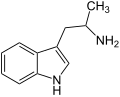
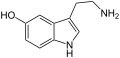
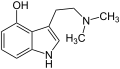
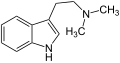
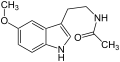
Tryptamine
Stoffklasse der Indole Aus Wikipedia, der freien Enzyklopädie
Tryptamine sind chemische Verbindungen, die vom 2-(Indol-3-yl)ethylamin abgeleitet sind. Sie sind Stoffwechselprodukte zahlreicher Lebewesen (vor allem Pflanzen) und zählen zu den Indolalkaloiden. Prominente Derivate mit Tryptamin-Struktur sind die Neurotransmitter Serotonin und Melatonin, die Aminosäure Tryptophan und die psychedelisch wirksamen Halluzinogene Dimethyltryptamin und Psilocybin sowie Psilocin.
Die wesentlichen Strukturmerkmale von Tryptaminen und Phenylethylaminen finden sich in den Lysergsäureamiden vereint.[1]
Tabellarische Übersicht
 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | R4 | R5 | Rα | RN1 | RN2 | chemischer Name | Herkunft |
| Tryptamin | H | H | H | H | H | 2-(Indol-3-yl)ethylamin | natürlich |
| N-Methyltryptamin (NMT) | H | H | H | H | CH3 | N-Methyltryptamin | natürlich |
| 5-Methoxy-N-methyltryptamin (5-MeO-NMT) | H | OCH3 | H | H | CH3 | 5-Methoxy-N-methyltryptamin | natürlich |
| Dimethyltryptamin | H | H | H | CH3 | CH3 | N,N-Dimethyltryptamin | natürlich |
| O-Methylbufotenin (5-MeO-DMT) | H | OCH3 | H | CH3 | CH3 | 5-Methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamin | natürlich |
| 5-Brom-N,N-dimethyltryptamin (5-Brom-DMT) | H | Br | H | CH3 | CH3 | 5-Brom-N,N-dimethyltryptamin | natürlich |
| Bufotenin | H | OH | H | CH3 | CH3 | 5-Hydroxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamin | natürlich |
| N-Methylserotonin | H | OH | H | CH3 | H | 5-Hydroxy-N-methyltryptamin | natürlich |
| Serotonin | H | OH | H | H | H | 5-Hydroxytryptamin | natürlich |
| Psilocin | OH | H | H | CH3 | CH3 | 4-Hydroxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamin | natürlich |
| Psilocybin | OPO3H2 | H | H | CH3 | CH3 | 4-Phosphoryloxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamin | natürlich |
| Baeocystin | OPO3H2 | H | H | CH3 | H | 4-Phosphoryloxy-N-methyltryptamin | natürlich |
| Norbaeocystin | OPO3H2 | H | H | H | H | 4-Phosphoryloxytryptamin | natürlich |
| Melatonin | H | OCH3 | H | O=C-CH3 | H | 5-Methoxy-N-acetyltryptamin | natürlich |
| Tryptophan | H | H | COOH | H | H | α-Carboxytryptamin | natürlich |
 | |||||||
| Name | R4 | R5 | Rα | RN1 | RN2 | chemischer Name | Herkunft |
| Alpha-Methyltryptamin (AMT) | H | H | CH3 | H | H | α-Methyltryptamin | synthetisch |
| 5-Methoxy-α-methyltryptamin (5-MeO-AMT) | H | OCH3 | CH3 | H | H | 5-Methoxy-α-methyltryptamin | synthetisch |
| α-Ethyltryptamin (AET) | H | H | CH2CH3 | H | H | α-Ethyltryptamin | synthetisch |
