剪切模量
来自维基百科,自由的百科全书
剪力模数(shear modulus)是材料力学中的名词,弹性材料承受剪应力时会产生剪应变,定义为剪应力与剪应变的比值。公式记为
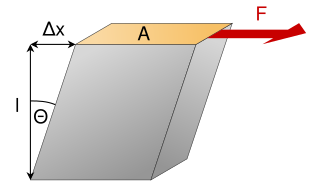
其中, 表示剪力模数, 表示剪应力, 表示剪应变。在均质且等向性的材料中:
波
在均匀各向同性固体中,有两种波:P波和S波。剪切波的速度,由剪切模量控制,
其中
- G是剪切模量
- 是固体的密度.
金属的剪切模量

金属的剪切模量通常随温度的升高而降低。在高压下,剪切模量也随外加压力的增大而增大。在许多金属中,熔点温度、空位形成能和剪切模量之间的关系已经被观察到。[3]
有几种模型试图预测金属的剪切模量(可能还有合金的剪切模量)。在塑性流动计算中使用的剪切模量模型包括:
MTS剪切模量模型为:
其中为处的剪切模量,和为材料常数。
剪切松弛模量
参见
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
















