The Democratic Republic of the Congo (French: République démocratique du Congo), commonly referred to as DR Congo, Congo-Kinshasa or the DRC, is a country in central Africa. It was known as Zaïre from 1971 to 1997. It is the second largest country in Africa by area and the eleventh largest in the world. With a population of over 71 million,[1] the Democratic Republic of the Congo is the nineteenth most populous nation in the world, the fourth most populous nation in Africa, as well as the most populous Francophone (French-speaking) country.
Democratic Republic of the Congo | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "Justice – Paix – Travail" (French) "Justice – Peace – Work" | |
| Anthem: Debout Congolais (French) "Arise, Congolese" | |
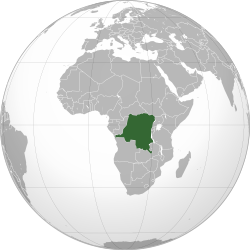 Location of Democratic Republic of the Congo (dark green) | |
| Capital and largest city | Kinshasa 4°19′S 15°19′E |
| Official languages | French & Swahili |
| Recognised national languages | Lingala Kikongo Tshiluba |
| Ethnic groups | See Ethnic groups section below |
| Demonym(s) | Congolese |
| Government | Unitary semi-presidential republic |
| Félix Tshisekedi | |
| Judith Suminwa Tuluka | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Senate | |
| National Assembly | |
| Formation | |
• Colonised | 17 November 1879 |
| 1 July 1885 | |
| 15 November 1908 | |
| 30 June 1960[1] | |
| 20 September 1960 | |
• Renamed to Democratic Republic of Congo | 1 August 1964 |
| 29 October 1971 | |
• Fall of Mobutu | 17 May 1997 |
• Current constitution | 18 February 2006 |
| Area | |
• Total | 2,345,409 km2 (905,567 sq mi) (11th) |
• Water (%) | 3.32 |
| Population | |
• 2021 estimate | 95,894,118[2][3] (16th) |
• Density | 34.83/km2 (90.2/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2017 estimate |
• Total | $67.988 billion[4] |
• Per capita | $785[4] |
| GDP (nominal) | 2017 estimate |
• Total | $40.415 billion[4] |
• Per capita | $446[4] |
| Gini (2006) | medium |
| HDI (2018) | low · 176th |
| Currency | Congolese franc (CDF) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 to +2 (WAT and CAT) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +243 |
| ISO 3166 code | CD |
| Internet TLD | .cd |

DRC borders the Central African Republic and South Sudan to the north; Uganda, Rwanda, and Burundi in the east; Zambia and Angola to the south; the Republic of the Congo, the Angolan exclave of Cabinda, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west. It is separated from Tanzania by Lake Tanganyika in the east.[1] The country has access to the ocean through a 40-kilometre (25 mi) stretch of Atlantic coastline at Muanda and the roughly 9 km wide mouth of the Congo River which opens into the Gulf of Guinea. It has the second-highest total Christian population in Africa.
History
When the Belgian Congo became independent, its leaders fought each other. The Soviet Union and later the United Nations helped destroy the groups who wanted independence from the new country.
The Second Congo War, beginning in 1998, devastated the country. It involved nine African nations and some twenty armed groups.[7] Despite the signing of peace accords in 2003, fighting continues in the east of the country. There, the prevalence of rape and other sexual violence is described as the worst in the world.[8] The war is the world's deadliest conflict since World War II, killing 5.4 million people since 1998.[9][10] The vast majority died from conditions of malaria, diarrhea, pneumonia and malnutrition.[11]
The Democratic Republic of the Congo was formerly, in chronological order, the Congo Free State, Belgian Congo, Congo-Léopoldville, Congo-Kinshasa, and Zaire (Zaïre in French).[1] Though it is in the Central African United Nations subregion, the nation is also economically and regionally affiliated with Southern Africa as a member of the Southern African Development Community (SADC).
Geography
The country is bordered by Angola, the South Atlantic Ocean, the Republic of Congo, the Central African Republic, South Sudan, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Tanzania across Lake Tanganyika, and Zambia.
The capital of the Democratic Republic of Congo is Kinshasa.
World Heritage Sites in the Democratic Republic of Congo include Virunga National Park (1979), Garamba National Park (1980), Kahuzi-Biega National Park (1980), Salonga National Park (1984) and Okapi Wildlife Reserve (1996).
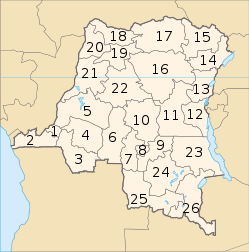
Provinces
The country is divided into twenty six provinces. The provinces are then divided into districts. The districts are divided into territories.[1]
Related pages
References
Wikiwand in your browser!
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.