| N-Ethyltryptamin (NET) | H | H | H | H | CH2CH3 | N-Ethyltryptamin | synthetisch |
| Diethyltryptamin (DET) | H | H | H | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | N,N-Diethyltryptamin | synthetisch |
| Diisopropyltryptamin (DiPT) | H | H | H | CH(CH3)2 | CH(CH3)2 | N,N-Diisopropyltryptamin | synthetisch |
| Dipropyltryptamin (DPT) | H | H | H | CH2CH2CH3 | CH2CH2CH3 | N,N-Dipropyltryptamin | synthetisch |
| Dibutyltryptamin (DBT) | H | H | H | CH2CH2CH2CH3 | CH2CH2CH2CH3 | N,N-Dibutyltryptamin | synthetisch |
| 4-Hydroxy-N-methyl-N-ethyltryptamin (4-HO-MET) | OH | H | H | CH3 | CH2CH3 | 4-Hydroxy-N-methyl-N-ethyltryptamin | synthetisch |
| 4-Hydroxy-N,N-diethyltryptamin (4-HO-DET) | OH | H | H | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | 4-Hydroxy-N,N-diethyltryptamin | synthetisch |
| 4-Phosphoryloxy-N,N-diethyltryptamin (4-PO-DET) | OPO3H2 | H | H | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | 4-Phosphoryloxy-N,N-diethyltryptamin | synthetisch |
| 4-Hydroxy-N,N-diisopropyltryptamin (4-HO-DIPT) | OH | H | H | CH(CH3)2 | CH(CH3)2 | 4-Hydroxy-N,N-diisopropyltryptamin | synthetisch |
| 4-Hydroxy-N-isopropyl-N-methyltryptamin (4-HO-MiPT) | OH | H | H | CH(CH3)2 | CH3 | 4-Hydroxy-N-isopropyl-N-methyltryptamin | synthetisch |
| 5-Methoxy-N,N-diallyltryptamin (5-MeO-DALT) | H | OCH3 | H | H2C=CH-CH2 | H2C=CH-CH2 | 5-Methoxy-N,N-diallyltryptamin | synthetisch |
| 5-Methoxy-N,N-diisopropyltryptamin (5-MeO-DiPT) | H | OCH3 | H | CH(CH3)2 | CH(CH3)2 | 5-Methoxy-N,N-diisopropyltryptamin | synthetisch |
| 5-Methoxy-N,N-methylisopropyltryptamin (5-MeO-MiPT) | H | OCH3 | H | CH3 | CH(CH3)2 | 5-Methoxy-N,N-methylisopropyltryptamin | synthetisch |
| Sumatriptan | H | CH2SO2NHCH3 | H | CH3 | CH3 | 5-Methylaminosulfonyl-N,N-dimethyltryptamin | synthetisch |
Synthese
Tryptamin kann durch das Abramovitch-Shapiro-Syntheseverfahren hergestellt werden.[2]

Grafische Übersicht
Übersicht über eine kleine Auswahl an endogenen, natürlichen und synthetischen Tryptaminen.
Körpereigene, pflanzliche und synthetische Tryptamine
- α-Methyltryptamin
- α-Ethyltryptamin
- Serotonin (5-Hydroxytryptamin)
- N-Methyltryptamin
- N-Ethyltryptamin
- Psilocin
- Dimethyltryptamin (N,N-Dimethyltryptamin)
- Diethyltryptamin (N,N-Diethyltryptamin)
- L-Tryptophan (natürliche Aminosäure)
- Melatonin
- MiPT
- DiPT
Literatur
- Alexander Shulgin, Ann Shulgin: TiHKAL: The Continuation. Transform Press, Berkeley 1997, ISBN 0-9630096-9-9.
- Keeper of the Trout & Friends: Some Simple Tryptamines (Second Edition). Mydriatic Productions, 2007, ISBN 978-0-9770876-5-5.
- Ana Margarida Araújo, Félix Carvalho u. a.: The hallucinogenic world of tryptamines: an updated review. In: Archives of Toxicology. 89, 2015, S. 1151, doi:10.1007/s00204-015-1513-x.
Einzelnachweise
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.