Lakes of Wada
Three disjoint sets that share a common boundary From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In mathematics, the lakes of Wada (和田の湖, Wada no mizuumi) are three disjoint connected open sets of the plane or open unit square with the counterintuitive property that they all have the same boundary. In other words, for any point selected on the boundary of one of the lakes, the other two lakes' boundaries also contain that point.
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (February 2023) |
More than two sets with the same boundary are said to have the Wada property; examples include Wada basins in dynamical systems. This property is rare in real-world systems.
The lakes of Wada were introduced by Kunizō Yoneyama (1917, page 60), who credited the discovery to Takeo Wada. His construction is similar to the construction by Brouwer (1910) of an indecomposable continuum, and in fact it is possible for the common boundary of the three sets to be an indecomposable continuum.
Construction of the lakes of Wada
Summarize
Perspective
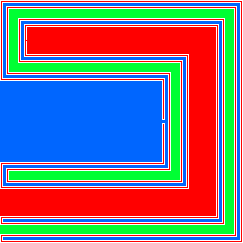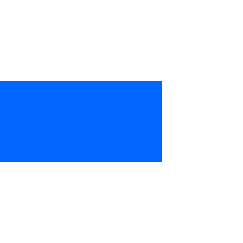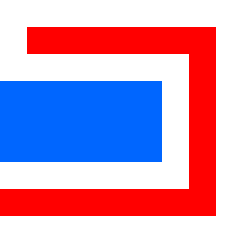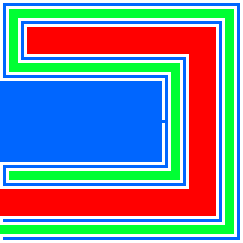
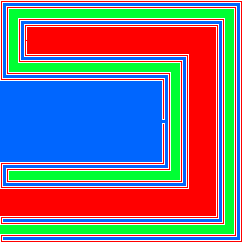
The Lakes of Wada are formed by starting with a closed unit square of dry land, and then digging 3 lakes according to the following rule:
- On day n = 1, 2, 3,... extend lake n mod 3 (= 0, 1, 2) so that it is open and connected and passes within a distance 1/n of all remaining dry land. This should be done so that the remaining dry land remains homeomorphic to a closed unit square.
After an infinite number of days, the three lakes are still disjoint connected open sets, and the remaining dry land is the boundary of each of the 3 lakes.
For example, the first five days might be (see the image on the right):
- Dig a blue lake of width 1/3 passing within √2/3 of all dry land.
- Dig a red lake of width 1/32 passing within √2/32 of all dry land.
- Dig a green lake of width 1/33 passing within √2/33 of all dry land.
- Extend the blue lake by a channel of width 1/34 passing within √2/34 of all dry land. (The small channel connects the thin blue lake to the thick one, near the middle of the image.)
- Extend the red lake by a channel of width 1/35 passing within √2/35 of all dry land. (The tiny channel connects the thin red lake to the thick one, near the top left of the image.)
A variation of this construction can produce a countable infinite number of connected lakes with the same boundary: instead of extending the lakes in the order 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, ...., extend them in the order 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 3, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, ... and so on.
Wada basins

Wada basins are certain special basins of attraction studied in the mathematics of non-linear systems. A basin having the property that every neighborhood of every point on the boundary of that basin intersects at least three basins is called a Wada basin, or said to have the Wada property. Unlike the Lakes of Wada, Wada basins are often disconnected.
An example of Wada basins is given by the Newton fractal describing the basins of attraction of the Newton–Raphson method for finding the roots of a cubic polynomial with distinct roots, such as z3 − 1; see the picture.
Wada basins in chaos theory
In chaos theory, Wada basins arise very frequently. Usually, the Wada property can be seen in the basin of attraction of dissipative dynamical systems. But the exit basins of Hamiltonian systems can also show the Wada property. In the context of the chaotic scattering of systems with multiple exits, basins of exits show the Wada property. M. A. F. Sanjuán et al.[1] has shown that in the Hénon–Heiles system the exit basins have this Wada property.
See also
- List of topologies – List of concrete topologies and topological spaces
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
