热门问题
时间线
聊天
视角
糖皮质激素受体
位於5号人類染色體的基因 来自维基百科,自由的百科全书
Remove ads
糖皮质激素受体(英语:Glucocorticoid receptor, GR),也称为NR3C1(核受体亚家族3,C组,成员1),是皮质醇和其他糖皮质激素结合的受体。[8]
GR几乎在身体的每个细胞中都有表达,并调节控制发育、新陈代谢和免疫反应的基因。因为受体基因以多种形式表达,它在身体的不同部位有许多不同的(多效性)作用。[9]
当糖皮质激素与GR结合时,其主要作用机制是调节基因转录。[10]未结合的受体存在于细胞的胞质溶胶中。受体与糖皮质激素结合后,受体-糖皮质激素复合物可以采取两种途径中的任一种。激活的GR复合物上调细胞核中抗炎蛋白的表达或抑制胞质溶胶中促炎蛋白的表达(通过阻止其他转录因子从细胞质转移到细胞核中)。[11]
Remove ads
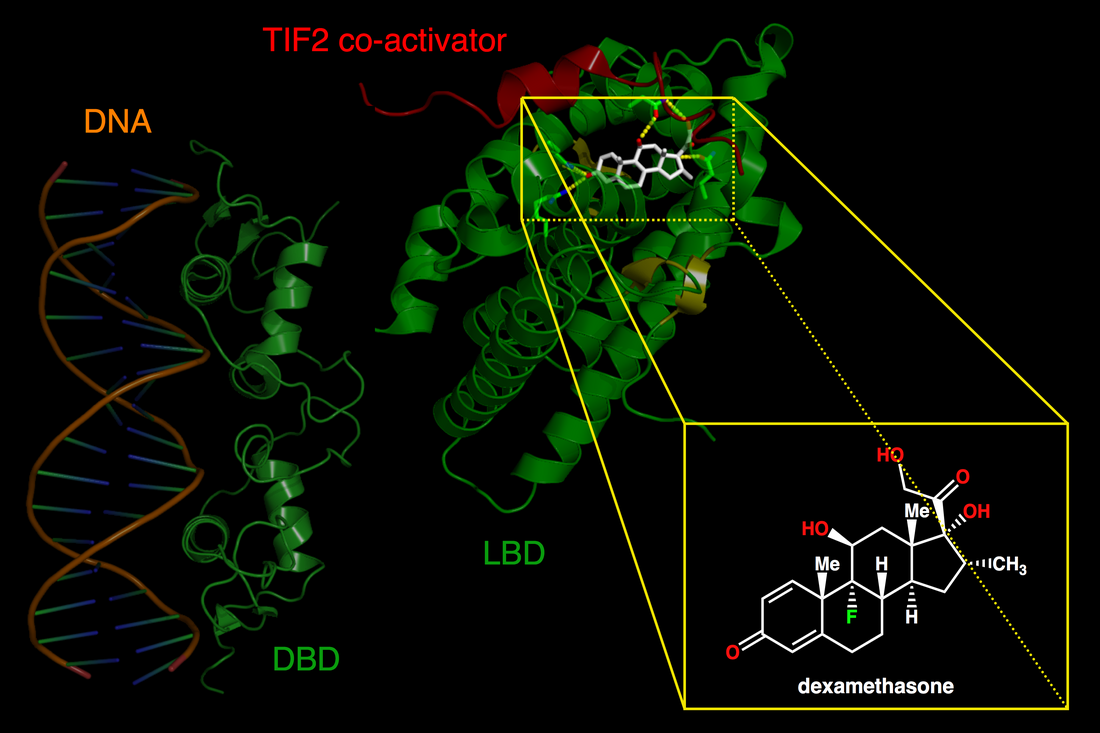
结构
配体结合和反应
在没有激素的情况下,糖皮质激素受体位于与多种蛋白质复合的细胞质中,包括热休克蛋白90(Hsp90)、热休克蛋白70(Hsp70)和蛋白FKBP4(FK506结合蛋白4)。[16]内源性糖皮质激素皮质醇通过细胞膜扩散到细胞质中并与糖皮质激素受体结合,导致热休克蛋白释放。所得的激活形式GR具有两种主要的作用机制,反式激活和反式阻遏,[17][18]如下所述。
一种直接的作用机制包括受体的同二聚化、通过主动转运进入细胞核的易位以及与激活基因转录的特定 DNA 反应元件的结合。该作用机制被称为转录激活。生物反应取决于细胞类型。
在没有激活的GR的情况下,其他转录因子如NF-κB或AP-1本身能够反式激活靶基因。[19]
临床意义
GR在家族性糖皮质激素抵抗中异常。[20]
在中枢神经系统结构中,糖皮质激素受体作为神经内分泌整合的新代表引起了人们的兴趣,作为内分泌影响的主要成分。该受体现在与对压力源的短期和长期适应有关,可能对理解心理障碍至关重要,包括部分或所有亚型抑郁症和创伤后应激障碍(PTSD)。[21]库欣病典型的情绪失调等长期观察结果证明了皮质类固醇在调节心理状态中的作用。最近的进展表明在神经水平上与去甲肾上腺素和血清素的相互作用。[22][23]
在先兆子痫(一种常见于孕妇的高血压疾病)中,可能靶向该蛋白质的miRNA序列水平在母亲的血液中升高。相反,胎盘提高了含有这种miRNA的外泌体的水平,可能导致分子翻译的抑制。该信息的临床意义尚未明确。[24]
激动剂和拮抗剂
相互作用
糖皮质激素受体与以下物质相互作用:
- BAG1[27][28]
- CEBPB[29]
- CREBBP[30]
- DAP3[31]
- DAXX[32]
- HSP90AA1[31][33][34][35][36][37][38]
- HNRPU[39]
- MED1[40][41]
- MED14[41]
- 盐皮质激素受体[42]
- NRIP1[40][43][44]
- NCOR1[45][46]
- NCOA1[40][47]
- NCOA2[40][48]
- NCOA3[40][49]
- POU2F1[50][51]
- RANBP9[52]
- RELA[52][53][54]
- SMAD3[55][56]
- SMARCD1[49]
- SMARCA4[49][57]
- STAT3[58][59]
- STAT5B[60]
- 硫氧还蛋白[61]
- TRIM28[62]
- YWHAH[63]
研究
2022年6月28日发表的一篇论文表明,NR3C1可能是肌萎缩侧索硬化(ALS)的潜在靶点之一。使用支持AI的生物靶点发现平台,发现NR3C1在CNS fALS和sALS中均被上调。通过靶点发现,可以进一步设计多种途径和药物来治疗ALS。[64]
参考文献
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads