റോക്കറ്റ്
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
ഒരു മിസൈലോ, ബഹിരാകാശവാഹനമോ, വിമാനമോ അല്ലെങ്കിൽ മറ്റു വാഹനങ്ങളോ അതിന്റെ സഞ്ചാരത്തിനാവശ്യമായ ശക്തി ഒരു റോക്കറ്റ് എഞ്ചിനിൽ നിന്നും സ്വീകരിച്ചാണ് സഞ്ചരിക്കുന്നതെങ്കിൽ അതിനെ ഒരു റോക്കറ്റ് എന്നു വിളിക്കും rocket (from Italian rocchetto "bobbin")[nb 1][1] റോക്കറ്റ് എഞ്ചിന്റെ നീക്കങ്ങൾക്കുള്ള ശക്തിമുഴുവൻ വിക്ഷേപണത്തിനുമുൻപുതന്നെ സംഭരിച്ചിട്ടുള്ള പ്രൊപ്പല്ലന്റിൽ നിന്നുമായിരിക്കും.[2] റോക്കറ്റ് എൻജിനുകളുടെ പ്രവർത്തനവും പ്രതിപ്രവർത്തനവും പുഷ് റോക്കറ്റുകൾ ഉപയോഗിച്ച് ഉയർന്ന വേഗതയിൽ എതിർ ദിശയിൽ അവയുടെ മുഴുവൻ ശക്തിയും വിനിയോഗിച്ചുകൊണ്ട് ശൂന്യാകാശത്തിൽ പ്രവർത്തിക്കാൻ കഴിയുന്നു.

ചരിത്രം
- Drawing of a Chinese soldier lighting a rocket's fuse (1890)
- Depiction of a rocket (1405)
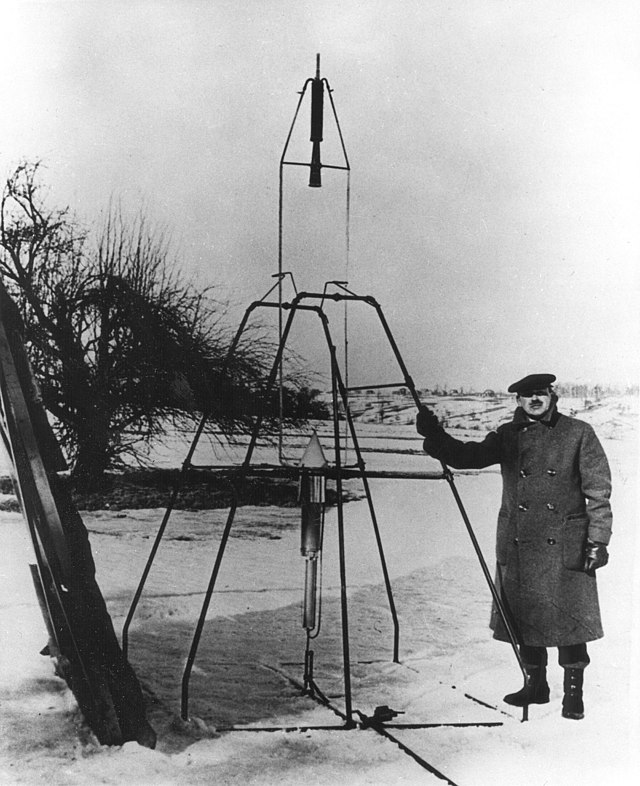


ഇനങ്ങൾ
രൂപകൽപ്പന
ഭാഗങ്ങൾ
എഞ്ചിനുകൾ

ഇന്ധനം

ഉപയോഗങ്ങൾ
സൈനികം

ശാസ്ത്രത്തിലും ഗവേഷണത്തിലും

ബഹിരാകാശയാത്രയ്ക്ക്
തിരികെയെടുക്കൽ

വിനോദാവശ്യത്തിന്
ശബ്ദം

ഭൗതികശാസ്ത്രം
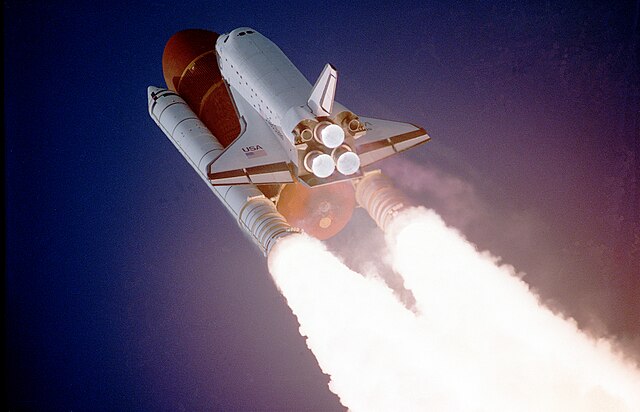
പ്രവർത്തനം

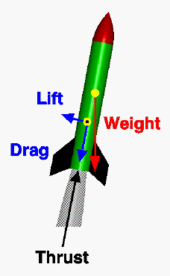
Forces on a rocket in flight
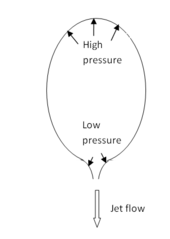
Drag
Net thrust

