Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Alpha Reticuli
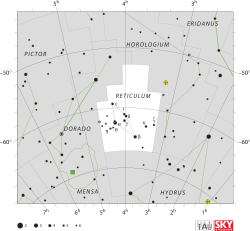
Brightest star in the constellation Reticulum From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Alpha Reticuli, Latinized from α Reticuli, also named Rhombus,[12] is the brightest star in the southern circumpolar constellation of Reticulum,[13] with an apparent visual magnitude of 3.3.[2] This appears to be a solitary star[14] located at a distance of 160 light-years from Earth.[1] Although it is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye, the declination of this star means that it is best viewed from the southern hemisphere and is only readily visible south of the Tropic of Cancer.[13]
Remove ads
Characteristics
This star has about three times the mass of the Sun and is about 300 million years old.[7] The spectrum of this star matches a stellar classification of G8 II-III,[3] with the luminosity class notation 'II-III' indicating it shows some traits of both a giant star and a bright giant. At this evolutionary stage, the surface has expanded to 13 times the radius of the Sun and the outer envelope has an effective temperature of 4,800 K.[8] X-ray emission has been detected from this star, with an estimated luminosity of 3 × 1029 erg s−1.[15]
Alpha Reticuli has a 12th-magnitude visual companion, CCDM J04144-6228B, at an angular separation of 48 arcseconds away along a position angle of 355°.[11] Since the two stars share a common proper motion across the celestial sphere, it is possible that Alpha Reticuli, rather than being solitary, may instead be the primary component of a binary star system with a projected separation of 2400 au and an orbital period of, at least, 60,000 years.[13][16] They have a 94% possibility to be related.[16]
Remove ads
Naming
In Chinese, caused by adaptation of the European southern hemisphere constellations into the Chinese system, 夾白 (Jiá Bái), means White Patches Attached, and it refers to an asterism consisting of α Reticuli and θ Doradus. Consequently, α Reticuli itself is known as 夾白二 (Jiá Bái èr, English: the Second Star of White Patches Attached.)[17]
The IAU Working Group on Star Names approved the name Rhombus for the primary component Alpha Reticuli A on 19 September 2024, after an obsolete name for the constellation Reticulum, and it is now so entered in the IAU Catalog of Star Names.[12]
Remove ads
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads