細胞外液(英語:extracellular fluid,縮寫:ECF)通常指位於細胞外的體液,包括血漿以及介於血管和組織細胞之間的組織間液,即組織液(包括淋巴)[1][2]。細胞外液的總量大約佔體重的20%,四分之一存在於血管系統中,其餘存在於組織間隙。細胞外液構成了機體封閉的水溶液內環境系統,並與細胞內液一起構成了體液。
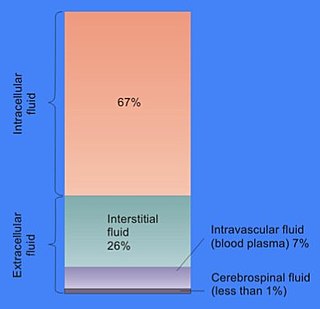
組成
在人體中,通過體內調節,細胞外液中正常的葡萄糖濃度大約為0.005M。細胞外液的pH值則被緩衝溶液控制在7.4左右。
細胞外液的化學組成與海水十分類似。從生物進化的角度看,這種相似在一定程度上說明生命的起源與海洋有密切的關係。而海洋的粒子總濃度比細胞外液大數倍,可能表明生命起源時的海水濃度比如今要小很多,細胞外液保留並維持了這種環境[2]。
功能
細胞外液可以被認為是一個獨立的系統。細胞外液是組織細胞運送營養物質和廢物的重要途徑,完成了與外界環境進行物質交換。同時也維護了體內氫離子濃度、滲透壓以及溫度等生理化學狀況保持相對穩定[2]。
參考文獻
外部連結
Wikiwand in your browser!
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.
