Niger–Congo languages
language family spoken over the majority of sub-Saharan Africa, uniting the Mande languages, the Atlantic-Congo languages and possibly several smaller groups of languages From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
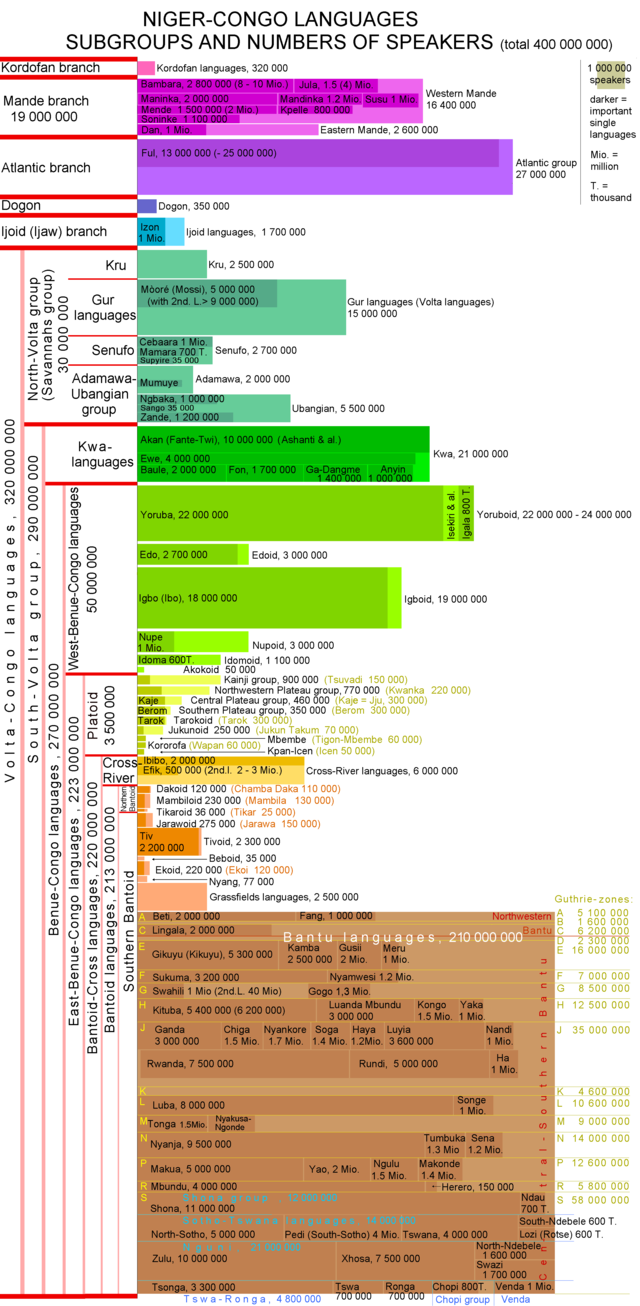
The Niger–Congo languages are a hypothetical language family. They are spoken in the southern half of Africa. They may be world's largest language family in terms of number of languages. Most of the most widely spoken languages of Subsaharan Africa belong to this group. A common part of many Niger-Congo languages is the use of a noun class system. The most widely spoken Niger-Congo languages by native speakers are Yoruba, Igbo, Fula and Shona. The most widely spoken by total number of speakers is Swahili.
| Niger–Congo | |
|---|---|
| Niger–Kordofanian (obsolete) | |
| Geographic distribution: | Sub-Saharan Africa |
| Linguistic classification: | If valid, one of the world's primary language families |
| Subdivisions: |
Dogon(inclusion disputed)
Ijoid (inclusion disputed)
Mande (inclusion disputed)
Katla (Kordofanian)(inclusion disputed)
Rashad (Kordofanian) (inclusion disputed)
Atlantic–Congo (noun classes)
|
| ISO 639-2 and 639-5: | nic |
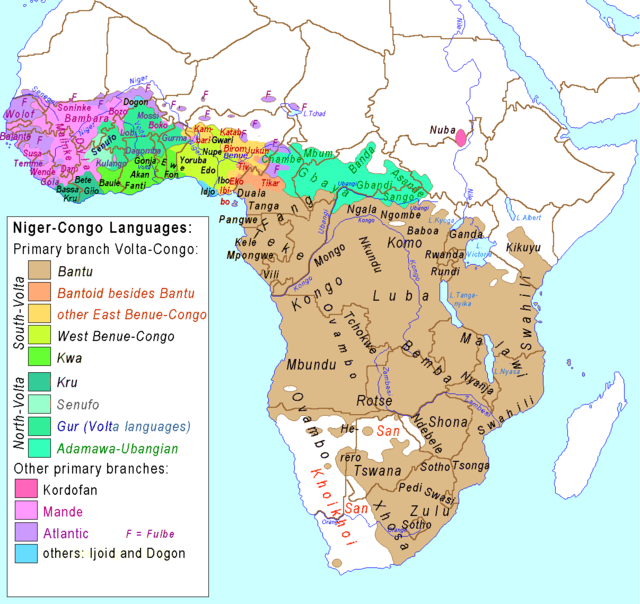
 Map showing the distribution of Niger–Congo languages (yellow). The area is divided into B (Bantu) and A (rest) to show the extent of the Bantu subfamily. | |

References
- Williamson, Kay (1989) 'Niger-Congo overview', in Bendor-Samuel & Hartell (eds.) The Niger-Congo Languages, 3-45.
- Williamson, Kay & Blench, Roger (2000) 'Niger-Congo', in Heine, Bernd and Nurse, Derek (eds) African Languages - An Introduction. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 11–42.
Other websites
- An Evaluation of Niger-Congo Classification Archived 2006-11-02 at the Wayback Machine, Kenneth Olson
- Ethnologue: Niger-Congo Family Tree
- The LINGUIST List MultiTree Project: Niger-Congo Family Trees Archived 2011-07-23 at the Wayback Machine
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
