and first aid to wounded.
Numbers (19–21 January):
Self-defense and creation of the barricades has been carried out by Right Sector, the UNA-UNSO, and other self-defense units. Notably, one such multi-ethnic unit is led by a Jewish man, and includes Georgians, Azerbaijani, Armenians, and Russians.[95]

According to medical workers on the ground: 300 were injured and treated on 20 January 250 on 21 January, more than 400 were injured on 22 January, and 70 on 23 January.[96]
In addition, according to city medical officials, a total of 157 protesters have sought medical aid between 19 and 23 January, with 72 admitted to hospitals.[97] The majority of complaints were made at the Maidan medical aid center which was set up near the barricades on Hrushevskoho Street on 19 January and most of those injured have avoided hospitals as those treated have been subject to arrest.[98][99]
MP Lesya Orobets was targeted by police in the open and beaten in a politically motivated attack, along with 3 guards she was with.[19] In an incident of cruel and unusual punishment, riot police detained two protesters, stripped them naked, doused them in water, and made them run back to Maidan on foot in the sub-freezing temperatures, while they were fired upon with rubber bullets.[19][100] Two protesters have lost their vision.[101]

Several journalists claimed they were targeted by the police, including many who say they were deliberately fired upon.[19][102] In total, 26 were injured, with at least two badly injured by police stun grenades;[103] a further 2 were arrested by police.[104] Over 30 activists were detained in total.[105] By the 22nd, at least 42 more journalists were victims of clashes at Hrushevskoho Street on 22 January 2014.[106]
On 21 January, the initial report indicated the first death occurred after a 22-year-old man fell from atop the 13-metre high colonnade in front of Dynamo Stadium while confronted by Berkut police, and suffered fractures to his spine's cervical vertebrae. Reports of the incident debate on whether the man jumped from the building to flee the beating, fell, or if he was pushed by police.[107][108] Later reports caused confusion after it was reported by medical staff that an additional man, 43 years old, fell from the roof, but survived;[109][110] however, he fell fixing an antenna and was not on Hrushevskoho.[111]

In the early morning of 22 January, police gunfire killed Serhiy Nigoyan, a 20-year-old ethnic Armenian Euromaidan participant from Dnipropetrovsk, while he was climbing the barricades in the conflict zone acting as security.[112][113] It was reported he received four gunshot wounds, including to the head, and died on the scene before being taken to hospital.[114][115][116]
Also killed was Belarusian citizen and UNA-UNSO member Mikhail "Loki" Zhyznewski, who was shot dead by police by a sniper rifle.[117][118][119][120][121] Forensics experts found that Nihoyan was killed with buckshot and Zhyznevsky with a rifle bullet,[122] while medics confirmed the bullet wounds to be from firearms such as the Dragunov sniper rifle (7.62 mm) and possibly a Makarov handgun (9mm).[57]
Two other shooting victims were announced by Euromaidan medical service coordinators by Wednesday evening,[63] based on TV footage in which police were seen dragging motionless bodies to their side of the fighting lines. These alleged deaths were not confirmed.[122] On 25 January, Roman Senyk died in a Kyiv hospital after being wounded in the chest in the Hrushevskoho Street riots on 22 January.[123]
A report published on 25 January by Armament Research Services, a specialty arms and munitions consultancy in Perth, Australia, says the mysterious cufflink-shaped projectiles presumably fired by riot police on Hrushevskoho Street at protesters during clashes this week are not meant for riot control, but for stopping vehicles, busting through doors and piercing armor. The bullets, writes Jenzen-Jones, who specializes in Eastern bloc weapons, are special armor-piercing 12-gauge shotgun projectiles, likely developed and produced by the Spetstekhnika (Specialized Equipment) design bureau, a facility located in Kyiv and associated with the Ministry of Internal Affairs.[124]
On 28 January, 52-year-old Bohdan Kalyniak died in hospital of pneumonia as a result of police water cannons being used against protestors in sub-freezing temperatures during clashes on Hrushevskoho Street.[125]

On 29 January two men, one younger and one older, were shot on Hrushevskoho Street and brought to a Kyiv hospital. The latter died from the gunshot wounds the following day.[126]
According to reports from the Interior Ministry, at least 100 riot police were injured in the clashes of 19 January with 61 of those officers being hospitalized.[127] According to the Interior Ministry's official website, demonstrators captured and beat one Berkut riot-police officer who was taken to the opposition-occupied House of Trade Unions and later sent to a hospital for treatment.[19] Videos show protesters throwing molotovs at riot police officers, injuring some of them.[128]
On 23 January 235 officers were reported injured with 104 hospitalized.[129] By 25 January, the MVS reported that 285 police officers were injured, 104 of which were hospitalised, and 1,340 had fallen ill (primarily from pneumonia and hypothermia).[130]
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.