1970 Pacific hurricane season
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The 1970 Pacific hurricane season was an active Northern hemisphere hurricane season, especially during its early months. It officially started on May 15, 1970, in the eastern Pacific Ocean (east of 140°W), and on June 1, 1970, in the central Pacific (between 140°W and the International Date Line). It ended on November 30, 1970, in both regions. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclogenesis occurs in these parts of the Pacific.
| 1970 Pacific hurricane season | |
|---|---|
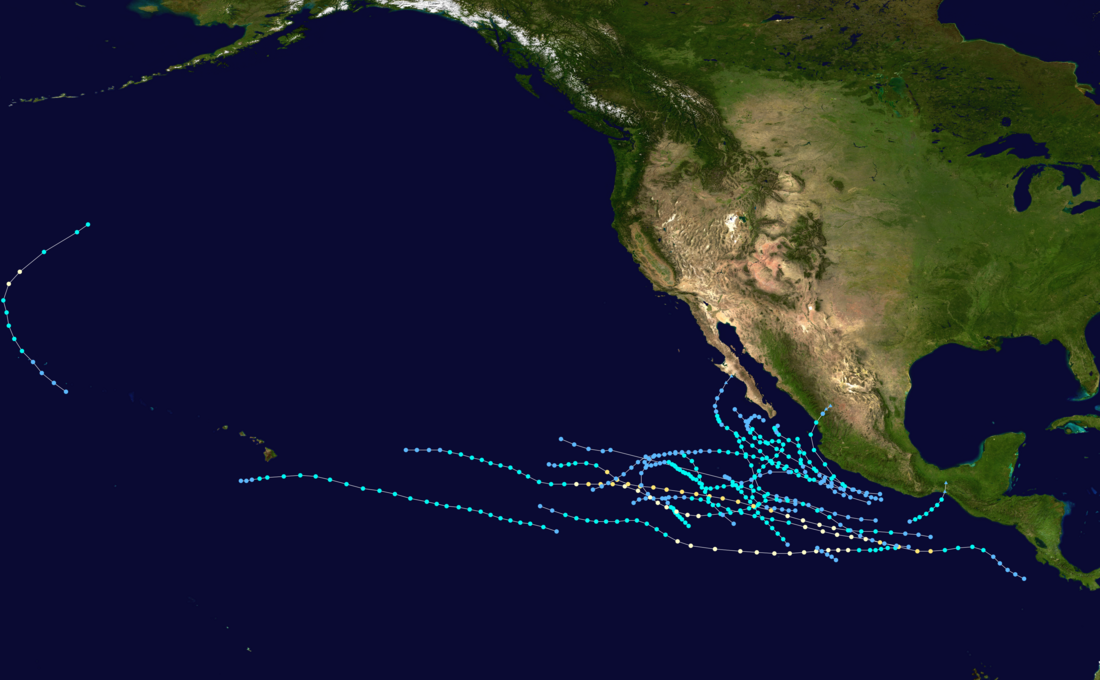
 Season summary map | |
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | May 30, 1970 |
| Last system dissipated | November 8, 1970 |
| Strongest storm | |
| Name | Lorraine |
| • Maximum winds | 100 mph (155 km/h) (1-minute sustained) |
| • Lowest pressure | 963 mbar (hPa; 28.44 inHg) |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 21 |
| Total storms | 19 |
| Hurricanes | 5 |
| Major hurricanes (Cat. 3+) | 0 |
| Total fatalities | 0 direct, 22 indirect |
| Total damage | Unknown |
| Related articles | |
This season had an above average number of storms. There were 21 tropical cyclones, of which 18 reached tropical storm strength. Four storms became hurricanes, of which none reached major hurricane strength. In the central Pacific, one hurricane and one tropical depression formed. One of the depressions crossed the Date Line to become a typhoon in the western Pacific.
Systems
Summarize
Perspective

Hurricane Adele
An area of low pressure lacked strong convection until May 30, when it strengthened into Tropical Depression One-E. On May 31, the system further intensified into Tropical Storm Adele, the first named storm of the season. As Adele tracked westward, it strengthened into a hurricane on June 1 and reached its peak intensity soon afterward. As Adele moved west, a hostile environment caused it to weaken into a tropical storm. Adele further weakened, and it was downgraded into a depression on June 7. It degenerated into an open trough later that day.
Tropical Storm Blanca
The tropical disturbance that became Blanca was first noted on June 8 from satellite pictures. The new disturbance would reach tropical storm strength 24 hours later. Blanca moved in a northwest direction throughout its short life, dissipating on June 12.
Tropical Storm Connie
Near the same location where Hurricane Adele formed two weeks earlier, a disturbance was noted on June 13. The disturbance abruptly became a tropical storm on June 17. The newly named Connie moved slowly to the northwest, reaching a peak intensity of 50 mph (80 km/h) on June 18. Connie started weakening on June 19, finally dissipating on June 21 after stalling 118 mi (190 km) from Clarion Island.
