Parotid duct
Salivary duct from the parotid gland to the mouth From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The parotid duct or Stensen duct is a salivary duct. It is the route that saliva takes from the major salivary gland, the parotid gland, into the mouth.[1]
| Parotid duct | |
|---|---|
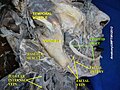
 Right parotid gland. Deep and anterior aspects. (Parotid duct labeled at center left.) | |
 Dissection, showing salivary glands of right side. (Parotid duct visible at center.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ductus parotideus |
| TA98 | A05.1.02.007 |
| TA2 | 2805 |
| FMA | 10420 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Structure
The parotid duct is formed when several interlobular ducts, the largest ducts inside the parotid gland, join. It emerges from the parotid gland. It runs forward along the lateral side of the masseter muscle for around 7 cm.[2] In this course, the duct is surrounded by the buccal fat pad.[2][3] It takes a steep turn at the border of the masseter muscle and passes through the buccinator muscle, opening into the vestibule of the mouth, the region of the mouth between the cheek and the gums, at the parotid papilla, which lies opposite to the second maxillary (upper) molar tooth. The parotid papillae can be palpated as small raised tissue area (papillae) on both sides of the mouth and protects the opening of the parotid duct. [4]
The buccinator acts as a valve that prevents air forcing into the duct, which would cause pneumoparotitis.[5]
Relations
The parotid duct lies close to the buccal branch of the facial nerve (VII).[2] It is also close to the transverse facial artery.[2]
Running along with the duct superiorly is the transverse facial artery, and the upper buccal nerve. The lower buccal nerve runs inferiorly along the duct.[citation needed]
Clinical significance
Blockage, whether caused by salivary duct stones or external compression, may cause pain and swelling of the parotid gland (parotitis).
Koplik's spots which are pathognomonic of measles are found near the opening of the parotid duct.
The parotid duct may be cannulated by inserting a tube through the internal orifice in the mouth.[2] Dye may be injected to allow for imaging of the parotid duct.[2]
History
Niels Stensen (also known as Nicolas Steno), a Danish anatomist (albeit best known as a geologist) is credited with the first detailed description of the duct in 1660,[6] hence the origin of its alternative name "Stensen duct".[2][6]
Additional images
- Outline of side of face, showing chief surface markings.
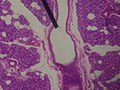
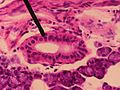
- Microscopic slide of a human interlobular duct.
- Microscopic slide of a human striated duct.
- The left papilla (soft tissue protuberance at the exit) of the parotid duct is clearly visible on the cheek in the right of the photo.
- Parotid duct
- Parotid duct
- Parotid duct
See also
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.