Tantalum boride
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Tantalum borides are compounds of tantalum and boron most remarkable for their extreme hardness.

Properties
The Vickers hardness of TaB and TaB2 films and crystals is ~30 GPa.[1][2][3] Those materials are stable to oxidation below 700 °C and to acid corrosion.[1][3]
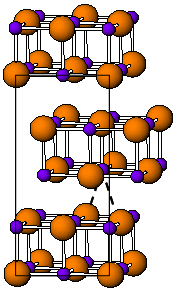
TaB2 has the same hexagonal structure as most diborides (AlB2, MgB2, etc.).[4] The mentioned borides have the following space groups: TaB (orthorhombic, Thallium(I) iodide-type, Cmcm), Ta5B6 (Cmmm), Ta3B4 (Immm), TaB2 (hexagonal, aluminum diboride-type, P6/mmm).[3]
Preparation
Single crystals of TaB, Ta5B6, Ta3B4 or TaB2 (about 1 cm diameter, 6 cm length) can be produced by the floating zone method.[2][3]
Tantalum boride films can be deposited from a gas mixture of TaCl5-BCl3-H2-Ar in the temperature range 540–800 °C. TaB2 (single-phase) is deposited at a source gas flow ratio (BCl3/TaCl5) of six and a temperature above 600 °C. TaB (single-phase) is deposited at BCl3/TaCl5 = 2–4 and T = 600–700 °C.[1]
Nanocrystals of TaB2 were successfully synthesized by the reduction of Ta2O5 with NaBH4 using a molar ratio M:B of 1:4 at 700-900 °C for 30 min under argon flow.[5]
- Ta2O5 + 6.5 NaBH4 → 2 TaB2 + 4 Na(g,l) + 2.5 NaBO2+ 13 H2(g)
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