Tropical Depression Dolores
A disturbance first noted on June 19 had efficient outflow to be called a tropical depression. Satellite photos taken the same day revealed cloud structure that resembled a tropical storm forming, resulting in the system being called Dolores. The day after, no traces of a storm or of "Dolores" were found by reconnaissance. Post season analysis revealed Dolores to have only been a tropical depression.
Tropical Storm Eileen
A tropical depression formed just off the southern coast of Mexico on June 26. It headed northwestward, reaching storm strength on June 28. The next day, Eileen turned to the northeast, reached a peak of 45 mph (72 km/h) winds, and hit western Mexico.
Hurricane Francesca
Francesca was a Category 2 hurricane which was, for a period of time, obscured by a cap of clouds above the hurricane's eye, distorting the appearance of the hurricane. The precursor disturbance to Hurricane Francesca was first noticed on July 1. The system became a tropical depression later that day and reached tropical storm strength the next day. On July 3, data from a ship indicated winds of near 100 mph (160 km/h), which indicate a storm of Category 2 strength, near the center of Francesca. The cloud cap, which remained over the hurricane since it first became a hurricane, started to move off the lower clouds around the center of the system around July 5. A center fix was obtained, but the maximum sustained winds were unobtainable from the sea surface because of cloud cover in and around the center. Francesca started weakening on July 6, a fact made clear by reconnaissance which indicated that the system had weakened to a tropical storm. The further weakening was obscured by the cloud cover. The final reconnaissance on the weakening system was reported on July 8, two days before Francesca dissipated.
Tropical Storm Gretchen
Gretchen was first noticed on satellite imagery on July 14. From then on out, Gretchen was a hard storm to predict, leading to large errors in forecasting. The storm dissipated on July 21.
Tropical Storm Helga
The system that became Helga was first noticed on July 16. The next day, reconnaissance found a minimal tropical storm with winds of only 40 mph (64 km/h). Based on satellite imagery, Helga was believed to be gaining strength as it approached Baja California. At one point during intensification, the storm abruptly started weakening, and on July 19, after stalling less than 118 miles (190 km) south of the tip of Baja California, Helga dissipated.
Tropical Storm Ione 1
A tropical depression developed off the southern coast of Mexico on July 22. A larger intensifying tropical cyclone was spotted by satellite at 2235 on the 24th near 17°N., 111°W. When the expanding circulation of this storm center reached the area of Ione, winds in the latter area decreased and it disappeared abruptly. The second storm, which was also named Ione, moved north-northwestward and began to weaken. Ione reached maximum sustained winds of 45 knots on the 25th near 20. N.,112°W. These winds decreased to 25 knots the next day as storm activity faded rapidly near 16 N., 113°W'. What was unusual about the system was that another tropical storm developed just to its northeast on July 24. That storm, also named Ione, tracked northward, reaching a peak of 60 mph (97 km/h) winds before dissipating on July 25. Operationally, these were considered to be the same storm.
Tropical Storm Ione 2
A tropical depression was discovered near 14°N.,102°W., at 1800 on July 22, but it became disorganized as seen on satellite pictures the next day. Later events indicate it was splitting into two tropical cyclones, both of which were to attain tropical storm strength. The tropical storm first called lone was encountered by the KANIKAWA MARU at 2100 on July 24. That ship was buffeted by 48-kn southeasterly winds and 15-ft seas near 21°N, 107°W. The storm washed out the next day.[1]
Tropical Storm Joyce
A broad, flat low-pressure area persisted south of Baja California after Ione dissipated. On July 29, a small low circulation developed with a center about 120 nautical miles (220 km) south of Manzanillo. The system was given the name Joyce after winds of 40 mph (64 km/h) were reported by a ship. In a similar way to Hurricane Francesca, Tropical Storm Joyce's low level center was unclear due to a cap of cirrus clouds. Joyce reached its peak intensity on July 31 with winds of near 60 mph (97 km/h) before weakening, becoming a depression on August 1. Joyce dissipated on August 4.
Tropical Storm Kristen
Kristen was a loosely organized storm that formed from a disturbance that was causing squalls near the Mexican coast. Tropical storm-force winds were found on August 5. Kristen was tracked by ship reports and satellite pictures. Kristen reached its peak intensity of 50 mph (80 km/h) winds on August 6. The storm dissipated on August 8 while over cold water.
Hurricane Lorraine
Tropical Storm Lorraine, which formed on August 16 south of Mexico, intensified to a hurricane on the 20th. Two days later over open waters, it reached a peak of 95 mph (153 km/h) winds, but estimates from the Central Pacific Hurricane Center estimated it had winds of 115 mph (185 km/h). Without a chance to strengthen further, Lorraine weakened, finally dissipating on August 27 due to dry air.
