Pelasgic wall
The Pelasgic wall or Pelasgian fortress or Enneapylon was a monument supposed to have been built by the Pelasgians, after levelling the summit of the rock on the Acropolis of Athens. Thucydides and Aristophanes call it "Pelargikon", "Stork wall or place". "Pelargikon" refers to the line of walls at the western foot of the Acropolis. During the time of Thucydides, the wall was said to have stood several meters high with a large, visible fragment at 6 m (20 ft) broad, located on to the south of the present Propylaia and close to the earlier gateway. Today, the beveling can be seen but the foundation of the wall lies below the level of the present hill.
Read article
Top Questions
AI generatedMore questions
Nearby Places

Temple of Athena Nike
Ancient Greek temple on the Acropolis of Athens

Athena Promachos
Bronze statue of Athena

Brauroneion
Temple on the Ancient Athenian Acropolis, Greece

Chalkotheke
Temple on the Ancient Athenian Acropolis, Greece

Frankish Tower (Acropolis of Athens)
Former medieval tower in present-day Greece
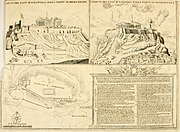
Siege of the Acropolis (1687)
Part of the Morean War

Propylaia (Acropolis of Athens)
The gate of the Acropolis of Athens

Beulé Gate
Fortified gateway on the Acropolis of Athens


