Indian Ocean
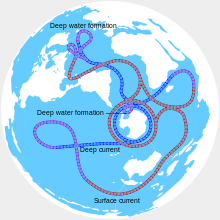
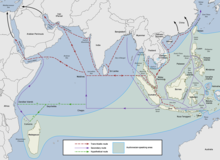
Ocean bounded by Africa, Asia, and AustraliaThe Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering 70,560,000 km2 (27,240,000 sq mi) or approximately 20% of the water area of Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by the Southern Ocean or Antarctica, depending on the definition in use. The Indian Ocean has large marginal or regional seas, including the Andaman Sea, the Arabian Sea, the Bay of Bengal, and the Laccadive Sea.
Read article
Top Questions
AI generatedMore questions
Timeline
AI Generated- 1515The Indian Ocean has been known by its present name since at least this year, when the Latin form Oceanus Orientalis Indicus was used.
- 1953The International Hydrographic Organization delineated the borders of the Indian Ocean, including the Southern Ocean but excluding the northern marginal seas.
- 1960sAnthropogenic warming of the global ocean began contributing to the global rise in sea level.