Ideally Expanded
Overexpanded
Grossly overexpanded
Total impulse
Specific impulse
Delta-v (rocket equation)

Mass ratios

| Vehicle | Takeoff Mass | Final Mass | Mass ratio | Mass fraction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ariane 5 (vehicle + payload) | 746,000 kg [6] (~1,645,000 lb) | 2,700 kg + 16,000 kg[6] (~6,000 lb + ~35,300 lb) | 39.9 | 0.975 |
| Titan 23G first stage | 117,020 kg (258,000 lb) | 4,760 kg (10,500 lb) | 24.6 | 0.959 |
| Saturn V | 3,038,500 kg[7] (~6,700,000 lb) | 13,300 kg + 118,000 kg[7] (~29,320 lb + ~260,150 lb) | 23.1 | 0.957 |
| Space Shuttle (vehicle + payload) | 2,040,000 kg (~4,500,000 lb) | 104,000 kg + 28,800 kg (~230,000 lb + ~63,500 lb) | 15.4 | 0.935 |
| Saturn 1B (stage only) | 448,648 kg[8] (989,100 lb) | 41,594 kg[8] (91,700 lb) | 10.7 | 0.907 |
| Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer | 10,024.39 kg (22,100 lb) | 1,678.3 kg (3,700 lb) | 6.0 | 0.83 |
| V-2 | 13,000 kg (~28,660 lb) (12.8 ton) | 3.85 | 0.74 [9] | |
| X-15 | 15,420 kg (34,000 lb) | 6,620 kg (14,600 lb) | 2.3 | 0.57[10] |
| Concorde | ~181,000 kg (400,000 lb [10]) | 2 | 0.5[10] | |
| Boeing 747 | ~363,000 kg (800,000 lb[10]) | 2 | 0.5[10] |
Staging


Acceleration and thrust-to-weight ratio
Energy
Energy efficiency

Oberth effect
ഇവയും കാണുക
Lists
- Chronology of Pakistan's rocket tests
- List of rockets
- Timeline of rocket and missile technology
- Timeline of spaceflight
General Rocketry
- Astrodynamics—the study of spaceflight trajectories
- Gantry
- Pendulum rocket fallacy—an instability of rockets
- Rocket garden—a place for viewing unlaunched rockets
- Rocket launch
- Rocket launch site
- Variable-mass system—the form of Newton's second law used for describing rocket motion
Propulsion and Propellant
- Ammonium Perchlorate Composite Propellant—Most common solid rocket propellant
- Bipropellant rocket—two-part liquid or gaseous fuelled rocket
- Hot Water rocket—powered by boiling water
- Pulsed Rocket Motors—solid rocket that burns in segments
- Spacecraft propulsion—describes many different propulsion systems for spacecraft
- Tripropellant rocket—variable propellant mixes can improve performance
Recreational Rockets
- High-powered rocket
- National Association of Rocketry
- Tripoli Rocketry Association
Recreational Pyrotechnic Rocketry
- Bottle rocket—small firework type rocket often launched from bottles
- Skyrocket—fireworks that typically explode at apogee
Weaponry
- Air-to-ground rockets
- Fire Arrow—one of the earliest types of rocket
- Katyusha rocket launcher—rack mounted rocket
- Rocket-propelled grenade—military use of rockets
- Shin Ki Chon—Korean variation of the Chinese fire arrow
- VA-111 Shkval—Russian rocket-propelled supercavitation torpedo
Rockets for Research
- Rocket plane—winged aircraft powered by rockets
- Rocket sled—used for high speeds along ground
- Sounding rocket—suborbital rocket used for atmospheric and other research
Misc
- Aircraft
- Equivalence principle—Einstein was able to show that the effects of gravity were completely equivalent to a rocket's acceleration in any small region of space
- Rocket Festival—Tradition bamboo rockets of Laos and Northeastern Thailand
- Rocket mail—the delivery of mail by rocket or missile.
കുറിപ്പുകൾ
പുറത്തേക്കുള്ള കണ്ണികൾ
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.