Tropical Storm Maggie
A flat low-pressure system appeared in an area of showers to the west-southwest of hurricane Lorraine around 1800 on the 20th. The French refrigerated cargo carrier BIAFRA was buffeted by 38-kn southerly winds, with a barometer reading 1006 mbar, near 13'N, 132'W, by the soon to be named tropical storm Maggie at 0000 on the 21st. Maggie intensified slowly while moving west-northwestward at 9 kn; her maximum winds were estimated at 55 kn at 0300 on the 25th. Maggie passed about 80 mi south of the island of Hawaii on the 25th, dumping torrential rains over the big island. Rainfall amounts ranged from 10 to 15 in on the windward side of the island from the Hamuka coast to Puna and from 1 to 7 in on the leeward side. Maggie was downgraded to a tropical depression at 0900 on the 26th near 18N, 157W. A westward turn saved Hawaii from a direct hit, but Maggie still brought strong surf and heavy yet beneficial rain to the island of Hawaii. There is some evidence that the remains of Maggie redeveloped into Hurricane Dot in the Central Pacific on September 1.
Tropical Storm Norma
Norma was an indirect but essential cause of a flood disaster in Arizona that became known as the "Labor Day Storm of 1970". A depression formed August 31 and rapidly intensified into a tropical storm. Moving rapidly, it headed out to sea before slowing down and weakening. Norma's circulation fed humid unstable air into a large extratropical cyclone over Arizona. As Norma dissipated, record rains fell over the state from September 4 to September 6.
The rains were deadly. There were a total of 22 deaths, including 14 from a flash flood on a creek. The damage amounted to over 1 million dollars.
Hurricane Dot
A tropical disturbance, possibly the remnants of Tropical Storm Maggie, became a tropical depression on September 1 to the northwest of Hawaii. It moved to the northwest, coming within miles of the International Date Line and Midway Island but remaining in the Central Pacific. Dot turned to the northeast, reaching tropical storm strength on September 2 and hurricane strength September 3 before being absorbed by a cold core system the next day. When Dot became a hurricane at 35° north, it became the highest latitude for a storm to reach hurricane strength east of the International Dateline. This record was soon eclipsed by Hurricane 12 of the 1975 season. A flight flown into Dot also flew into Typhoon Clara.
Tropical Storm Orlene
65 mph (105 km/h) Tropical Storm Orlene hit Mexico in eastern Oaxaca on September 8, having maintained a northeast track for its short lifetime.
Hurricane Patricia
Hurricane Patricia was a strong Category 2 hurricane with winds of 95 mph, Patricia formed on October 4 and dissipated on October 11.
Tropical Storm Rosalie
Rosalie's existence was confirmed on October 21 by observation from a ship. Reconnaissance on the 22nd reported a central pressure of 1006 mb. After a slight regeneration on the 23rd, Rosalie began rapid dissipation, finally dissipating on the 23rd.
Tropical Storm Selma
The final storm of the season, Tropical Storm Selma, developed on November 1 to the southwest of Mexico. It meandered to the north, turning to the northeast and northwest before heading southeastward and dissipating on November 8.
Storm names
Summarize
Perspective
The following list of names was used for named storms that formed in the North Pacific Ocean east of 140°W in 1970.[2] It was the same list used in the 1966 season, with the exception of Kristen, which replaced Kirsten.[3] Storms were named Kristen, Norma, Orlene, Patricia, Rosalie, and Selma for the first time this season.[4] The name Kristen was later respelled as Kirsten for 1974.
|
|
|
One named storm, listed below, formed in the North Pacific between 140°W and the International Date Line in 1970. At the time, storm names within this region were assigned by the Joint Typhoon Warning Center on Guam.[2][4] Named storms in the table above that crossed into the area during the season are noted (*).[5]
|
Retirement
The name Adele was later retired without explanation.[6] It was replaced with Aletta for the 1974 season.[3]
Administrative changes
This is the first season that the Redwood City-based Eastern Pacific Hurricane Center started issuing advisories on tropical cyclones in the eastern north Pacific. It replaced the previous forecaster, Fleet Weather Central. Also. the Central Pacific Hurricane Center started to issue advisories on tropical cyclones in its area of responsibility this season. It replaced the Joint Hurricane Warning Center.[citation needed]
See also
- List of Pacific hurricanes
- Pacific hurricane season
- 1970 Atlantic hurricane season
- 1970 Pacific typhoon season
- 1970 North Indian Ocean cyclone season
- Australian cyclone seasons: 1969–70, 1970–71
- South Pacific cyclone seasons: 1969–70, 1970–71
- South-West Indian Ocean cyclone seasons: 1969–70, 1970–71
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.