Turkistan (city)
City in Turkistan Region, Kazakhstan From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Turkistan (Kazakh: Түркістан, romanized: Türkıstan [tʉrkɘ̆sˈtɑn]; Russian: Туркестан, romanized: Turkestan) is a historic city and the administrative center of the Turkistan Region in southern Kazakhstan, located near the Syr Darya River. Positioned 160 km (100 miles) northwest of Shymkent, it lies along the Trans-Aral Railway, which connects Kyzylorda to the north and Tashkent to the south.
Turkistan
| |
|---|---|
 | |
| Coordinates: 43°18′07″N 68°16′09″E | |
| Country | Kazakhstan |
| Region | Turkistan Region |
| Government | |
| • Akim (mayor) | Azimbek Pazylbekuly[1] |
| Population (2023) | |
• City | 300,000 |
| • Urban | 250,000 |
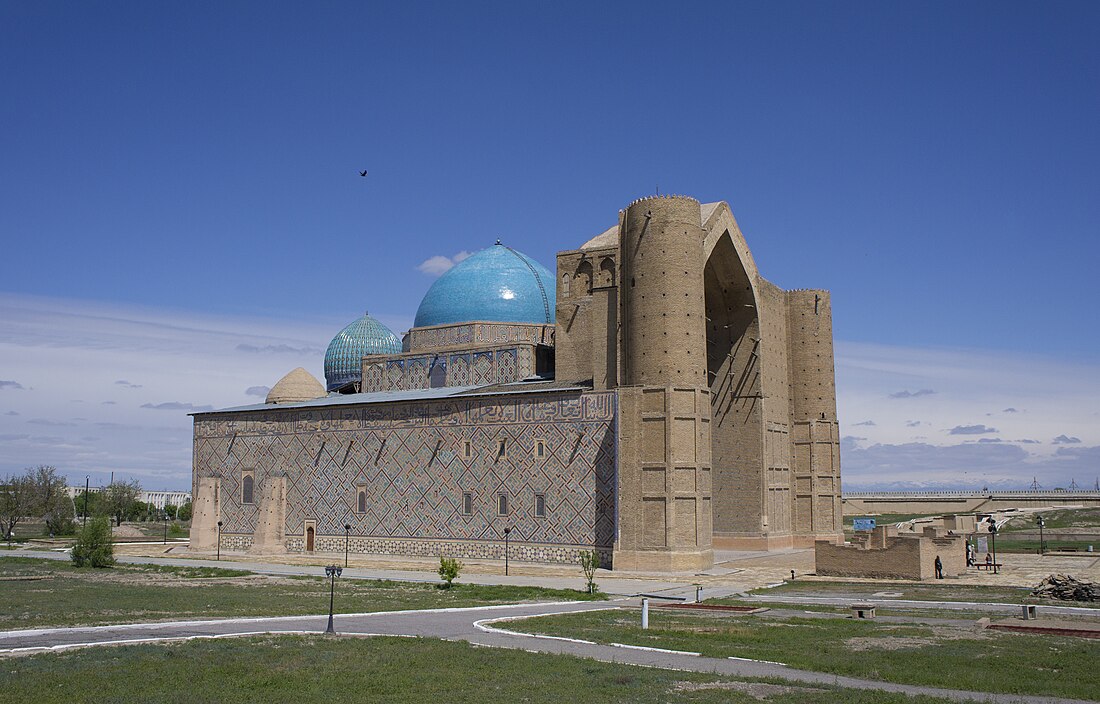
Turkistan holds historical and cultural significance of Kazakhstan, particularly due to the Mausoleum of Khoja Ahmed Yasawi, a UNESCO World Heritage site. This mausoleum is a key symbol of the city, drawing pilgrims and tourists alike. Khoja Ahmed Yasawi was a prominent Sufi mystic and philosopher, and his tomb is a revered site for followers of Islam in Central Asia. The city's rich cultural heritage is further reflected in its many historical monuments, mosques, and buildings that showcase the region's architectural and spiritual legacy.
