Isochrone map
Map that depicts the area accessible from a point within a time threshold From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
An isochrone map in geography and urban planning is a map that depicts the area accessible from a point within a certain time threshold.[1] An isochrone (iso = equal, chrone = time) is defined as "a line drawn on a map connecting points at which something occurs or arrives at the same time".[2] In hydrology and transportation planning isochrone maps are commonly used to depict areas of equal travel time. The term is also used in cardiology[3][4][5] as a tool to visually detect abnormalities using body surface distribution.[6]

History
Summarize
Perspective



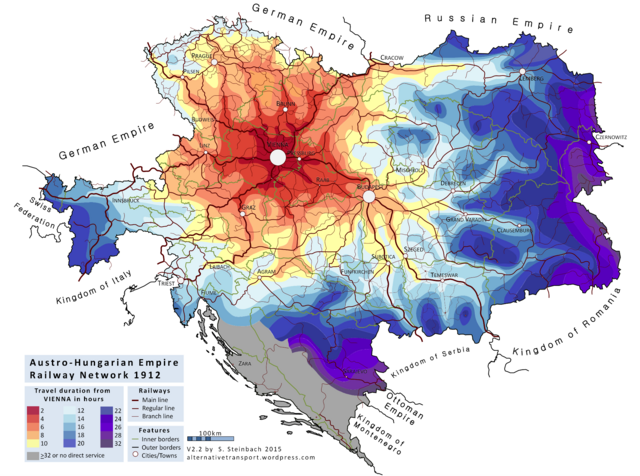
Early examples of Isochrone maps include the Galton's Isochronic Postal Charts and Isochronic Passage Charts of 1881 and 1882,[8] Bartholomew's Isochronic Distance Map and Chart first published 1889,[9] and Albrecht Penck's Isochronenkarte first published 1887.[10] Where as Galton and the Bartholomews published maps depicting the days or weeks it took to travel long distances, Albrecht further developed the idea to not only depict long distances and world travel but also smaller areas. Penck also created a series of maps that only depict the travel times of a certain transportation mode, for example rail transport. Isochrone maps are commonly used in the UK in connection with development control.[11][12][13][14] Isochrones are currently typically computed by via generating shortest-path trees on network graphs, and then generating a convex hull around the accessible nodes. Increases in computation, data storage, and improvements in algorithms have facilitated the rapid generation of isochrones.[1][15] Recent techniques in visualization include linking travel times to network edges to show the paths accessible from a point rather than show the area accessible from a point.[1]
Usage
Summarize
Perspective
Hydrology
Isochrone and related maps are used to show the time taken for runoff water within a drainage basin to reach a lake, reservoir or outlet, assuming constant and uniform effective rainfall.[16][17][18][19] An early example of this method was demonstrated by Clark in 1945.[20]
Transport planning
Isochrone maps have been used in transportation planning since at least 1887.[21][22] Isochrone maps in the context of transport planning are essentially maps of accessibility where travel time is used as the cost metric. Isochrone maps can be created for different modes of transportation,[23] e.g. foot, bicycle, motor vehicle. Put simply, the output of an isochrone map for transport will show how far (in distance) is reachable from a start point, including the parameter of time.
Such maps for private motor transport were widely used in a 1972 study into airport accessibility in Hampshire, South East England.[24] At that time, their use was disadvantaged by being time-consuming to create.[24]
The term isodapane map is used to refer to a map were the contour represent transportation cost instead of transportation time.[25]

General public
Journey time websites have been built using mapping technologies and open data.[26][27] Isochrones can be used by house hunters wishing to evaluate residential areas.[28] An isochrone map of the London Underground network was made available in 2007.[29]
Services and applications
Summarize
Perspective
Several digital tools exist which can generate isochrone maps.
openstreetmap-based solutions:[30]
- CommuteTimeMap – Build and visualize isochrones worldwide[31]
- Geoapify Isochrone API – API service to build isochrones for drive, truck, bicycle, walk and transit modes. Worldwide.[32]
- GraphHopper[33] can be used to calculate a detailed time information for every point within a certain time or distance reach.
- GRASS v.net.iso module[34]
- instaGIS[35]
- Iso4App – Public Transport Isochrone maps (Isochrones based on GTFS data)[36]
- Mapbox Isochrone API[37] (interactive Mapbox example[38])
- Mapumental
- OpenRouteService Isochrones Service – uses OSM data and map, shows isochrones worldwide (no source code available)[39]
- OpenTripPlanner – a development branch has work on an Analytics Extension, which currently provides isochrones based on the OSM network and GTFS data (source code available)[40]
- OSRM Isochrone – Generate drivetime isochrones from OSM using OSRM.[41]
- pgRouting – The creation of journey time isochrones to airports in Finland has been explained using the GIS software QGIS and pgRouting (an extension of PostGIS).[42]
- pysochrone is a Python script and simple web interface for computing and displaying isochrones from an OGR-supported data source (e.g. PostGIS)[43]
- Reachability Analysis – An application (built using WhereOS and OSM data) which calculates reachability (isochrone) from given set of addresses.[44]
- Safe Routes to School Mapping Toolkit – working to create travel distance/time web app for pedestrians and bicyclists using OSM data (source code available)
- TargomoAPI – Travel times, Routing, Points of Interests, Isochrones[45] – developer tools to build state-of-the-art geospatial analytics applications, enhance location search, and personalize user experience. (Interactive Demo[46])
- TravelTime API[47] Uses some OSM Data and has a free isochrone generator tool using public transport, cycling, walking, driving and combined bike and train. Available as a plugin for QGIS[48] and ArcGIS.[49]
- Valhalla isochrone service[50]
- Walkscore Travel Time API – uses GTFS and OSM data for maps of Seattle, San Francisco, and Washington DC. Built on the open source Graphserver library. (no source)[51]
- WNYC Transit Time – public transit isochrones for NYC[52]
- Stadia Maps Isochrone API (tutorial[53] with an interactive JSFiddle)[54]
GTFS-based solutions:
Proprietary data solutions:
- Google Maps API
- PedCatch
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
