Taoudeni Basin
Basin in western Africa From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
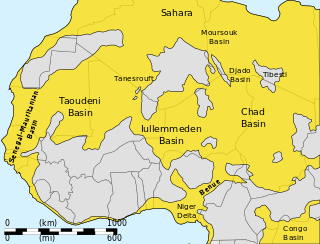
The Taoudeni Basin is a major Sedimentary basin in West Africa, named after the Taoudenni village in northern Mali. It covers large parts of the West African craton in Mauritania and Mali. It is of considerable interest due to its possible reserves of oil.[1] In addition to its economic importance, the basin contains scientifically important fossils from the Late Mesoproterozoic and Early Neoproterozoic eras, which correspond to a time interval known as the Boring Billion.[2]

Description
The Taoudeni is the largest sedimentary basin in Northwest Africa, formed during the Middle to Late Proterozoic. It continued to subside until the Middle Paleozoic, when Hercynian deformation and uplift occurred. It contains up to 6,000 metres (20,000 ft) of Late Precambrian and Paleozoic sediments. Exploratory drilling since the 1980s has found indications of petroleum in the Late Precambrian, Silurian and Late Devonian formations.[3]
Sediments are thicker in the western half of the basin.[4]
Petroleum geology

The government of Mali, one of the poorest countries in the world, is eager to create an oil industry.[5] Companies that have been exploring in the area include Baraka Petroleum, Sonatrach, Eni, Total S.A., Woodside and CNPC.[6]
However, the remote location and harsh environment of the Sahara Desert would make extraction expensive.[7]
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