In 2021, Turkistan was designated as the "Spiritual Capital of the Turkic World" by the Organization of Turkic States, a recognition of its central role in the history and culture of Turkic-speaking nations.[2] This title has elevated the city's status as a cultural and religious center, attracting visitors and fostering deeper ties between the Turkic-speaking peoples of Central Asia.[3]
Turkistan is also becoming increasingly recognized as a key tourist destination. In the same year, it was named one of the top ten tourist destinations in Kazakhstan, due to its historical sites, cultural landmarks, and growing infrastructure. The city is served by Hazrat Sultan International Airport, which connects it to other regions and countries, making it accessible to international tourists and business travelers.
Etymology
The modern city name of Turkistan (Kazakh: Түркістан, romanized: Türkıstan, pronounced [tʉrkɘ̆sˈtɑn]) is derived from the Turco-Persian phrase Hazrat-i-Turkistan[4] (Chagatai and Persian: حضرت ترکستان, meaning "Saint of Turkistan"), which is in reference to Ahmad Yasawi, a prominent 11th-century poet and Sufi who was associated with and rested in this city.
Prior to Ahmad Yasawi's era, and during a significant portion of the medieval to early-modern era, the city was referred to as Iasy (Chagatai and Persian: یسی) or Shavgar (Chagatai and Persian: شاوغر).
History
Summarize
Perspective
Turkistan, one of Kazakhstan's historic cities, has an archaeological record dating back to the 4th century.[5]
The city emerged as a commercial hub following the decline of Otrar, an ancient city with remnants located southeast near the Syr Darya. Owing to the impact of Ahmad Yasawi, and in honor of his legacy, the city evolved into a significant hub for spiritual growth and Islamic education for the inhabitants of the Kazakh steppes. In the 1390s, Timur, the Turco-Mongol leader and the originator of the Timurid dynasty, constructed an impressive domed mazar or mausoleum over Yasawi's resting place. This structure stands as one of the most notable architectural landmarks in Kazakhstan. Until 2006, its image was featured on the reverse side of the country's banknotes.
The city also boasts other significant historical landmarks such as a medieval bath-house and four mausoleums. One of these is dedicated to Rabiya Sultan Begim, Timur's great-granddaughter, while the other three pay tribute to Kazakh khans (rulers).
Prior to the 19th-century Russian arrival, Turkistan was positioned at the boundary between the established Perso-Islamic oasis civilization of Transoxiana to its south and the vast expanse of the Kazakh steppes to its north.
Between the 16th and 18th centuries, Turkistan rose to prominence as the capital of the Kazakh Khanate,[6] becoming the political epicenter of the Kazakh steppe. However, as the Russian Empire expanded its conquests and weakened the Kazakh Khanate, smaller southern states were overtaken. By 1864, Russian General Veryovkin had captured Turkistan for the Kokand Khanate. Subsequently, under Russian rule, it became a part of the Syr-Darya Oblast in the Governor-Generalship of Russian Turkistan. Following the collapse of the Tsarist regime between 1917-18, it briefly joined the Turkistan Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic. By 1924, it became a part of the Kazakh ASSR within Soviet Russia.
On June 19, 2018, Shymkent was removed from the South Kazakhstan Region and placed directly under the governance of Kazakhstan. Concurrently, Turkistan became the regional administrative hub, and the region was renamed the Turkistan Region.[7]
In 2021, it was announced that the first 5G city will be set up in Turkistan. This project will be sponsored by Kcell and Ericsson.[8][clarification needed]
Pilgrimage

The city draws thousands of pilgrims. As per local tradition, visiting Turkistan three times is akin to a single hajj to Mecca, a sentiment echoed in other revered sites across the Muslim world. Such high regard for the Saint led to Turkistan being dubbed the Second Mecca of the East, profoundly influencing the spiritual essence of Kazakhstan's Muslim community.[9]
Demographics
Turkistan had a population of 165,000 in the 2019 census. The population rose by 10% from 1989 to 1999, making it the second fastest-growing town in Kazakhstan, after the new capital Astana.
The ethnic composition of the city:
The ethnic composition of the city according to the 1897 census:[10]
- total – 11,253
- Uzbeks – 8,940 (79.4%)
- Kazakhs – 1,415 (12.5%)
- Tatars – 506 (4.4%)
- Russians – 312 (2.7%)
At the same time the ethnic composition of the Chimkent uyezd (Chimkent district) which included the city of Turkistan according to the 1897 census:[11]
Tourism
In 2021, Keruen-Saray, Central Asia’s largest tourism complex, was opened in Turkistan. This unique attraction features merchants, artisans, a flying theater,[clarification needed] an amphitheater for equestrian shows, a bazaar, hotels, restaurants, a spa and fitness center, a cinema, and a family entertainment center. [12]
Transport
The city transport in Turkistan consists of buses and taxis.
Turkistan is served by Hazrat Sultan International Airport. It is located 15 km (9.3 mi) NE from the centre of city.
Geography and climate
Summarize
Perspective
Turkistan may be reached by train from Almaty, in a journey of nearly 20 hours. The road trip from the nearest airport at Shymkent takes about two hours.
Turkistan experiences a cool semi-arid climate (Köppen BSk) with short, cold winters and long, dry, very hot summers. The vast majority of the annual precipitation falls between late autumn and late spring.
| Climate data for Turkistan (1991–2020, extremes 1882–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 18.7 (65.7) |
26.4 (79.5) |
30.7 (87.3) |
37.7 (99.9) |
40.5 (104.9) |
46.9 (116.4) |
47.9 (118.2) |
46.5 (115.7) |
41.9 (107.4) |
35.3 (95.5) |
27.9 (82.2) |
21.6 (70.9) |
47.9 (118.2) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 1.8 (35.2) |
5.4 (41.7) |
14.2 (57.6) |
22.2 (72.0) |
28.9 (84.0) |
34.6 (94.3) |
36.4 (97.5) |
35.2 (95.4) |
28.9 (84.0) |
20.8 (69.4) |
10.5 (50.9) |
3.2 (37.8) |
20.2 (68.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −2.9 (26.8) |
−0.1 (31.8) |
7.4 (45.3) |
15.3 (59.5) |
21.8 (71.2) |
27.2 (81.0) |
29.0 (84.2) |
27.3 (81.1) |
20.7 (69.3) |
12.5 (54.5) |
4.2 (39.6) |
−1.7 (28.9) |
13.4 (56.1) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −7.0 (19.4) |
−4.7 (23.5) |
1.6 (34.9) |
8.6 (47.5) |
14.3 (57.7) |
18.8 (65.8) |
20.4 (68.7) |
18.8 (65.8) |
12.2 (54.0) |
5.1 (41.2) |
−1.0 (30.2) |
−5.7 (21.7) |
6.8 (44.2) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −33.6 (−28.5) |
−38.6 (−37.5) |
−25.0 (−13.0) |
−8.4 (16.9) |
−2.8 (27.0) |
3.2 (37.8) |
6.4 (43.5) |
3.4 (38.1) |
−5.5 (22.1) |
−14.3 (6.3) |
−31.8 (−25.2) |
−33.0 (−27.4) |
−38.6 (−37.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 25 (1.0) |
26 (1.0) |
31 (1.2) |
23 (0.9) |
21 (0.8) |
8 (0.3) |
4 (0.2) |
2 (0.1) |
2 (0.1) |
12 (0.5) |
26 (1.0) |
26 (1.0) |
207 (8.1) |
| Average extreme snow depth cm (inches) | 4 (1.6) |
2 (0.8) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
2 (0.8) |
4 (1.6) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1 mm) | 5.4 | 5.4 | 4.5 | 4.3 | 3.4 | 1.6 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 2.4 | 4.6 | 4.9 | 37.9 |
| Average rainy days | 5 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 7 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 7 | 6 | 60 |
| Average snowy days | 7 | 6 | 2 | 0.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.3 | 2 | 5 | 23 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 79 | 73 | 63 | 50 | 43 | 33 | 34 | 32 | 36 | 51 | 69 | 79 | 54 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 138 | 155 | 199 | 247 | 337 | 382 | 401 | 383 | 315 | 248 | 167 | 122 | 3,094 |
| Mean daily sunshine hours | 4.5 | 5.5 | 6.4 | 8.2 | 10.9 | 12.7 | 12.9 | 12.4 | 10.5 | 8.0 | 5.6 | 3.9 | 8.5 |
| Source 1: Pogodaiklimat[13] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: NOAA (sun 1961-1990),[14][15] Deutscher Wetterdienst (daily sun 1961-1990)[16] | |||||||||||||
Twin towns – sister cities
See also
Footnotes
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.