Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
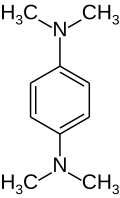
Tetramethylphenylenediamine
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Tetramethylphenylenediamine (TMPD) is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(N(CH3)2)2. It is most studied of three isomers of this formula. It is a colorless solid. With two dimethylamino substituents, the ring is particularly electron rich.
Remove ads
Remove ads
Redox behavior
Summarize
Perspective
One-electron oxidation of TMPD gives the deep blue radical cation called Wurster's blue, C6H4(N(CH3)2)+2. It was one of the first radical cations to be reported. Many properties have been described including its rapid rate of self-exchange:[1]
- C6H4(N(CH3)2)2 + [C6H4(N(CH3)2)2]+ ⇌ [C6H4(N(CH3)2)2]+ + C6H4(N(CH3)2)2
X-ray crystallography of the TMPD and its iodide salt reveals that oxidation most strongly contracts the C-N(CH3)2 and the HC---CH bonds, indicating that oxidation gives a quinoid-like species.[2]
The monocation illustrates an early step in the oxidation of p-phenylenediamine derivatives, which are widely used for hair dying.[3] N,N-Dimethylphenylenediamine (H2NC6H4N(CH3)2) also easily oxidizes to a radical cation, called Wurster's Red.
The hydrochloride salt of TMPD has been used as a redox indicator in the oxidase test and is also used in electron transport chain analysis as it is capable of donating electrons to cytochrome c. The midpoint potential for titration of the first electron is given as 0.276 V vs Standard hydrogen electrode, and this transition is useful in potentiometric titrations as both a redox mediator and indicator.
Remove ads
History
TMPD was reported in 1879 by Casmir Wurster (7 August 1854 – 29 November 1913), hence it is known as Wurster's reagent.[4]
Further reading
- L. Michaelis; M. P. Schubert; S. Granick (1939). "The Free Radicals of the Type of Wurster's Salts". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 61 (8): 1981–1992. Bibcode:1939JAChS..61.1981M. doi:10.1021/ja01877a013.
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads