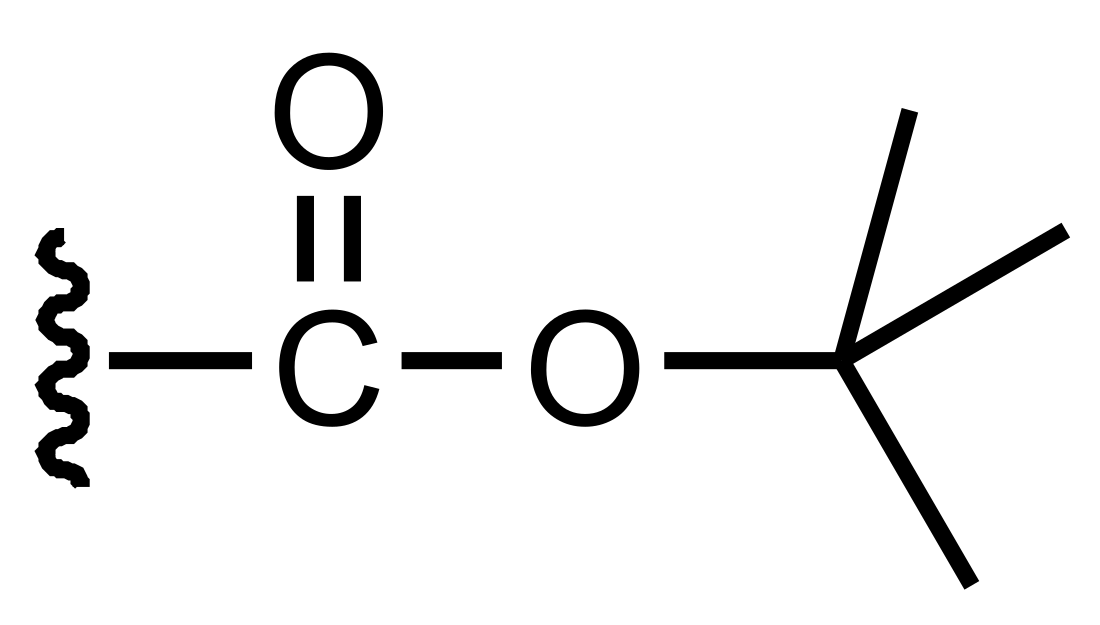
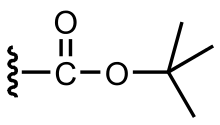
Tert-Butyloxycarbonyl protecting group
Protecting group used in organic synthesis From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The tert-butyloxycarbonyl protecting group or tert-butoxycarbonyl protecting group[1] (BOC group) is an acid-labile protecting group used in organic synthesis.
The BOC group can be added to amines under aqueous conditions using di-tert-butyl dicarbonate in the presence of a base such as sodium hydroxide:
Protection of amines can also be accomplished in acetonitrile solution using 4-dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP) as the base.
Removal of the BOC group in amino acids can be accomplished with strong acids such as trifluoroacetic acid in dichloromethane, or with HCl in methanol.[2][3][4] A complication may be the tendency of the t-butyl cation intermediate to alkylate other nucleophiles; scavengers such as anisole or thioanisole may be used.[5][6] Selective cleavage of the N-Boc group in the presence of other protecting groups is possible when using AlCl3.
Sequential treatment with trimethylsilyl iodide then methanol can also be used for Boc deprotection,[7][8] especially where other deprotection methods are too harsh for the substrate.[9] The mechanism involves silylation of the carbonyl oxygen and elimination of tert-butyl iodide (1), methanolysis of the silyl ester to the carbamic acid (2) and finally decarboxylation to the amine (3).[10]
| R2NCO2tBu + Me3SiI → R2NCO2SiMe3 + tBuI | 1 |
| R2NCO2SiMe3 + MeOH → R2NCO2H + MeOSiMe3 | 2 |
| R2NCO2H → R2NH + CO2 | 3 |
Amine protection
Summarize
Perspective

The tert-butyloxycarbonyl (Boc) group is used as a protecting group for amines in organic synthesis.
Common amine protection methods
- Simple rapid stirring of a mixture of the amine and di-tert-butyl dicarbonate (Boc2O) suspended in water at ambient temperature, an example of an on-water reaction.[11]
- Heating a mixture of the amine to be protected and di-tert-butyl dicarbonate in tetrahydrofuran (THF) at 40 °C[12]
- Add the amine to sodium hydroxide and di-tert-butyl dicarbonate in water and THF at 0 °C then warm to ambient temperature.[13]
- Heating a mixture of the amine to be protected and di-tert-butyl dicarbonate in a biphasic mixture of chloroform and aqueous sodium bicarbonate at reflux for 90 minutes.[14]
- Add the amine to di-tert-butyl dicarbonate, 4-dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP), and acetonitrile (MeCN) at ambient temperature[15]
BOC-protected amines are prepared using the reagent di-tert-butyl-iminodicarboxylate. Upon deprotonation, this reagent affords a doubly BOC-protected source of NH−
2, which can be N-alkylated. The approach is complementary to the Gabriel synthesis of amines.
Common amine deprotection methods
- Mix the protected carbamate to be deprotected with 3 M hydrochloric acid (HCl) in ethyl acetate for 30 min at ambient temperature[16]
- Heat the carbamate in a mixture of aqueous hydrochloric acid and toluene at 65 °C[17]
- Dissolving desired protected compound in a 50/50 mix of dichloromethane and trifluoroacetic acid[18]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.