series of United States uncrewed space missions From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Pioneer program is the name of a few unmanned space missions done by NASA between 1958 and 1978. The best-known of these probes were Pioneer 10 and 11, launched in 1972 and 1973 respectively. Both carried a plaque as shown.


The first spacecraft in Pioneer program, Pioneer 0 was launched on August 17, 1958. 77 seconds after launch the Thor engine failed and a spacecraft has failed at launch. The next spacecraft, Pioneer 1, was the first spacecraft in Pioneer Program to be launched successfully, on October 11, 1958. Like its successor, Pioneer 2, which was launched on November 8, 1958, it was launched to the Moon. The most famous spacecraft in Pioneer program, Pioneer 10 and Pioneer 11 were launched on March 2, 1972 and April 5, 1973 respectively. Both reached the Jupiter system on December 4, 1973 and December 2, 1974 respectively. Pioneer 11 became the first spacecraft to approach Saturn, on September 1, 1979. Both spacecraft aren't functional anymore, the last signal from Pioneer 11 was received on Earth on November 24, 1995 at a distance 44 AU (7 Billion km; 3 Billion miles), while the last signal from Pioneer 10 was received on January 23, 2003 at a distance of 82 AU (12 Billion km; 7.6 Billion miles) from Earth. Pioneer 10 was the most distant spacecraft from Earth until February 17, 1998 when it was passed by Voyager 1 and will be the 3rd farthest spacecraft from Earth once it'll be passed by Voyager 2 around March 2023.
The earliest missions were attempts to escape the pull of Earth’s gravity and to study the Moon. This included the first launch by NASA which was formed from the old NACA. These missions were carried out by the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division, Army, and NASA.
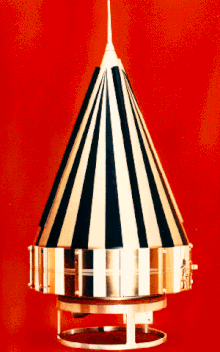

Pioneer P-1, P-3, 5, P-30, and P-31 probe
Pioneer 0
Pioneer 1
Pioneer 2
Pioneer P-1
Pioneer P-3
Pioneer 5
Pioneer P-30
Pioneer P-31

Five years after the early Able space probe missions ended, NASA Ames Research Center used the Pioneer name for a new series of missions, to gather information at the inner Solar System, before the flyby missions to Jupiter and Saturn. While successful, the missions returned much poorer images than the Voyager program probes would five years later. In 1978, the end of the program saw a return to the inner Solar System, with the Pioneer Venus Orbiter and Multiprobe, this time orbiting instead of flying by planets.
The new missions were numbered beginning with Pioneer 6 (other names in brackets).
The spacecraft in Pioneer missions 6, 7, 8, and 9 that research interplanetary space weather:
Pioneer 6 and Pioneer 9 are orbiting the Sun at 0.8 AU, with orbits slightly shorter than Earth. Pioneer 7 and Pioneer 8 are in solar orbits with 1.1 AU distance to the Sun. Their orbits are slightly longer than Earth's. Since the probes' orbital periods are different from that of the Earth, from time to time, they face a side of the Sun that cannot be seen from Earth.


Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.