细胞外液
来自维基百科,自由的百科全书
细胞外液(英语:extracellular fluid,缩写:ECF)通常指位于细胞外的体液,包括血浆以及介于血管和组织细胞之间的组织间液,即组织液(包括淋巴)[1][2]。细胞外液的总量大约占体重的20%,四分之一存在于血管系统中,其余存在于组织间隙。细胞外液构成了机体封闭的水溶液内环境系统,并与细胞内液一起构成了体液。
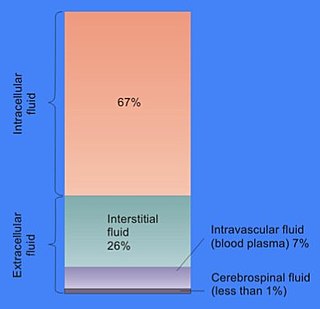
组成
在人体中,通过体内调节,细胞外液中正常的葡萄糖浓度大约为0.005M。细胞外液的pH值则被缓冲溶液控制在7.4左右。
细胞外液的化学组成与海水十分类似。从生物进化的角度看,这种相似在一定程度上说明生命的起源与海洋有密切的关系。而海洋的粒子总浓度比细胞外液大数倍,可能表明生命起源时的海水浓度比如今要小很多,细胞外液保留并维持了这种环境[2]。
功能
细胞外液可以被认为是一个独立的系统。细胞外液是组织细胞运送营养物质和废物的重要途径,完成了与外界环境进行物质交换。同时也维护了体内氢离子浓度、渗透压以及温度等生理化学状况保持相对稳定[2]。
参考文献
外部链接
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
